A Microsoft specialist has discovered vulnerabilities in Linux systems, the exploitation of which allows quickly gaining superuser rights.
In total, two vulnerabilities were discovered (CVE-2022-29799 and CVE-2022-29800) and united under the common name Nimbuspwn.
Problems are found in the networkd-dispatcher component of many Linux distributions, which dispatches network status changes and can run various scripts to respond to the new status. When the computer system is turned on, networkd-dispatcher starts with superuser rights.
By the way, we wrote that Google Offers up to $91,000 for Linux Vulnerabilities …hey, Microsoft guy, Google money are here!
The discovered vulnerabilities combine directory traversal, symbolic link race, and the TOCTOU (time-of-check time-of-use) error. After examining the networkd-dispatcher source code, Microsoft researcher Jonathan Bar Or noticed that the “_run_hooks_for_state” component implements the following logic:
- Finds the list of available scripts by using the get_script_list method to call a separate scripts_in_path method to return all files stored in the “/etc/networkd-dispatcher/.d” directory.
- Sorts the list of scripts.
- Runs each script with a subprocess.Popen process and provides custom environment variables.
You might also be interested in the following information: Experts list 15 most attacked Linux vulnerabilities.
Run_hooks_for_state exposes Linux systems to the directory traversal vulnerability (CVE-2022-29799) because none of the functions it uses properly clean up the states used to build the correct script path from malicious input. Hackers can use the vulnerability to get out of the “/etc/networkd-dispatcher” directory.
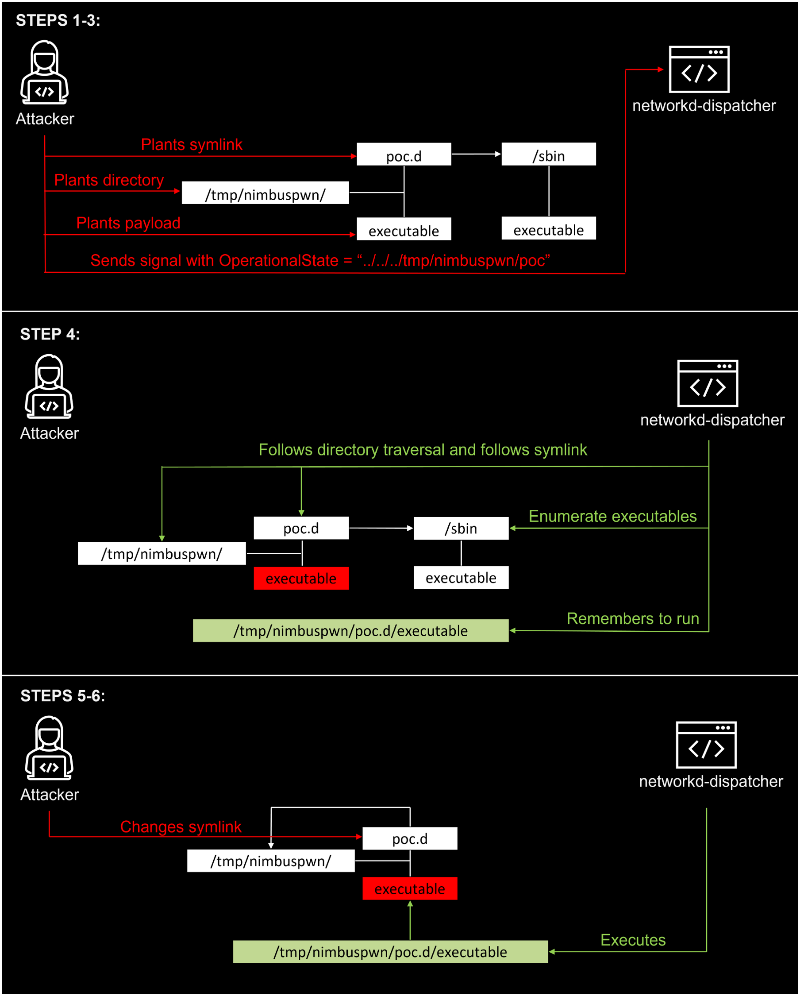
Run-hooks_for_state also contains a CVE-2022-29800 vulnerability that makes systems vulnerable to a TOCTOU race condition as a certain amount of time elapses between detecting scripts and running them. An attacker could use this vulnerability to replace scripts that networkd-dispatcher believes belong to the root user, with malicious scripts.
The researcher also found several processes running as the systemd-network user, which is allowed to use the bus name needed to run arbitrary code from writable locations.
Vulnerable processes include several gpgv plugins that run when apt-get is installed or updated, and the Erlang Port Mapper daemon, which allows arbitrary code to be run in some scripts.
The vulnerability in networkd-dispatcher was fixed, but it is not known when and in what version. Linux users are strongly advised to upgrade to the latest version.




