A security breach is an unauthorized access to a device, network, program, or data. Security breaches result from the network or device security protocols being violated or circumvented. Let’s see the types of security breaches, the ways they happen, and methods to counteract security breaches.
What is a Security Breach?
First of all, let’s have a look at the definitions. A security breach is when an intruder bypasses security mechanisms and gets access to data, apps, networks, or devices. Despite their close relations, there’s a difference between security breaches and data breaches. A security breach is more about getting access as such – like breaking into someone’s house. On the other hand, the data breach results from a security breach – as the latter may aim at tasks other than leaking data. It is instead a specific consequence of security breaches.
What are the types of Security Breaches?
Threat actors may create a security breach in different ways, depending on their victim and intentions. Here are the three most important ones.
1. Malware injection
Cybercriminals often employ malicious software to infiltrate protected systems. Viruses, spyware, and other malicious software are transmitted via email or downloaded from the Internet. For instance, you might receive an email that contains an attachment – generally, an MS Office document. Moreover opening that file can end up infecting your PC. You may also download a malicious program from the Internet without any tricky approaches. Often hackers will target your computer to get money and steal your data, which they can sell on the Darknet or other appropriate places.
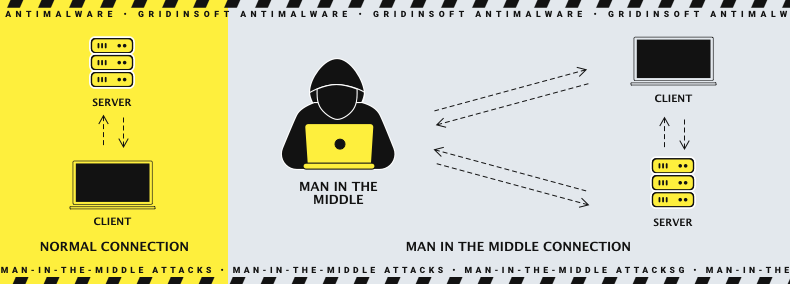
2. Man-in-the-Middle-attack
As the name says, the assailant’s route is in the middle. Now we’ll determine what it means. Also hacker can intercept communications between two parties, which results in one party receiving a false message, or the entire communication log may be compromised. Such an attack is often carried out due to hacked network equipment, such as a router. However, some malware examples may fit that purpose as well.
3. Insider threat
Insider threat is the danger of a person from within the company using their position to utilize their authorized access to commit a cybercrime. This harm can include malicious, negligent, or accidental actions that negatively affect the organization’s security, confidentiality, or availability. Other stakeholders may find this general definition more appropriate and valuable to their organization. CISA defines an insider threat as the danger that an insider will knowingly or unknowingly misuse his authorized access. It does so to harm the department’s mission, resources, personnel, facilities, information, equipment, networks, or systems. This danger can be manifested through the following behaviors of insiders:
- Corruption, including participation in transnational organized crime
- Terrorism
- Sabotage
- Unauthorized disclosure of information
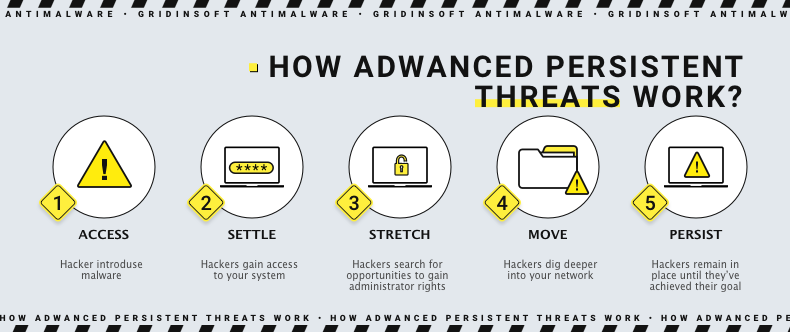
4. Advanced persistent threat
An advanced persistent threat is a persistent cyberattack that employs advanced tactics to remain undetected in a network for an extended time to steal information. An APT attack is meticulously planned and executed to infiltrate a specific organization, circumvent existing security measures and remain undetected. Also APT attacks are more complex and require more advanced planning than traditional cyberattacks. Adversaries are typically well-funded, experienced teams of cybercriminals that target organizations with a high value. They’ve devoted significant time and resources to investigating and identifying vulnerabilities within the organization.
Examples of Security Breaches
Recent high-profile breaches include:
- Facebook: In 2021, the personal information of over half a billion Facebook users was leaked, including phone numbers, dates of birth, locations, email addresses, and more. As a result, the attack was a zero-day exploit that allowed hackers to harvest a large amount of data from the company’s servers.
- Equifax: In 2017, the US credit bureau Equifax experienced a security breach via a third-party software vulnerability that was similar to the EternalBlue exploit. Fraudsters gained access to the personal information of over 160 million people; this is considered one of the most significant identity theft cyber crimes to date.
- Yahoo!: In 2016, 200 million Yahoo users were active. A schedule of usernames and passwords for Amazon accounts posted for sale on the dark web. Yahoo! The company blamed the breach on “state-sponsored hackers,” who could manipulate cookie data to gain access to user accounts.
- eBay: In 2014, it experienced a severe security breach resulting in the widespread disclosure of personal information.
How to help Protect yourself from a Security Breach
Monitor your accounts and devices
After a security incident, closely monitor your accounts and devices for any unusual activity. If one is present, ask the site administrator to suspend your account and help prevent the threat actor from accessing it.
Change your passwords
Choose complex passwords on all devices that need configuring. Ensure that you pay special attention to routers and utilize public Wi-Fi. Remember to update your password frequently. The password must include all upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special characters.

Contact your financial institution
Contact your bank immediately to prevent fraudulent transactions if your credit card or other financial information is compromised. They can tell you what the problem is and how to fix it. Sometimes, it may take time to resolve issues with your card. The best thing to do in these cases is to block your card so that fraudsters can’t withdraw money from it.
Perform an antivirus scan
If someone has gained access to your computer or home network, they may be infected with malware. Use a reliable antivirus software to identify and remove any threats that may be present. Run an initial scan to determine if your computer has any issues or bugs. Depending on the scan you run, it may take time for the scan to complete. The default is to run a quick scan. The standard scan is recommended, but it takes longer.
Report the incident to the appropriate authorities
Contact your local law enforcement agency if you’ve been the victim of identity theft or fraud. They will assist you in the necessary steps to regain control over your accounts.
You should know that avoiding any attack is possible if you take the proper steps to protect yourself. This requires creating strong passwords, using two-factor authentication, and keeping track of your credentials with a strong password manager.
Good digital hygiene also includes using comprehensive security and privacy software to prevent threats from infiltrating your devices and protecting your data. This makes it harder for hackers to enter your device, get your data, and sell it on third-party paywalls.





