
What is XDR?
Security products for corporations went a long way to the form they are currently in. The Endpoint Detection and Response conception appeared in 2013, and was tremendously innovative for that point of time. However, times have changed, and so did the threats which EDR was created to counteract. The conception that originally overwhelmed the requirements ended up being much less competitive against hackers. Cybercriminals found new ways of malware injection, and EDRs were incapable of doing even a thing with these methods. Moreover, the number of possible attack surfaces increased, which challenges this security software.
Extended Detection and Response
Extended Detection and Response system, or XDR, is a cybersecurity technology that aims at being more complex and all-encompassing than the endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems do. EDRs, as its predecessor, concentrate on protecting and monitoring the endpoints and all related elements. Meanwhile, more and more cyberattacks breaching the network were happening away from the endpoint - on the employees’ machines, IoT devices, and so on. In particular, during the COVID pandemic, the share of breaches through RDP exploitation was over 60% - and EDRs do not have a lot of chances to counteract it.
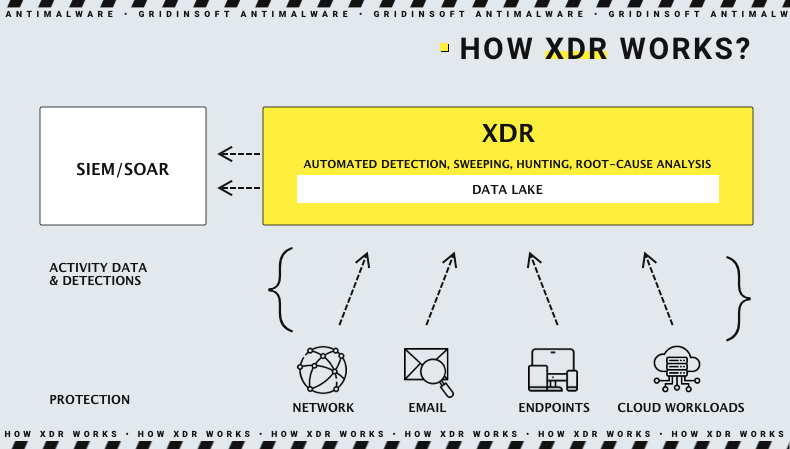
XDR fills the gaps that allow crooks to get into the network without counteracting. Besides keeping an eye on endpoints , it also tracks the application activity on the devices via monitoring the telemetrics gathered from these apps. Identity confirmation and access rights are also under the XDR management - this step brings a new level to counteracting an insider threat. Network analysis, email, and cloud security nail the most popular malware injection approaches - through phishing letters and network protocol issues.
Saying briefly, after establishing the XDR solution, your cybersecurity team will be capable of taking control of all possible sources of threat - at least as of 2022. Both malware injections, data leaks or the vulnerabilities that can make it possible are tracked by XDR and reported to the analyst's team in real-time. With the help of remote monitoring and alarms, it is possible for the cybersecurity team to respond to the threat as soon as possible. The benefits are next:
- On-flow threat intelligence, with the ability to share the detection with both internal analytics and outsource agents;
- Deductive methods of incident investigation. A well-done XDR analyses the detected threats and outputs a single alarm that fully describes the threat;
- Assuming the previous point, using XDR decreases the required skills of personnel who will interact with the system (compared to EDR);
- Eased threat analysis. New malware analysis technologies, such as neural networks, appeared earlier in EDR solutions, but XDRs rely upon these approaches.
XDR Key Capabilities
After mentioning the key profits of the XDR system, it is still important to explain its key functionality, to understand why it is better than regular anti-malware solutions. It is also necessary to explain the absolute, not relative, qualities of this type of security system.
Extended detection and response system is about keeping an eye on all elements of the corporate network. It provides protection, logs everything that happens inside the system, and reports suspicious activity. XDR, same as EDR, mostly relies upon a heuristic detection system in its automated procedures. When the suspicious item is detected, the other detection mechanisms turn on and proceed with the threat analysis, giving the complete image of what has been detected.
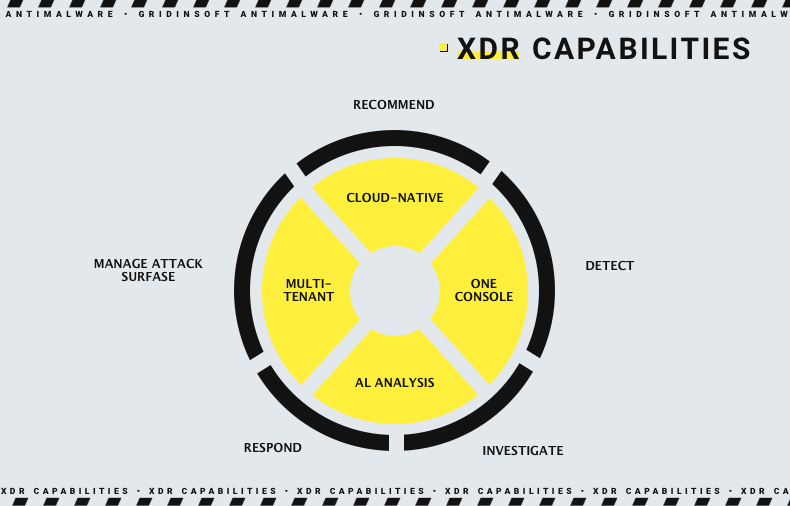
The key feature of XDR is not only detection methods. Correspondingly to the detected threat, it forms a response that should nail the intruder. The key characteristic of this response is its homogeneity - all controlled elements involved in the incident will respond. It is possible since XDR controls all entities in the network, from endpoints and domain controllers to IoT devices. Such a reaction makes it impossible to repeat the attack or exploit the same injection method once again.
The control over cloud services connections and email clients is the other edge that makes extended detection and response systems very effective. According to the last FBI research, over 90% of all cyberattacks happen because of phishing. Malicious email attachments in MS Outlook can easily circumvent the poor protection of outdated versions of this mailing client and launch the malware in the live system. Preventing it means making the corporation less vulnerable. At least, when all other protection mechanisms (like IAM) are running, the threat will likely be stopped. But that is still a bad idea to give it a try.
Let’s see what the difference between three different security conceptions is - ordinary anti-malware software, EDR, and XDR system.
Ordinary anti-malware software
- Controls only a single machine, sometimes can monitor network directories;
- Can run on Windows and sometimes macOS;
- Generally relies upon database detection, all other systems are complementary;
- Have primitive to no events journaling.
Endpoint Detection and Response
- Covers the endpoint and devices connected to it;
- Monitors the incoming and outgoing connections;
- Runs any operating system but generally aims at *NIX;
- Leading detection mechanism is heuristics. Databases and neural networks are complementary. Still, the last two are obligatorily used during the detection analysis;
- Logs any activity within its protection range.
Extended Detection and Response
- Protects the whole corporate network, including endpoints, domain controllers, workstations, and IoT devices;
- Runs any OS, but most often - Linux or FreeBSD derivatives;
- Offers an extended threat analysis and consolidated notifications about detected threats;
- Offers cloud security features;
- Tracks the inner activities with a heuristic engine, calls for others when the threat is detected;
- Journals all events in the network; the ones related to a possible attack surface are recorded in max details.
What is Managed Detection and Response (MDR)?
MDR is a specific variant of XDR application. It supposes extended support from the app developer - even bigger than the default SaaS scheme offers. Regular software-as-a-service supposes that the developer will help its customers with setup, support the client in technical aspects, and possibly adjust the product for the client's needs. Meanwhile, MDR additionally offers support with routine activities, like malware analysis, threat intelligence or investigating the cybersecurity incident. Such a concept is great for companies that lack qualified personnel who can manage the XDR system.
However, the MDR form of software application means higher cost and, more importantly, less control over the staff members who are responsible for this. At the same time, the outsource workers will have less motivation to do all jobs on time and properly - just because they do not belong to the company. The latter depends exclusively on the MDR vendor, but the risks are always there. And you will likely understand if the problem is only after the cyberattack has happened.
XDR vs EDR vs MDR - What to Choose?
As an older and less capable solution,Endpoint detection and response solutions look pretty poor in front of XDR. However, this impression is only partially true. Modern EDR solutions feature most features available in XDRs - inside the range of EDR responsibilities. Again - EDR is designed only to provide extended monitoring capabilities for endpoints and network elements that contact it. For some companies (small businesses), EDR will be more than enough. Since the attack surface that is away from the endpoint (i.e. away from the solution’s capabilities) is pretty small, there is no need for such a heavy and all-encompassing thing as XDR.
Another factor that makes EDR a better option for small companies is its price. Both initial establishment, retention and related features for EDR systems are way cheaper than for XDR. That’s reasonable just because the latter features more elements and things that should be set up correspondingly to the company’s needs.
Extended detection and response systems, on the other hand, are way more effective in big corporations, with several offices and a great differentiation of access rights among the personnel. While smaller companies can artificially decrease the attack surface by clustering the network or setting up a honeypot, large companies will not get a significant effect from these actions. Sure, these measures will still have an effect - but it will be miserable. For such a large number of attack surfaces, XDR will be much more relevant. Moreover, big businesses can easily afford the XDR despite its higher price.
Companies that lack qualified personnel or rely on remote vacancies for their employees will likely appreciate the MDR form of application. The outsourced security specialists will keep an eye on your security, so you don’t have to form a separate department and manage it in any way. Still, there could be the negatives we’ve talked about several paragraphs before. In some situations, MDR is the only acceptable form of the cybersecurity solution, so you have little to no choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
XDR is a completely different conception of a protective system, which differs sharply from the essence of an ordinary antivirus. The latter offers a protection for a single or several devices, but they are always served separately from each other. XDR manages the security of all devices in the network, including even IoT devices, and forms a simultaneous response of all participants.
For corporations, XDR really replaces antivirus, as the last one does not offer suitable protection for a massive corporate network. To correspond with the modern threat landscape, a complex solution is required - and XDR is the one.
Yes, most of the XDR systems apply the use of artificial intelligence for different purposes. Similarly to EDRs, they use AI as a separate detection mechanism that allows them to detect especially sneaky threats. The feature of most artificial intelligences is that they can detect miserable signatures that are impossible to detect with the systems set up by a human. Generally, machine learning algorithms became more and more popular in anti-malware software.
Aside from the detection, XDR systems use AI to analyse cybersecurity incidents. Based on logs and the data from other event logging systems, extended detection and response systems can give the analysts a full picture of what is happening. Additionally, it may give advice on how to respond properly in that case.
- The hierarchy of security signals, delivered to analysts;
- Closed-circuit automated responses that do not involve human interruption;
- Detection system that consists of heuristic, AI-based and database-backed subsystems;
- Behavioural and cross-correlated analytics of the detection as a resulting part of detection system.
