Many people remain unaware of the substantial benefits of malware protection. While most have encountered the concept of computer threats, their understanding tends to be imprecise. In the past, the term “virus” frequently surfaced; now, “malware” has become the prevalent, albeit nebulous, term that casts a shadow of uncertainty over online threats. This vagueness partly stems from ongoing debates among computer security experts over the classification of threats and malware.
Despite the clear dangers, many users still overlook the importance of safeguarding their computers with security software. The process of selecting, installing, and configuring an antivirus, not to mention the system resources it consumes, might seem daunting and unnecessary. However, it’s crucial to remember that safety measures, though they might appear excessive, prove their worth when you most need them.
Understanding Malware Protection
Let’s start by defining malware. The term “malware” — short for “malicious software” — encompasses a variety of harmful programs designed to infiltrate and damage computers. Besides malware, there are non-executable scripts and other network threats like phishing, which doesn’t rely on directly infecting a computer with programs.
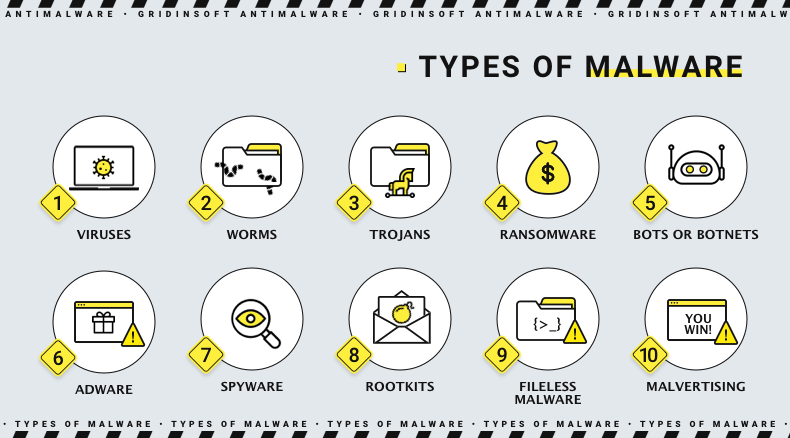
Now let us see what malware does from the standpoint of the attacker. The list of damages types below may not be exhaustive, but it summarizes the harm hackers usually inflict by malware nowadays and the reason for such their activities.
Data Theft via Spyware
Hackers deploy spyware, a category of malware, to execute data theft. This group includes diverse programs with a common espionage function. For instance, keyloggers record all keystrokes, while rogue browsers spy on online activities. Their capabilities vary: some might only transfer your browsing history to third parties, while others can record keystrokes or intercept your internet traffic.
Beyond the immediate privacy invasion, spyware also consumes CPU resources in the background, slowing down your computer.
The most severe risk of spyware is identity theft, which can have devastating consequences, including the loss of financial credentials and all the money in your account.
Cryptocurrency Mining Malware
Specialized malware, often introduced to systems as Trojans or downloaded by other Trojans, exists solely to use the infected device’s resources for mining cryptocurrency for others. This process, which involves cryptographic tasks, is handled by the victim’s CPU.
Infected devices typically experience reduced processing speeds and slower internet connections as a result of these mining activities.
Botnet Involvement
Botnets are networks of malware-infected computers controlled remotely by hackers. This collective control allows hackers to perform large-scale operations like DDoS attacks or massive automated posting, activities that are impossible with a single machine. Furthermore, a botnet can propagate itself, potentially growing to tens of millions of infected devices.
For users, the signs of a botnet infection include an overloaded CPU and unexplained internet traffic, with most botnet activities occurring without their knowledge.
Adware: Turning Browsing into a Billboard
Adware encompasses a wide range of software, including overt malware and potentially unwanted applications (PUPs). Malicious adware transforms your browsing experience into a barrage of distractions, reminiscent of the Las Vegas Strip, with bright flashing banners constantly appearing and obstructing your view. Additionally, adware can embed advertisement links within the text of web pages you visit to provoke accidental clicks. Some adware even extends beyond your browser, displaying ads throughout the operating system.
Adware may manifest as easy-to-remove browser extensions, rogue browsers, or various “handy” applications. Some adware operates covertly, appearing only as unremarkable processes in your Task Manager.
The negative effects of adware are obvious and typically prompt users to cleanse their computers. If you find adware on your system, removing it is crucial, as its presence can lead to further malware infections.
Ransomware: Encrypting Data for Ransom
Ransomware is one of the most destructive types of malware. Once it infiltrates a device, it encrypts all data files of specific types, making access to these files impossible, and leaves a ransom note demanding payment in cryptocurrency. The note details the payment amount necessary for the decryption key, which cybercriminals typically provide after receiving the ransom—this ensures that future victims also pay, trusting the scheme will resolve their issues.
Ransomware attacks have become a highly profitable malware-based enterprise, generating millions in annual revenue for perpetrators and are now more rampant than ever. For more insights, read about the business model of ransomware.
Taking Control Over the System with Rootkits
Rootkits represent a particularly perilous class of malware due to their ability to grant hackers administrative-like control over a system. Found at rootkits, these programs are notorious for their capability to create a backdoor—an unauthorized pathway circumventing access controls. This backdoor allows hackers to issue commands directly from the core of the infected system, with potential damages limited only by the attackers’ objectives.
The threat of rootkits highlights the necessity for robust system security measures to detect and counteract such invasive control.
Recognizing Symptoms of Malware Infection
Understanding the symptoms of a malware infection is crucial for early detection and response. This section summarizes the key signs to watch for, regardless of the specific type of malware affecting your device. By paying close attention to these indicators, you may be able to identify the type of malware based on the symptoms alone.
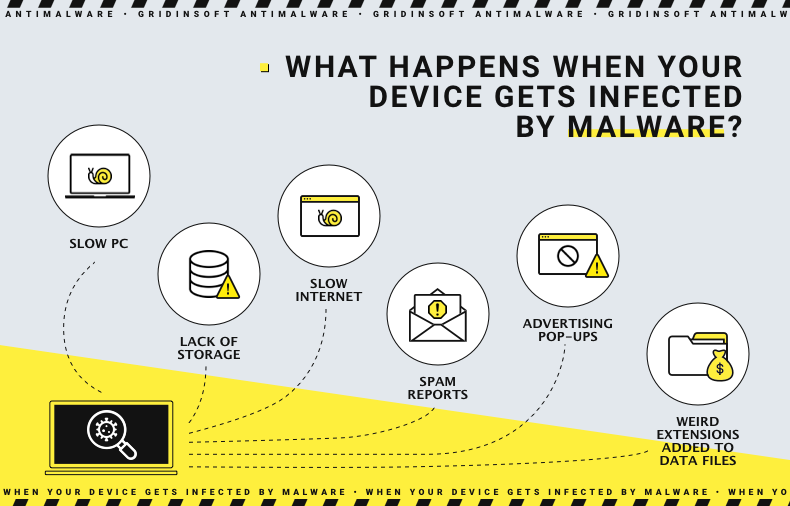
- Slow PC and Crashing Programs: Various types of malware, especially those like cryptocurrency miners, operate in the background, consuming substantial system resources. This can noticeably decrease your PC’s performance and cause frequent program crashes.
- Lack of Storage: Some malware types use significant amounts of hard drive space, leaving insufficient room for your regular activities.
- Slow Internet: Malware can also degrade your Internet speed by generating background traffic that consumes your bandwidth.
- Spam Reports: If friends report spam from your email or social media accounts, it’s likely that malware has hijacked your accounts.
- Advertising Pop-ups: Unexpected ads and unfamiliar applications are common signs of adware infection. These can be both annoying and risky if they lead to inadvertent clicks.
- Weird Extensions Added to Data Files: This is a hallmark of ransomware. Encrypted files become inaccessible, and a ransom is demanded for their release— a harsh reminder of the dangers of online carelessness.
Not Only Malware Protection
Enhancing cybersecurity involves more than just installing software; it requires a proactive approach to safeguard your digital environment. Staying vigilant is crucial, especially within a workgroup. Educating your team on basic security principles can significantly reduce the risk of malware infections which often exploit human errors such as inattention and gullibility through social engineering tactics. For example, phishing attacks might not always carry malware directly, but they frequently aim to compromise devices as part of their strategy. You can learn how to recognize and avoid phishing scams to better protect yourself.
Another vital measure is to be wary of unknown email attachments, links, or banners. Malware commonly infiltrates systems through scripts embedded in files or websites that users inadvertently access. Regular updates to your operating system are also essential; they minimize vulnerabilities and boost the efficacy of antivirus solutions. Stay informed about the latest security practices to keep your system robust against threats.
Furthermore, employing two-factor authentication wherever possible can drastically enhance the security of your online accounts, effectively minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. Lastly, the cornerstone of a solid cybersecurity strategy is the installation of trustworthy antivirus software. A vigilant approach, combined with reliable security programs, forms the most effective defense, detecting and eliminating threats before they can cause any damage.
How Malware Protection Can Help?
We were going to discuss the benefits of using malware protection, and now, let’s delve into what an antivirus does. Consider the example of Gridinsoft Malicious Software Removal. This program offers comprehensive triple protection.
The first layer is On-Run Protection. The program monitors all new files on your machine. Before any incoming file can cause damage, it scans it. If identified as malicious or unwanted, the file is immediately quarantined, allowing the user to decide whether to delete it or restore it.
Next, there’s Internet Protection. This function blocks hazardous websites and alerts you about suspicious ones. Websites are deemed dangerous if they contain malicious scripts or lack an SSL certificate. These blocks and warnings, though overridable, provide essential protection in most scenarios.
The most thorough option is the Deep Scan. You can choose the scope of the scan: a more comprehensive scan takes longer but increases the likelihood of detecting and eliminating malware. Some malware types can only be uncovered and removed through such in-depth scanning.
Malware Protection Parting Wishes
By integrating various virus detection methods, Gridinsoft products showcase versatility and effectiveness, performing robustly on both home and corporate devices. You can deploy this software as your primary security system or as a supplementary antivirus scanner. Its cost-effectiveness is matched by its efficacy.
As for the general benefits of using antivirus software, they are undeniable. Threats may seem distant until they directly impact you. Cybersecurity is no exception to this rule. However, any doubts about the necessity of antivirus will likely dissipate after the first successful interception of a dangerous Trojan, ideally neutralized by your antivirus.







I’m wondering if Grindin soft has any Malware for Telephones that will stop infectious calls. AS I am getting several calls that are non communicative and are tracking my usage. I asked carrier and they say no. So I would like to install something from the only supplier that I trust. I do hope that you can help. My phone has been hacked Twice. If you have anything please advise.
Thank You
Ronald RS Welch Sr