In a recent security alert, Google has addressed a critical zero-day vulnerability in its Chrome browser and ChromeOS software, urging users to update to the latest version (119.0.6045.199). The flaw, tracked as CVE-2023-6345, allows attackers to bypass sandbox security measures by compromising the browser’s rendering process, leading to potential remote code execution or access to sensitive data.
Google Fixes CVE-2023-6345 0-day Vulnerability
Limited public information is available about CVE-2023-6345, but it is identified as an integer overflow issue affecting the Skia component within Chrome’s graphics engine. The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) describes it as a high-severity bug that allows a remote attacker, who has compromised the renderer process, to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a malicious file.
Actually, soon after the official announcement of the vulnerability fix, the real-world exploit appeared. Due to this, Google has rated the CVE-2023-6345 fix as a high-priority update due. The company has refrained from disclosing technical details until the majority of users and vendors employing the Chromium browser engine implement the fixes.
Security analysts note that Google TAG researchers reported CVE-2023-6345, highlighting its connection to spyware and APT activity. Comparisons are drawn with a previous similar flaw (CVE-2023-2136), suggesting the latest patch aims to prevent attackers from bypassing the earlier update.
More Security Patches
Alongside the zero-day fix, Google has released a total of seven security updates addressing various vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2023-6348: Type Confusion in Spellcheck
- CVE-2023-6347: Use after free in Mojo
- CVE-2023-6346: Use after free in WebAudio
- CVE-2023-6350: Out of bounds memory access in libavif
- CVE-2023-6351: Use after free in libavif
This latest announcement marks the fourth zero-day vulnerability Google has disclosed and patched in its Chrome browser this year.
Update Google Chrome
As we said earlier, patches and updates are the best way to fix vulnerabilities. So if you’re using Mac or Linux, the update will take your browser to version 119.0.6045.199, while Windows users will be upgraded to version 119.0.6045.199/.200. To check if the update is available, go to “Help” in your Google Chrome menu, and then click on “About”. If the update is ready, it will automatically start downloading.
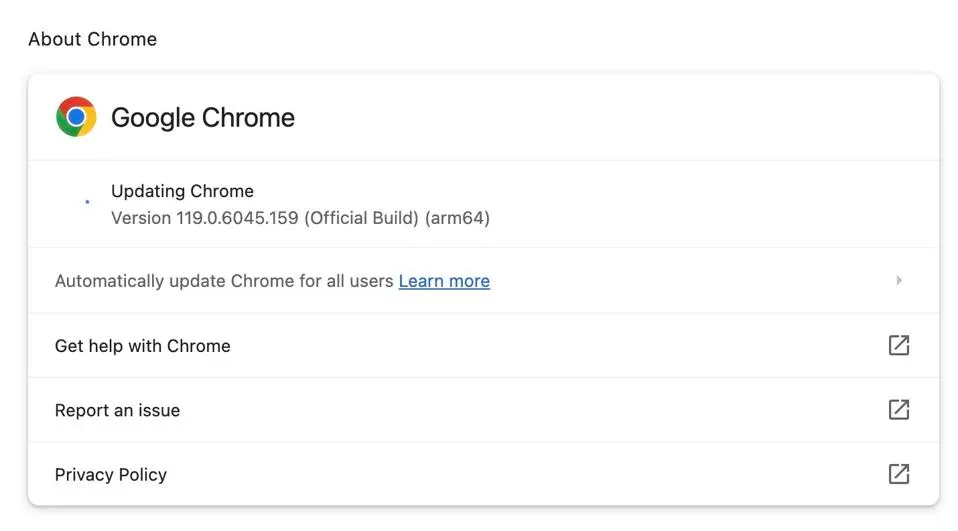
It may take a few days for the update to be available to everyone. Once you have installed the update, make sure to restart your browser for the changes to take effect. Otherwise, your browser will remain vulnerable to attacks.