Today, phishing sites are commonplace. But unfortunately, this seemingly old, deceptive tactic, which everyone seemed to have figured out long ago, still brings enormous profits to scammers today. The problem is that while Internet users are becoming more cautious, cyber scammers are developing more sophisticated ways to trick them. One such method is ImBetter malware. The authors of such malware use sophisticated techniques when creating their phishing websites to make them appear legitimate and appealing to users.
What is ImBetter malware?
ImBetter Stealer is the name of malware whose mission, as its name suggests, is to steal information. Not so long ago, researchers came across some phishing websites that targeted Windows users. These websites imitate popular crypto wallets and online file converters. However, instead of its purported function, they trick users into downloading the “ImBetter Stealer” malware. This malware targets sensitive data such as cryptocurrency wallets, browser credentials, and session cookies. In addition, it can take screenshots of the system and send them to the C&C server.
ImBetter Malware Spreading
Researchers discovered that the main channel for spreading ImBetter are malicious sites masquerading as well-known legit cryptocurrency sites, such as MetaMask, etc., and online file format converters. Nevertheless, experts do not rule out that ImBetter also uses other distribution methods, such as phishing and social engineering. In some cases, this malware is getting bundled with pirated software or is supplied instead of it. In turn, sites that distribute pirated programs are promoted via spam mailings, search engine poisoning, malicious browser pop-ups, etc.
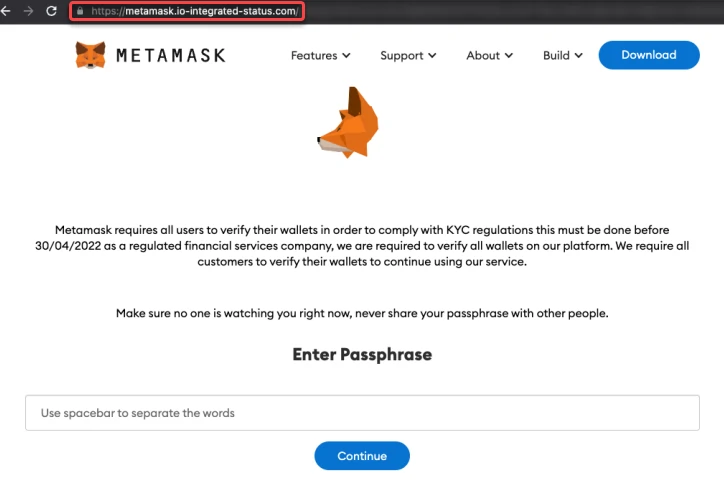
However, the infection process only begins when a visitor interacts with the website by clicking on a specific content. The ImBetter Stealer malware binary is a 32-bit GUI-based executable file. Immediately after starting the execution, the malware obtains language and region data for the system. If the malware detects Russian, Moldova, Belarusian, Bashkir, Tatar, Kazakh, or Yakut region/languages after checking the LCID code of the infected system, it would stop further execution. This clearly hints at the virus’s origin and indicates that the attackers are Russian-speaking.
ImBetter Data Stealing
Suppose the system victim does not belong to any of the above regions. In that case, ImBetter takes a screenshot of the infected system’s desktop and saves it to the C:\Users\Public folder with the image name “Scr-urtydcfgads.png“. The malware will then send this screenshot to attackers on the C&C server. ImBetter then creates a socket connection to the C&C IP address, after which it can obtain the hardware ID, CPU, GPU, and system memory size, as well as screen and name information from the infected system. Each type of system information is saved separately as a string of key-value pairs in memory and then encoded in Base64 format and sent to the C&C server.
Following system information, the malware checks for the presence of Chromium-based web browsers installed in the system. ImBetter is interested in the following web browsers:
- Google Chrome
- Edge
- Opera Stable
- Vivaldi
- AcWebBrowser
- Epic Browser
- Titan Browser
- Baidu Spark
- CoolNovo
- Yandex
- Torch
- BlackHawk
- Comodo Dragon
- Rockmelt
- Brave
- Sleipnir
- CentBrowser
- Go!
- SRWare Iron
- Flock
There is a pretty straightforward reason for attacking these browsers. Their popularity increases the chance of finding something valuable among the browser files – like passwords, user accounts, cookies and so forth. By default, this information is stored in the AppData/Local/%BrowserName% directory, the one that is created during its installation. It contains login credentials, cookies, stored credit card numbers, user profiles, and cryptocurrency extensions. Cybercriminals do all this for one purpose – to gain control over the victim’s personal information and/or funds.
How to avoid malware?
The following cybersecurity tips create a first line of defense against attackers. We recommend that you follow the next tips to reduce the risk of ImBetter infection, as well as other malware:
- Download from trusted sources. Avoid downloading and using pirated software from warez/torrent websites. Most cracked programs contain malware.
- Use strong passwords. Using easy-to-guess or predictable passwords makes it easy for crooks to crack your password by brute force.
- Use Multifactor Authentication. Suppose attackers discovered or cracked your password and tried logging into your account. The system will send you a notification to your phone and a one-time confirmation code. Without it, attackers cannot log in to your account.
- Always install the latest updates on your devices. Updates contain important security fixes and sometimes new features. Therefore, we recommend enabling automatic software updates on your computer and smartphone.
- Use reliable anti-malware software. This way, antivirus software blocks and removes malicious files while downloading.
- Please do not click on links from emails or open email attachments unless you know their authenticity.
Tips for organizations:
- Train employees to identify threats such as phishing/insecure URLs.
- Monitor the beacon on the network level to block data exfiltration by malware or TAs.
- Use blocking URLs that employees may use to download malware, such as Torrent/Warez.
- Use data loss prevention (DLP) solutions on employee systems.





