Network Detection and Response
Generally, NDR solutions monitor network traffic and incoming/outgoing connections using proactive neural networks or heuristic engines. Together with SIEM, EDR/XDR, UBA and distributed deception platform, NDR form a pack of corporate security tools that provides surveillance, threat detection and response on all surfaces.
As it was mentioned, most of the threats come from the Internet, both to single users and to corporations. In the case of the latter, cyberattacks begin as brute force, , or a DDoS-attack, which may then lead to compromising the whole network. System administrators or security teams are generally aware of this threat source, and securing the network is an important part of their job. However, when it comes to large companies with a huge clustered network, this task becomes torture. Moreover, classic tools used to track network activity manually have enough weaknesses to consider them unsuitable for consistent corporate-scale security.
Network detection and response solutions aim to fix these problems, offering a more encompassing check-up surface and a more advanced detection system. Signature-based method appears ineffective when it comes to network security, as cyberattacks will likely always start from a different IP-address. Meanwhile, blocking all unknown addresses from the connection is not a good idea in the modern environment - when many users connect from a remote place (i.e. from home). Hence, to provide effective protection, NDR bears upon the heuristic method and neural network detections.
How Does NDR Work?
The key function of NDR is creating a centralised and, where possible, automated all-encompassing network security shield. Initially, after being launched in the environment, it gathers data about the regular network traffic and creates the image of “normal” network behavior. Thanks to the increased coverage, the solution can have as comprehensive a picture as possible, minimizing the possibility of intrusion in areas that are not under control.
After the initial information gathering, NDR keeps an eye on each event in the network. In conjunction with SIEM, it can show the cybersecurity team the full chain of events in detail (threat detected → threat recognised → actions done → report created). However, even solely the NDR solution will show you its own opinion on what’s happening in the network - both injection moment, lateral movement through the network, data exfiltration, or communication with C&C.
For sure, just showing is not a thing NDR is purchased for. The automated counteraction to the events is provided by both default settings for each detection and predetermined by a security team for a certain environment. Things like malicious traffic flow or brute force attempts can be cut down automatically by adjusting the firewall settings with several commands. However, to nail some more complex things, human interruption is required.
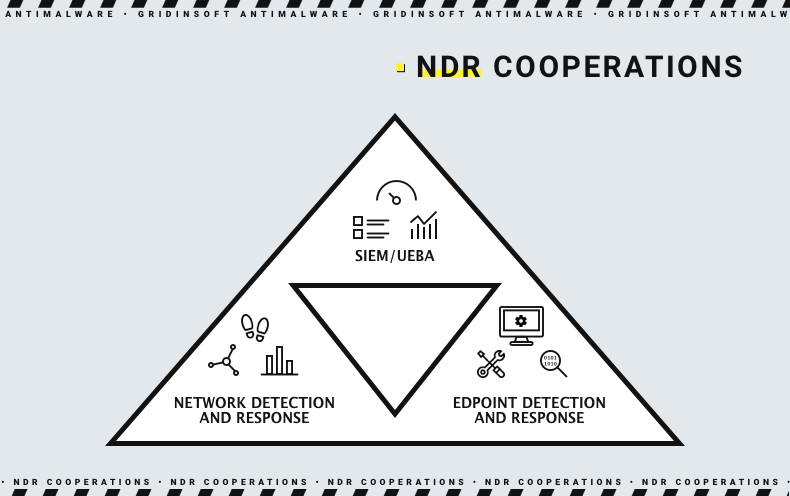
Most network detection and response systems are oriented at interacting with other protection system elements, in particular security orchestration and response (SOAR) and SIEM. The latter acts as a global journal of all security events in the environment, which also proceeds the data, making it easier to understand. SOAR, on the other hand, allows the cybersecurity team to manage the security settings according to the output of NDR.
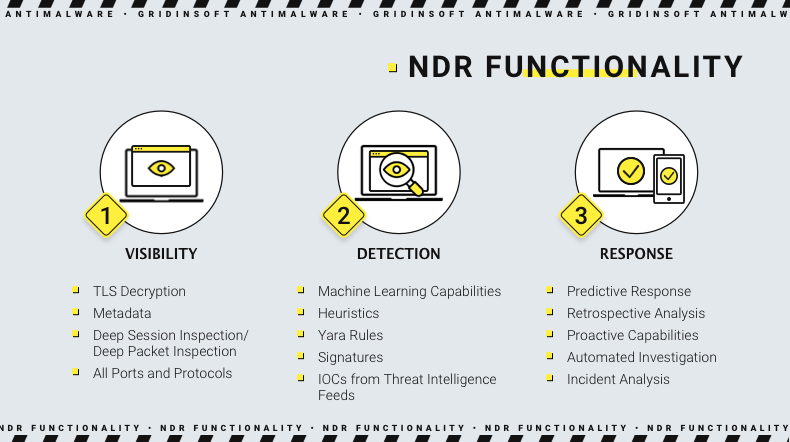
Additional NDR Functionality
Aside from the direct counteraction to a threat, NDR solutions are also capable of detecting dangerous trends and reporting them to security specialists. Machine learning in this software kind is used not only to understand the pattern of a default behavior in the network but also to spectate the inside and outside activity passively. The vendors who develop network detection and response solutions usually learn most of the known patterns of network behavior before any cyberattack. Hence, it can warn the cybersecurity team about what is coming even before the action starts.
Same system is also useful for threat intelligence. New ways of cyberattacks appear very often, as crooks pay a lot of attention to breaching through in an unexpected way. Regarding detecting and taking action against the most novel threat, AI and ML-based solutions are the best choice. The flexibility of such technologies allows the companies to retain the suitable level of protection corresponding to their environment and potential attack vectors as closely as possible.
What Kinds of Attacks are NDR Solutions Most Effective Against?
As mentioned, the bearing upon the proactive ways of malware detection makes the NDR solutions most effective against novel and non-linear attack vectors in their classic iteration. Those are APT deployment and targeted attacks that are styled exclusively for the attacked company. When everything in the hacker’s toolkit works precisely against the setup present in your network, only the most advanced counteraction measures will help. And network detection and response systems are essential at this stage.
Some brand-new threats, in particular ones that are deployed with the use of zero-day vulnerabilities, are the other place where NDR is irreplaceable. At the injection stage, most of the breaches are related to network design flaws - and the proper network protection can effectively detect the potentially vulnerable elements and spot them to you.
Risky actions inside the network, particularly insider threats, is the other thing NDR can mitigate and notify about. All users who have increased privileges can sometimes make a mistake by using an unprotected connection or connecting to a dubious domain. The latter, actually, may be a sign of malicious activity of one of your employees - that is what’s called an insider threat. And as practice shows, there is no automated way to deal with that hazard - only humans can correctly judge what the other human does.
Do I need NDR?
The vast majority of NDR solutions available on the market suppose their usage jointly with other security tools. EDR/XDR, their variations, SOAR and SIEM are the things that are essential to provide the full efficiency of the network detection and response solution. Solely, it will still be capable of analyzing, detecting, and dealing with threats, but the absence of complementary software will constrain this tool's application scale. Therefore, it is obvious that using NDR means much more expenses than you can expect by just checking up on a single price tag.
Small companies with a tiny network and no complicated system of domain controllers and endpoints will likely do well with the network protection capabilities offered by EDR or custom antivirus software. Still, there is also a possibility to manage the network security in a 100% manual mode - but that is troublesome and less effective. Network security is important, but smaller cos that cannot afford a full-packed NDR and complementary apps can find the substitutions that will fit their needs.
Meanwhile, for big companies, NDR is a thing that is pretty much essential for providing sequential network monitoring. Once again, it is possible to find a way to use a bunch of other tools for the same purpose - but they will barely reach even half of the specialized solution efficiency. Cybersecurity is still a weak spot for many corporations, and it is better to improve it to the maximum if you don’t want to be hacked.
Frequently Asked Questions
XDR, or Extended Detection and Response system, is the solution that spectates the whole corporate network (or the other type of environment) for malicious activity. It acts like a holistic antivirus that checks all devices simultaneously, from endpoints to IoT devices. Like NDR, XDR solutions usually bear upon proactive protection systems - generally heuristic engines and neural networks. However, a signature-based method is in use as well - it still works well for malware detection on workstations.
Meanwhile, NDR software concentrates their attention only on network security - as their specification says. It can be connected to the same data processing utility (SIEM for example), use the same scanning mechanisms, but still pay attention only to network connections, and possibly to the activity in LAN.
