
WEP and WPA Meaning
Across the entire existence of Wi-Fi as a technology, it gained a bunch of security standards. Contrary to a signal that goes through a cable, Wi-Fi signal travels by air, meaning everyone with the proper equipment can intercept it. Both WEP, WPA and its newer variants – WPA2 and WPA3 – are the way to secure the signal from such siphoning.
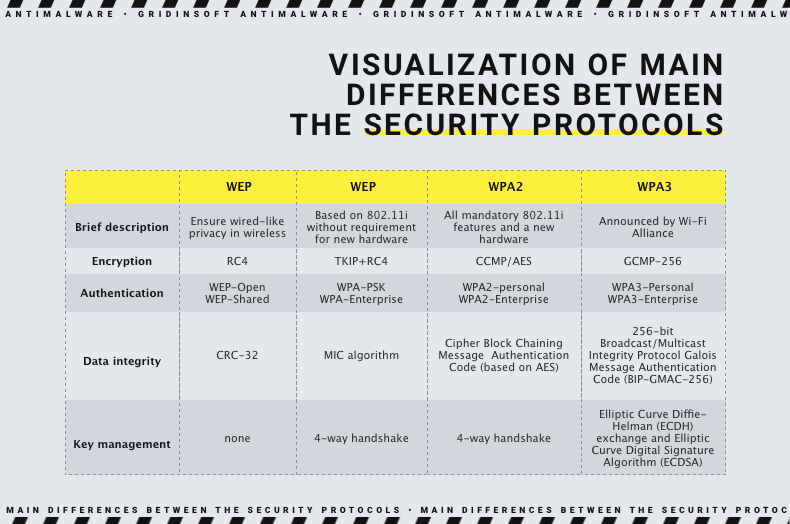
Wired Equivalent Privacy, or WEP, is the earliest Wi-Fi security standard, adopted back in 1999. It was supposed to do what its designation sounds like – providing the security equivalent of a wired connection of the time. Though, as it turned out soon after, there were a lot of design flaws that made it easily hackable even with the technologies of its epoch. Though, the problems of a novice technology were too bad and hard to fix to keep it going. Stopgap solutions like WEP2 or WEP+ never saw massive use since they were too hardware-reliant.
Wi-Fi Protected Access, or WPA, is what appeared in late 2000 to substitute the flawed technology. The Wi-Fi Alliance – the organization responsible for the development of Wi-Fi as a technology – developed WPA keeping in mind all the flaws made in WEP. This, essentially, led to the creation of a technology we use even these days. Together with using much more secure encryption, which was now protecting each separate Internet package with a unique key, it also featured a couple of new anti-spoofing tricks. The latter was especially useful against Man-in-the-Middle attacks, which were particularly popular at the time.
Further versions of the WPA are meant to keep the technology up to date. WPA2, introduced in 2004, brought the support of AES encryption and some enhancements to the package integrity protection features present in the original version. WPA3 is the newest version of the security protocol, presented in 2018, that hikes up the security to modern standards and patches some of the known vulnerabilities.
WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3 – what is better?
After all the information above, the obvious question arises – what is better? Well, the answer is pretty straightforward, but with some deviations depending on the purpose.
It is most likely obvious that WEP is a no-go these days. A firstling of Wi-Fi protection technologies, it has some severe design flaws; some of them were not corrected due to the technology abandonment back in 2004. Modern Wi-Fi routers do not even support WEP, leaving you to choose from WPA generations. And even for older hardware, there are the options for at least the original WPA or WPA2, so take your time and make the correct setup. It is about your safety, after all.
In the case of WPA, the choice is not that simple. Instead of one obviously bad option, we have 3. Nonetheless, by the rule “newer is better” we may already excise the original WPA. Why not together with WPA2? Because the latter is broadly supported, even by the most modern hardware, and has the early design flaws fixed. This already gives it a huge head start, and makes it viable for use in modern environments.
WPA2 is still an OK option for home usage. While corporate networks should comply with the latest security standards to prevent any hackery, a home Wi-Fi access point is not likely to face any protocol-based attacks. Moreover, if you’ve purchased a router before 2020, there is a huge chance that it does not support WPA3 at all. Some of the models though could get firmware updates that unlock that feature, and will probably bring some improvements – which are always a desirable thing.
Meanwhile, when we talk about corporate security, or the users really concerned about potential cyberattacks, WPA3 is the best choice. In the places where trade-offs are unacceptable, we recommend using the latest technologies available. This includes not only software, but also hardware – older devices may support WPA3, but have hardware vulnerabilities or incompatibility with certain technologies.
Personal or Enterprise?
While roaming through a router setup page, you could have noticed two WPA modes – Personal (or PSK) and Enterprise. In simple words, Enterprise is a more secure version that features more sturdy encryption and protection against dictionary attacks. At the same time, setting up the Enterprise requires quite a bit of network engineering skill. Though, as it comes from its name, this option is mostly suitable for corporate networks that require advanced security measures for obvious reasons.
For home users or small businesses, Personal mode will be enough. Though, the security measures that derive from common sense are still needed. Setting up a reliable password, adjusting the signal power to prevent it from reaching further than your place, giving the network a distinct name – all these steps will minimize the effectiveness of popular attack vectors.
How To Get Better Protection for Home Wi-Fi Network?
In addition to having the appropriate Wi-Fi security protocol, you also need to follow some critical cybersecurity tips concerning your Wi-Fi network security:
💡 Turn off the remote administration feature.
If you don't need this feature regularly, it would be better not to have it turned on. Because it's one of the common ways for threat actors to get your wifi settings and change them without you. See the administration section of your router to change this setting.
✨ Turn on MAC address filtering.
This setting will allow you to restrict devices connecting to your home network, giving permission only to those you registered. In such a way, you can enable additional security measures for your network.
🧱 Enable Firewall.
Most wifi routers have in-built firewalls, but sometimes they can be turned off. Make sure you have one in place and it's not disabled. Firewalls protect against network attacks from threat actors.
🏠 Place your router in the center of your home.
An obvious thing to do. If any hacker doesn't have access to your wifi router signal, they can't attack you by intercepting the signal. Don't place your router near windows or doors and make threat actors' life easier.
🔁 Regularly update the router firmware.
While some routers have the auto-update feature - most of them won't, so make sure your router firmware is updated. Because if there's any vulnerability found, threat actors will likely try to exploit it.
🔕 Hide your network from being seen by everyone.
You can use a unique feature to help you hide your network from people in the surrounding area. Changing your network's default name will make it harder for threat actors to hack into your network. Because every router has assigned by the manufacturer its SSID (Service Set identifier) and you can change it and make your network invisible.
❗ Don't use the default password and username.
Just saying that anything default can be easily looked up on the internet, and that's the first thing that threat actors will try to do. So be creative and make up your complex and strong password that no one outside your network will easily guess. The same goes for username - also, don't make it something obvious. A quick reminder that your strong password should consist of letters of all registers, numbers, and various characters.
Known attacks on WEP & WPA protocols
Both WEP and WPA are not invulnerable, even when we talk about the latest WPA revision. WEP though is worse by orders of magnitude, as it was bad back in early ‘00s, leave alone modern times. Let’s check out the most widespread approaches, beginning with WEP.
WEP Attacks
As WEP is not even supported by modern network routers, all the dangers and attacks related to this security technology are now historical legacy. Still, reviewing these attack vectors are important for understanding how network attacks were developing as the attack vector.
Network Eavesdropping
Due to the extremely poor strength of ciphering applied by WEP, it was pretty easy to eavesdrop on a Wi-Fi network protected with this protocol. Using special software, like an infamous aircrack-ng, it will not take long to retrieve the RC4 key, effectively allowing the threat actor to read any data sent through the router.
In fact, it was not even necessary to eavesdrop for a long time to be able to perform malicious activities. One packet may be enough to perform the attack – hackers can decrypt it and retrieve the info needed to malform a package. The latter leads to the real-time traffic decryption – a dream of any threat actor.
Caffe Latte Attack
Caffe Latte attack is outstanding for the fact that it could be performed without the connection to the target network. Instead, using an “evil twin” trick with their own Wi-Fi network, hackers may convince the user device into thinking it is connected to a corporate one, for example. Hackers make the victim’s device to send ARP requests, and get enough of them to scrape an RC4 key. Then, they are able to decrypt any of the Internet packages sent from the network, as well as convince the victim’s device into communicating with the fake access point as if it was a real one.
WPA Attacks
As WPA was intended to fix all the flaws present in the WEP, it lacks the vast majority of design flaws, leaving hackers to at least a mix of design features and setup mistakes. Moreover, WPA3 lacks the vast majority of known exploitable areas – and that is why it is recommended.
Weak Pre-Shared Key Security
In Personal mode, WPA protocol supposes sending the pre-shared security key (PSK) to the counterpart upon establishing the connection. Then, the server and the client exchange their own keys, the connection finalizes, and the normal Internet browsing continues. However, the way this key is transmitted is not entirely secure, and leaves the hackers with opportunities to recover it. And having one PSK, they can decrypt all the Internet packages sent with the use of this PSK both in the past and in future. That vulnerability is obviously not present in the Enterprise version, but is also fixed in WPA3.
Packet Decryption & Spoofing
A pretty complicated technique, that was a point of vast discussions in the past. Packet spoofing attack, also known as TKIP attack, bears on the ability to simply guess the identification key and thus take the packet instead of the actual receiver. The attack, actually, grows from the similar approach to hack WEP-protected networks, but includes a delay before repeating the request. Such a trick circumnavigates the protection present in the WPA mechanism, while allowing to pick the needed key and intercept all the further packages.
