
How is Egregor still running?
Just as the majority of ransomware groups that aim at companies appeared in 2020, Egregor group uses the ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model. That way of distribution means that the exact developers of ransomware don’t touch the distribution in a usual way. They don’t have to cover their hands in mud doing the dirty job. Searching for the possible exploits in companies, composing the email message that looks legit - they are free of these duties.
The developers of Egregor ransomware sell their virus to the third party in Darknet. You can spectate a lot of offers from various ransomware groups in that place, and Egregor is just among them. Of course, the initial sum is pretty high, but attacks on relatively big companies can bring a pretty big profit. As developers ensure, even the first ransom paid to you may cover the spendings on the source code. But the problem of such a dream is that distributors in RaaS scheme are just a consumable thing. You may see a lot of news from executive authorities that state about another ransomware group caught. However, almost always they talk about a small division of distributors - and not the developers.
People who decide to buy the ransomware source code are likely doing this hoping to get a fast and big profit. But they often forget that it is a pretty big problem to spend this money when you are imprisoned for cybercrimes. It is important to remember that any offer that contains the promises of fast and big profit always implies the big risk. This time, you are risking not with your money, but with your freedom.
How does Egregor work?
First thing that each ransomware uses during the attack is the distribution method. A lot of corporate-aimed ransomware uses RDP vulnerabilities to inject the virus, and Egregor is not an exclusion. Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) was always the technology with a lot of security problems, but all of them upscaled after the start of the pandemic. People were forced to work from home, and remote access to their workstations in the office is the best way to make their efficiency as high as without the remote work.
RDP vulnerabilities are related to certain connection ports. To prevent the exploitation, you must establish the connection through other ports and close the vulnerable ones. When the RDP access is set up by the system administrator, these breaches are about to be closed. But in the pandemic rush, when sysadmins have no time to set up the thing for everyone, users are forced to do it themselves, using the guides from YouTube or somewhere else. But these manuals can barely show you the way to make the RDP secure.
Fraudsters scan the RDP ports of the corporate network, using the special utility - Advanced Port Scanner. This tool is 100% legit and created by Microsoft, but used sometimes for malevolent purposes. When they see the vulnerable port left opened, they are starting the brute force. In this way, they get into the system, infecting a computer that had this vulnerable connection. Then, crooks use either brute force or hack tools to get the passwords from other computers, including the Domain Controller (DC) - the administrator’s PC. Getting access from one computer to another, they encrypt every PC they can reach, and steal the data that is stored on those computers. This stolen information will be used in future to perform the so-called double extortion.
There are no strict facts about the encryption type used by Egregor. Most likely, it uses a popular combination of AES-256 and RSA-2048. First one is enough to prevent any possibilities for the decryption besides the ransom paying, but they have likely added RSA-2048 to scare their victims. As it was mentioned, file encryption is not a single target - this malware also steals the files from the infected machines. For this purpose, crooks use other tools - IceID, Qakbot and Ursnif. Those programs were initially created for malicious actions, such as data stealing or spying on the computer they are launched on. All of them may be classified as stealer trojans and spyware.
Technical details
| Note | RECOVER-FILES.txt |
| File pattern | %filename% . %original_extension% . %ransomware_extension% (last one is random for each encrypted file) |
| Algorithm | AES-256+RSA-2048 |
| Features | Famous for its attacks on various corporations through all over the world |
| Damage | Disables MS Defender and Volume Shadow Copies, steals the corporate data |
| Distribution | RDP vulnerabilities exploiting |
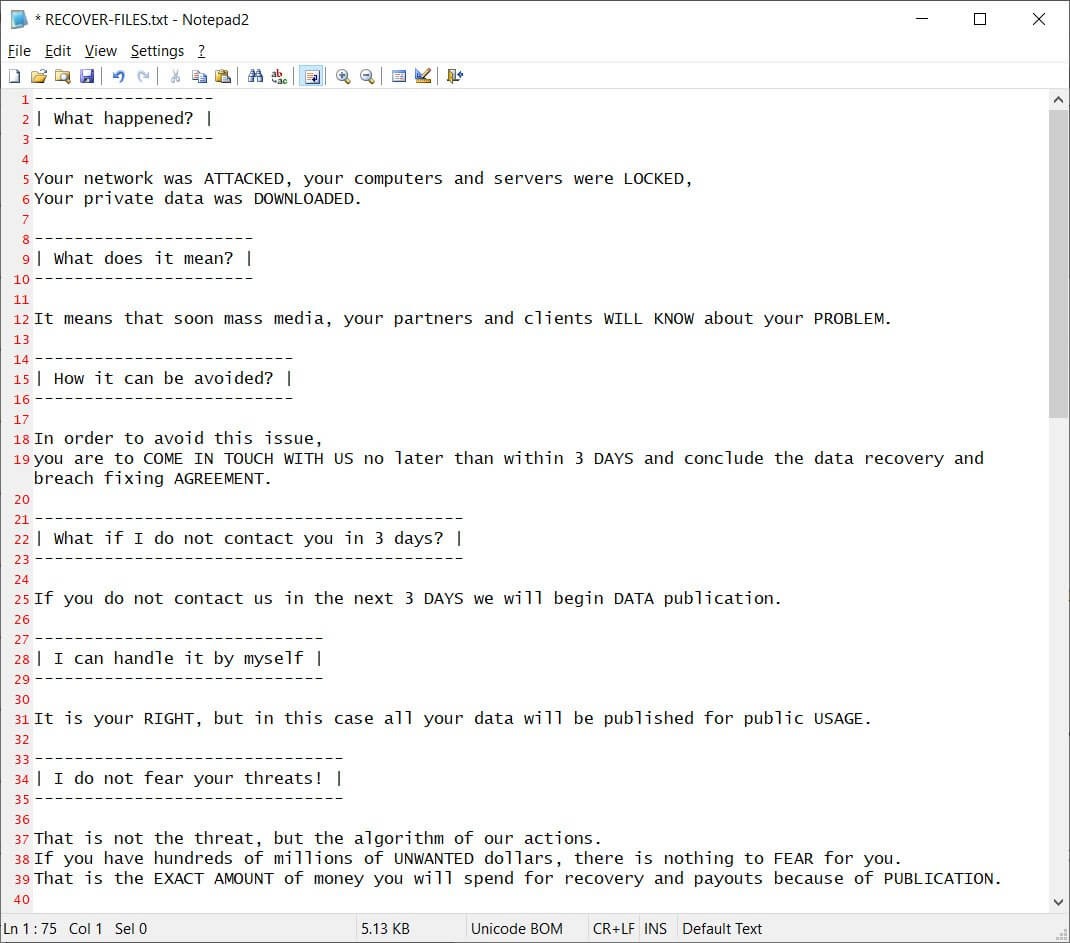
Here is the Egregor’s ransom note:
Countries under attack
Egregor ransomware group don’t stop on a certain country, or several ones. It is known for attacks on companies from all over the world. Currently, the biggest activity of Egregor group is spectated in USA, Canada, Russia (a newbie!), India, Indonesia, Mexico, France, UK, Bulgaria and Morocco. The ransom amount is different, and depends on the country and company size. It is a very typical situation for the RaaS-distributed ransomware: different groups charge different ransoms.
Counteraction measures: how countries compete against Egregor
Such an active ransomware group could not force the executive authorities to pay attention to it. It is obvious that they have a lot of chances to catch the distributors, but a low chance to get the exact developers. However, since Egregor was spread by large groups of distributors, it was easy to stop the spreading for a while by catching these boys. So do the Ukrainian cyber police, who captured the Maze group in February 2021. In June 2021, another group of cybercriminals was captured - again in Ukraine, but this time by the joint operation of the US Intelligence community and Ukrainian cyber police.
Both of these capturings dealt a very heavy damage to the ransomware distribution. Since the group caught in February was also employed in the distribution of several other ransomware variants, the overall ransomware activity throughout the world decreased significantly. However, those actions did not stop the ransomware developers from selling their “product” as a service to other cybercriminals, so the distribution will definitely be back.
