Hellminer.exe is a process you can see in the Task Manager that indicates a malicious software activity. It stands out by the high CPU load it creates, making the system much less responsive. Let’s figure out what this process is, and how to get rid of it.
Hellminer malware has a potential to attack a wide range of devices, from IoT to server clusters. The final target of its activity is bringing profit to its masters with the use of your hardware. Ignoring the activity of this malicious program may lead to premature hardware failure and overall performance deterioration.
What is the Hellminer.exe process?
This is a process associated with a malicious coin miner. Such malware aims at exploiting the system’s hardware to mine cryptocurrencies, mainly DarkCoin and Monero. To maximize profits, hackers who stand behind this malware establish huge networks of infected computers. Hellminer takes up to 80% of CPU power in order to get substantial mining performance, making the system sluggish and uncomfortable to use.
Malicious miners like this one typically get into the user systems through malvertising on the Web, or with the use of dropper malware. Both spreading ways though are commonly used by other malware, which means the risk that Hellminer is not the only infection running in the system.
This malware appears to be different from other miners, as it is not based on XMRig, a popular open-source mining software. Instead, it appears to be written in Python, and is likely a private development. Let’s check out other interesting stuff I’ve found during the analysis.
Hellminer Malware Analysis
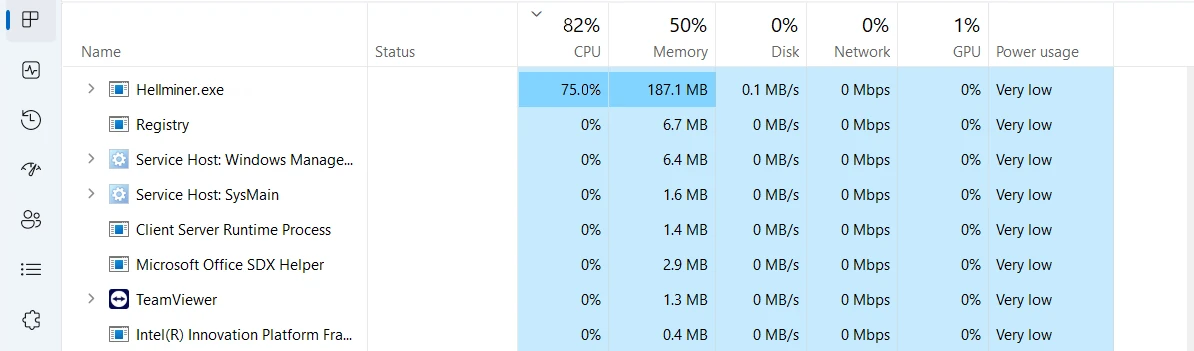
It is not completely clear how Hellminer gets into the system; I suspect it is not much different from how malware miners typically spread – via dropper malware and malvertising. After the launch, the malware begins with a selection of anti-VM and anti-debug checks.
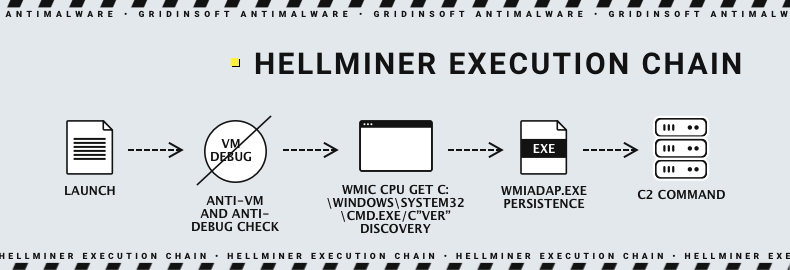
Using the calls to WMI, it gets the info about the CPU, trying to find any signs of virtualization. Why I don’t think it is just an immediate info gathering is because the very next step is listing the services and processes. Hellminer specifically seeks for traces of the VMWare virtualization environment. After these checks, the main payload is unfolded. Though, malware may as well use the info collected at this stage, to configure the mining process or as a part of the system fingerprint.
wmic cpu get Name,CurrentClockSpeed,L2CacheSize,L3CacheSize,Description,Caption,Manufacturer /format:list
Fingerprinting starts with another call to WMIC, wmic os get Version. Malware attempts to receive quite a basic, if not scarce, set of data – just the info about the operating system. After that, malware gains persistence through the manipulation with another command and series of changes in Windows registry.
%windir%\System32\svchost.exe -k WerSvcGroup – starting Windows error reporting service to make it run the malware. This increases the level of privileges the malicious program has, also providing it with a disguise.
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\FeatureControl\FEATURE_USE_IETLDLIST_FOR_DOMAIN_DETERMINATION
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Security – changing network security policies.
The final round of persistence involves another call to WMI, specifically to its Adaptation Service. Hellminer forces it to recursively launch the payload, ensuring continuous execution. This specific command is also a part of resource allocation for the mining process.
wmiadap.exe /F /T /R
Command Server Connectivity
Same as other malware miners, Hellminer does not have any extensive C2 communication. After finishing the steps from the above, it sends the blob of system information to the command server, effectively notifying it about the readiness. C2 returns the configuration file, which specifies the mining pool and the IP address to connect to.
Still, there is a thing that catches an eye – the form of command servers used by this malware. They do not look like C2 of a classic model, instead being a peer-to-peer one. In such a network, the role of a command server is given to one of the infected computers. “Real” server sporadically communicates with one, retrieving the information about the new devices and assigning the next system to get the C2 role. This drastically increases the sustainability of the network, making it particularly hard to disrupt through the command server disruption.
During the analysis, I’ve detected these command servers:
- 20.99.184.37:443
- 20.99.186.246:443
- 23.216.147.64:443
- 192.229.211.108:80
- 20.99.133.109:443
Hellminer.exe Removal Guide
Removing Hellminer malware requires anti-malware software scanning. Such threats typically duplicate itselves to numerous folders across the system, with each acting as a backup. GridinSoft Anti-Malware is what would remove the malicious miner and all its copies in the matter of minutes.
Download and install Anti-Malware by clicking the button below. After the installation, run a Full scan: this will check all the volumes present in the system, including hidden folders and system files. Scanning will take around 15 minutes.
After the scan, you will see the list of detected malicious and unwanted elements. It is possible to adjust the actions that the antimalware program does to each element: click "Advanced mode" and see the options in the drop-down menus. You can also see extended information about each detection - malware type, effects and potential source of infection.
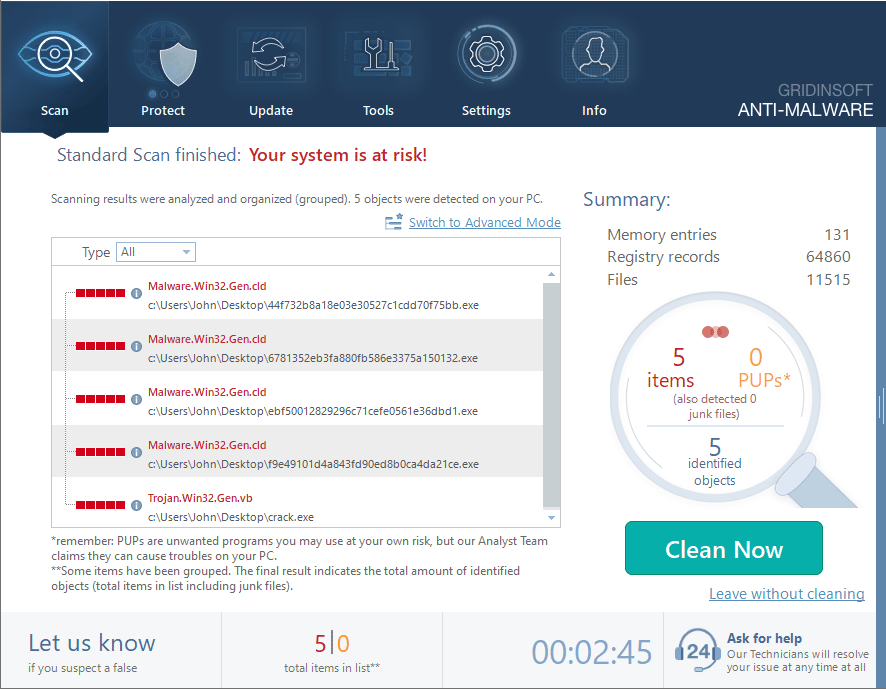
Click "Clean Now" to start the removal process. Important: removal process may take several minutes when there are a lot of detections. Do not interrupt this process, and you will get your system as clean as new.
Miner malware activity always correlates with cryptocurrency prices. At the moment, they are on the rise, meaning that more and more frauds will opt for this malware. The typical ways of spreading for malicious miners is malvertising, particularly ones in search engines. Avoiding it requires user attention: they typically mimic legitimate sites that spread freeware, but always have a different, mangled URL.




