Is the dark web legal?
Despite Darknet’s association with illegal activity, accessing and browsing the dark web is legal. However, most Darknet websites are used for criminal activities – such as buying drugs, money laundering, and trading stolen credentials. If your personal information is exposed through a data breach, spyware, or phishing attack, there’s a good chance it will show up on the dark web, where you can wait for your buyer. You may have heard the infamous stories about Silk Road, the first online Darknet platform used to sell illegal drugs for bitcoins, launched back in 2011.
- Is the dark web legal?
- What is the dark web?
- Difference between a dark web and a surface web
- Legal uses of the Darknet
- How does Tor work?
- How can I get into the Darknet?
- How to use dark web safe The main rule when using the Darknet is “safety first”. So be vigilant and follow these guidelines to stay safe on the Darknet: Follow only trusted URLs The .onion websites themselves won’t hurt you if you have a secure connection. However, you might stumble across some illegal websites or sensitive content by mistake. So be careful and filter the sites you intend to access. Be careful what you share The Darknet is an unregulated site and a breeding ground for illegal activity. Once again, ensure you only visit .onion sites you trust and do not share personal information. Don’t download files Just like a surface web, a dark web can contain malware. Apparently, the chance of getting something malicious to your system in the Darknet is way higher. Do not download anything that you are not 100% sure is safe to avoid the risk of compromising your data. Don’t transfer money to anyone Although some dark online stores may be legitimate, it’s best not to take any chances if you’re not 100% sure of their reliability. The Darknet is crawling with scammers, and most of them are waiting for a moment to scam you. Keep your software up to date Sometimes updates come at the most inopportune moment and are occasionally annoying. However, it is a necessary part of using any software product. System updates and any software updates are designed to keep you safe. Update them on time, including Tor and anti-malware software. You may have a good and legitimate reason to go into the dark web. However, it would help if you did so with caution because even unknowingly, you can unknowingly break the law by working online. Can I browse the surface web with the Tor browser?
Unfortunately, there are a lot of similar platforms today. However, there are more unpleasant things like Besa Mafia, a marketplace for violent activities such as robberies, contract murders, sex trafficking, blackmailing, arms dealing, and terroristic acts organisation. As unrealistic as it sounds, this is a criminal world that exists and trades online with real consequences. However, not all activities on the Darknet are illegal. For example, Facebook and the New York Times have websites accessible through the Darknet. It seems like a paradox, the Darknet itself is not unlawful, yet it is often used for illegal things. Let’s dig deeper to clarify the Darknet and how it differs from the network we know.
What is the dark web?
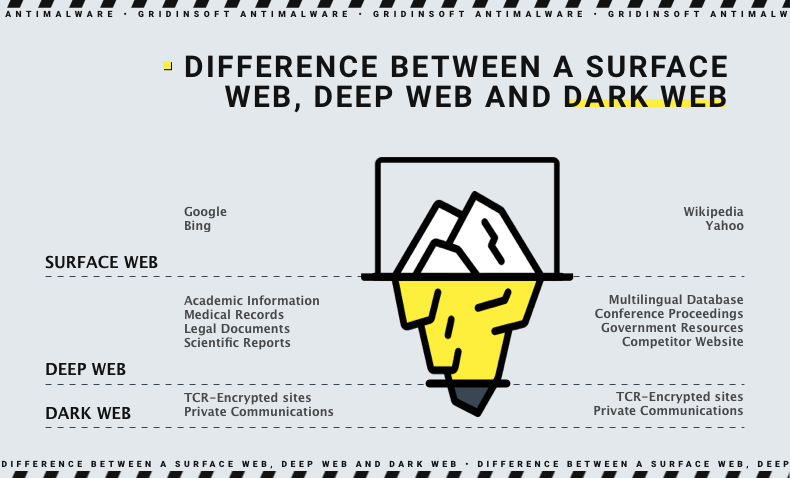
The Darknet is a part of the global Internet hidden from search engines. It allows you to browse websites anonymously using disguised IP addresses. The Darknet can only be accessed through the Tor browser, preventing tracking and ad targeting. As mentioned above, the Darknet is often used for illicit trade. This is why scammers and abusers buy and sell stolen databases, which in turn may contain usernames and passwords, email addresses, phone numbers, home addresses and other confidential information. The World Wide Web can be divided into three levels: the surface web, the deep web, and the Darknet.
The surface web
The surface web (indexed or visible web) is web content indexed by search engines. Anything you can find with a Google search is part of the surface web. You can see this web part and access it in normal browsing – that’s just the tip of the iceberg.
The deep web
The deep web is the next layer. Although “deep web” and “dark web” are used interchangeably, they are not the same. The deep web contains material that is not indexed by search engines. You may be surprised, but you go to the deep web every day because it makes up about 90% of the entire web. For example, your Facebook posts are not indexed and cannot be found through Google search. Your mailbox and online banking are unreachable through a web browser – all this is a deep web. In other words, these are parts of the Internet that are not themselves hidden, but other users cannot access them. Sometimes the term “deep web” is misused when what is meant is “dark web”.
The dark web (Darknet)
There is another part of the Internet. Here it is already called the dark web. Darknet websites are so hidden that they cannot, in principle, be accessed using regular browsers without special tools. Instead, the Darknet can only be accessed using Tor browser or its analogs. Additionally, there are plugins for Chrome and Firefox that can make the Darknet pages reachable for your regular browser – but they lack anonymity settings offered by Tor.
Difference between a dark web and a surface web
At first glance, dark websites are similar to ordinary websites. They contain text, images, interactive content, and site navigation buttons. But there are some differences.
- Naming structure. Domain addresses of the Darknet websites end exclusively on .onion, instead of our usual .com or .net.
- Complex URLs. Along with this, the URL characters preceding .onion look like an incoherent set of characters compared to the addresses we’re used to. They are also nearly impossible to remember. For example, SecureDrop is a Darknet site that allows whistleblowers to send confidential information or anonymous tips to news organizations. It also contains sites for major news organizations such as The Guardian, The Washington Post, and The Associated Press.
- Frequent address changes. While most websites on the surface web try to make it as easy to remember and find as possible, the Darknet is the opposite Darknet sites often change their URLs to maximize privacy.
Darknet lives in the Tor ecosystem, whose name is an acronym for “The Onion Router“, so Darknet can only be accessed using the Tor browser or with a regular browser but with the installation of additional plug-ins. However, the security of this method will be much lower, so Tor is still the best solution. It is free, open-source software that uses a global network of servers to help you stay anonymous on the Internet.
Legal uses of the Darknet
While for some people, the Darknet is the source of all trouble, for others, it can be a chance to save their lives. For example, since no one controls anyone here, some human rights organizations use the Darknet to help people in regions without freedom of speech to escape political persecution and flee to another country. There are also special Darknet messengers that are untraceable. Sure, both these things may have an application for outlaw purposes as well, but statistic shows the contrary. Most such facilities really help people to communicate and plan their actions with no risk to be caught by law enforcement.
How does Tor work?
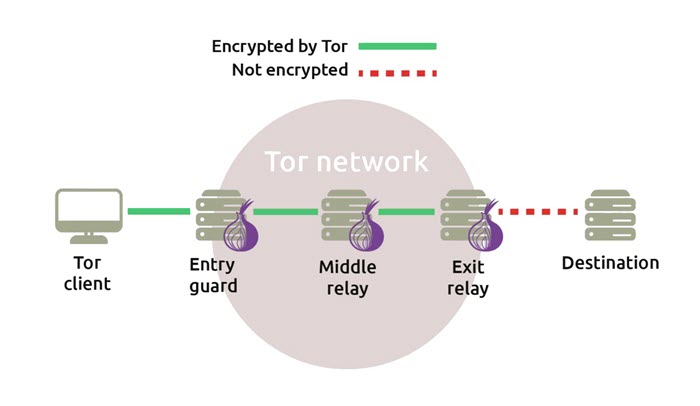
When you access the Internet via Tor, your data goes through several stages of encryption, routed through random servers called “nodes”. So, each node decrypts your data one layer at a time and then sends it to its intended Darknet destination. This type of layered encryption means that each node in the chain only knows where your data came from and which server to send it to next, and that’s it. This makes it very difficult to track your Darknet activity from start to finish. However, you shouldn’t confuse Tor with a VPN, which uses tunnels to protect your data. Tor’s encryption system ensures that your activities are anonymous and hides the host sites. This explains why this ecosystem is a favorite place for those who engage in criminal activity. Nevertheless, many legitimate reasons exist to use Tor to explore the Darknet.
How can I get into the Darknet?
Unfortunately, most Darknet sites are used for illegal activities. Therefore, it is essential to understand that this environment can be dangerous. If you ignore precautions and look for problems on the Darknet, you are likely to find them. However, if you use it for legitimate purposes and act cautiously, you can have a safe experience. Here’s how to access the Darknet safely:
Use anti-malware protection
Whether you use a surface network, a deep network, or a dark network, you need to have robust protection for your devices against malware. This will prevent unwanted software from being installed on your device.
Download Tor Browser
Now that your anti-virus software is active and a VPN enabled, you can start downloading and installing Tor from the official website. The first time you start Tor Browser, you will see a window allowing you to change some settings if necessary. You may want to return to them later, but for now, try to connect to the Tor network by pressing the “Connect” button.
Go to the Darknet website you want to visit
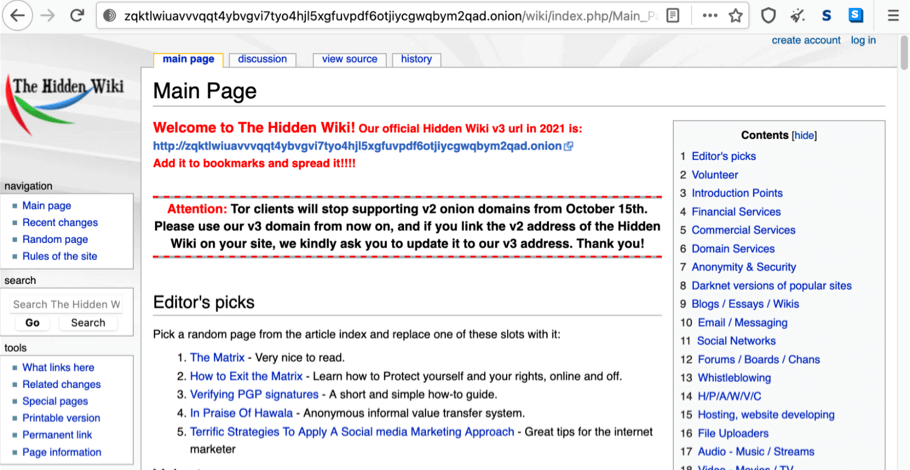
Next, you need to find some .onion sites. For example, you can visit The Hidden Wiki. To do so, go to:
http://zqktlwiuavvvqqt4ybvgvi7tyo4hjl5xgfuvpdf6otjiycgwqbym2qad.onion/wiki/index.php/Main_Page (only works in the Tor browser). This page contains links to other dark websites.
How to use dark web safe
Actually, yes, but it can be uncomfortable. Although Tor gives you access to sites in the .onion ecosystem, you can also use it to browse regular websites for added security and privacy. However, due to certain features, this will not be a pleasant user experience. First, many websites block Tor users because they cannot track you, and user data collection greatly benefits websites. Although the use of Tor is legal, law enforcement doesn’t like it, so just using the Top browser can already attract attention. That’s why you should only use it in conjunction with a VPN. Finally, since Tor’s encryption system is very complicated, traveling from browser to server over the network can be very slow. If fast browsing is essential to you, this is probably not the right way to surf the web daily.




