WogRAT, also known as WingsOfGod RAT, is a novice remote access trojan that attacks users from Asian countries. Named after its own file – Wingsofgod.dll, this malware attacks people since late 2022, spreading through the online notepad service.
What is WogRAT (WingsOfGod.dll)?
WogRAT is a classic example of a remote access trojan, a backdoor-like malicious program that focuses on providing remote access to the infected system. ASEC researchers were first to detect and track the malware campaign. They additionally emphasize that this malicious program primarily targets Asian countries – China, Japan, Singapore and Hong Kong in the first place.
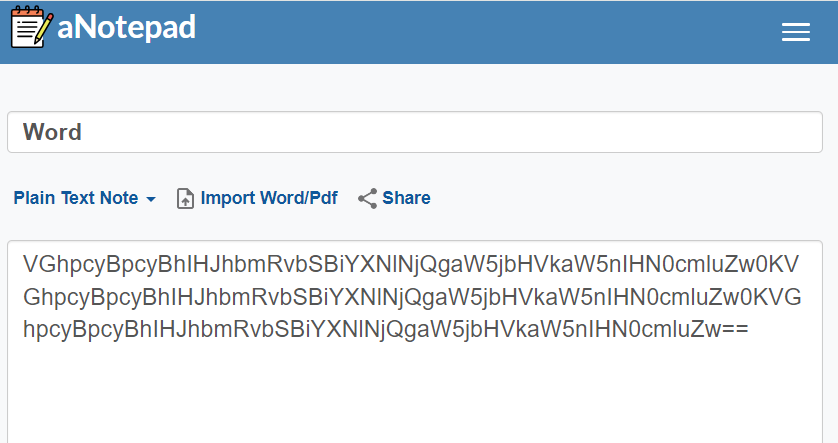
The strange thing about WogRAT is that its spreading campaigns were not detected, even though some of the methods were explained in the original research. Malware (more specifically – its loader) is disguised as a file posted on an online notepad service. Its naming supposes that frauds offer WogRAT as a system/program tweaking utility of some sort. This, in turn, supposes that initial spreading of the malware happens in “closed” places, like chats in messengers or the like.
Names for malware loader files that are available from aNotepad:
BrowserFixup.exe, ChromeFixup.exe, WindowsApp.exe, WindowsTool.exe, HttpDownload.exe, ToolKit.exe, flashsetup_LL3gjJ7.exe
WogRAT Malware Technical Analysis
As I said, the original downloading from the aNotepad site gets only the malware loader in the encoded form. Upon execution, it compiles itself on the run and requests the actual payload from a different page hosted on the same site. Depending on the attack, the source for the second-stage payload may differ.
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\cvtres.exe /NOLOGO /READONLY /MACHINE:IX86 /OUT:C:\Users\
The downloaded file is a similar .NET assembly, encoded with Base64 and present as a text string on the source website. Loader decrypts the payload and loads it into the memory using process hollowing technique.
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WerFault.exe -u -p 8008 -s 2068
Upon startup, WogRAT collects basic system information by checking different registry keys and executing commands. In particular, it gathers info about network connections, system version, username and some of the info regarding system policies. Malware stacks this data with the info of its own process and sends it to the command server in the HTTP POST request. After that, malware switches to idle, waiting for the commands.
act=on&bid=4844-1708721090438&name=System1\User1
WogRAT has a rather interesting set of commands and properties that it is expecting to receive. The simplified formula consists of 3 elements, and looks like this:
| Element | Value and purpose |
|---|---|
| task_id=%id% | text value, corresponds to the task |
| task_type=%type% | numeric value, corresponds to the action |
| task_data=%data% | Path to the file that the task should be applied to (URL for downloads) |
The resulting command is like the following:
task_id=upldr&task_type=3&task_data=C:\\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
This malware supports 5 different types of operations: running specific files, downloading or uploading the files, altering the idle time, and terminating the execution. Not a huge list at the first glance, but in combination with different task types this gives a full-fledged backdoor functionality.
How to remove WogRAT?
WogRAT is not the stealthiest malware out there; it is in fact more reliant on the tricky spreading method and double-staged loader. Still, the amount of hooks it creates in the system makes it particularly hard to remove manually. For that reason, I recommend using GridinSoft Anti-Malware: a full scan with that program will be enough to repel the RAT and all of its parts across the system.





