Trojan:Win32/Tnega!MSR is a malicious program that functions to deliver other malware. It uses numerous anti-detection tricks and is often distributed as mods and cheats for popular games. Such threats are capable of delivering spyware, ransomware and pretty much any other malware.
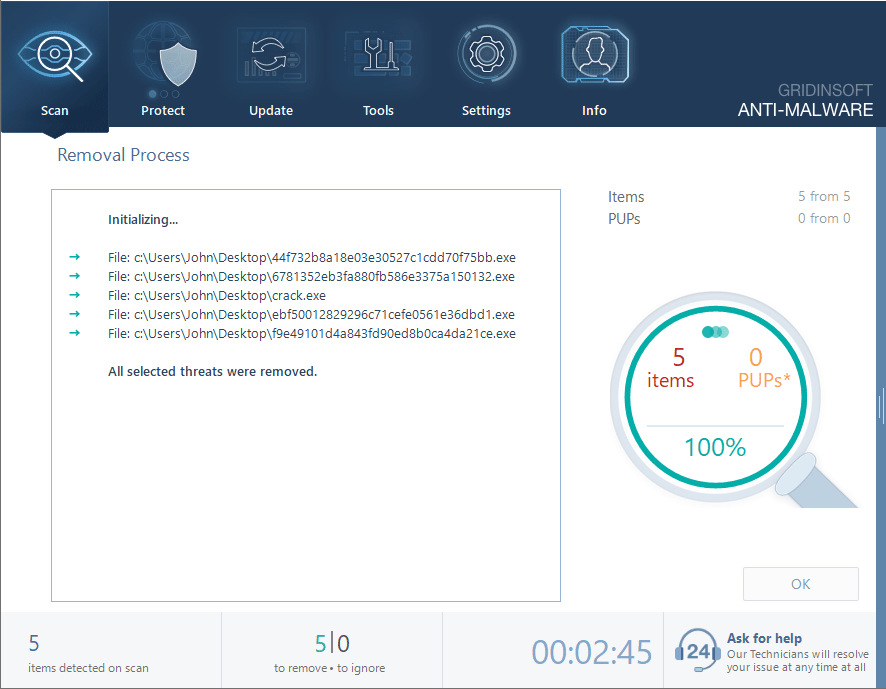
Trojan:Win32/Tnega!MSR Overview
Trojan:Win32/Tnega!MSR is a Microsoft Defender detection that refers to malware that acts as a downloader. As the name suggests, such malware’s main task is to deliver additional malicious components to the infected device, i.e., payload. It may also include extra features like collecting system information or other basic details.
Main spreading ways for Tnega trojan are modified versions of games, cheats, or game add-ons. Since such tools always require antivirus software to be disabled, such a disguise creates ideal conditions for malware to run in the system. In addition to this, Tnega has a protection mechanism against antivirus detection and analysis. Everything is standard here – various techniques like code encryption, polymorphism, obfuscation, and checking for the presence of virtual environments. These techniques make it difficult to be detected and analyzed by antivirus programs and malware analyzers.
Technical Analysis
For a more detailed breakdown, I chose a sample that spreads as some kind of a mod for Roblox. As the detection is not specific to a malware family, there can be variations from one sample to another, but the general course of action will remain the same. Let’s break down some of the key behaviors and actions observed.
Once launched, the malware performs some checks to determine if the application is running in a virtual environment or sandbox. A rather common check, but it is still effective in weeding out artificial environments. To do this, it checks the following registry values:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\HARDWARE\ACPI\DSDT\VBOX__
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\HARDWARE\DESCRIPTION\System\SystemBiosVersion
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\HARDWARE\DESCRIPTION\System\VideoBiosVersion
These keys display the BIOS version, which is particularly hard to spoof when it comes to basic virtual machines. Such a check gives much more precise results than more classic ones, that view video driver information and the list of installed applications.
Persistence
To gain persistence, Trojan:Win32/Tnega!MSR uses Task Scheduler to run its executable file. This allows it to run periodically or on a schedule with elevated privileges. Registering a task as .NET code contains functionality that can also be used to launch other malicious programs.
After tinkering with the Task Scheduler, the malware’s executable file is injected into other system processes, allowing it to execute with elevated privileges in the context of these processes. It uses the WerFault.exe process with parameters -u -p
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WerFault.exe -u -p 1036 -s 1912
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WerFault.exe -u -p 1200 -s 1908
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WerFault.exe -u -p 1256 -s 1908
This is only a few of the commands where Tnega abuses WerFault functionality. During the runtime testing, it interacted with the error reporting module for 9 times, which corresponds to the number of files it has downloaded from the C2. So yes, each one of these is about to run malware with max privileges.
C2 Connection
The malware communicates with C2 servers via HTTP to blend in with legitimate traffic. DNS resolutions are made to domains such as query.prod.cms.rt.microsoft.com. IP traffic is observed on specific ports like TCP 80, TCP 443, and UDP 137.
TCP 104.80.89.50:80
TCP 13.107.4.50:80
TCP 131.253.33.203:80
UDP 192.168.0.1:137
UDP 192.168.0.55:137
Payload
Next, Trojan:Win32/Tnega!MSR performs its primary function of dropping the payload. It writes files to the disc in various directories – C:\Users\
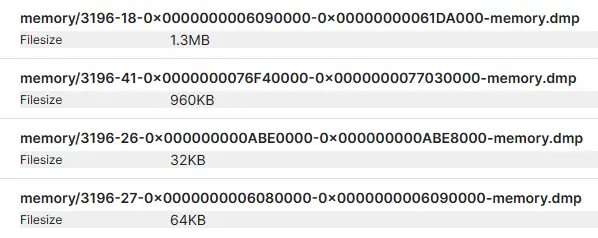
How To Remove Trojan:Win32/Tnega!MSR?
To remove Trojan:Win32/Tnega!MSR, it is best to use an advanced anti-malware tool. GridinSoft Anti-Malware is the optimal option. Since some users have encountered problems with Tnega removal using default Windows tools, a third-party solution is designed to remedy this situation. Moreover, using GridinSoft Anti-Malware does not require you to disable Windows Defender. So, they can work in pairs, complementing each other.
Download and install Anti-Malware by clicking the button below. After the installation, run a Full scan: this will check all the volumes present in the system, including hidden folders and system files. Scanning will take around 15 minutes.
After the scan, you will see the list of detected malicious and unwanted elements. It is possible to adjust the actions that the antimalware program does to each element: click "Advanced mode" and see the options in the drop-down menus. You can also see extended information about each detection - malware type, effects and potential source of infection.
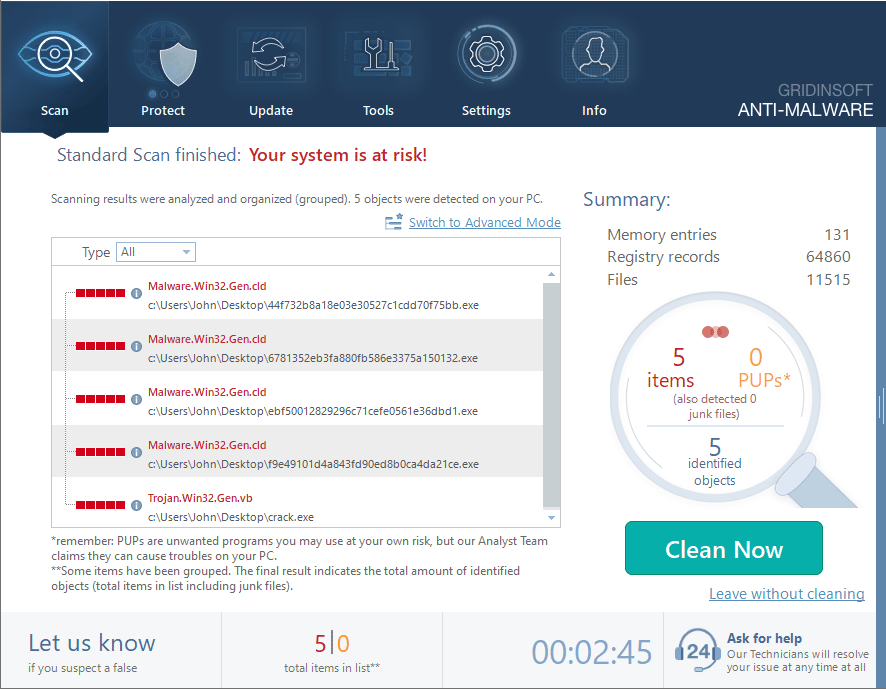
Click "Clean Now" to start the removal process. Important: removal process may take several minutes when there are a lot of detections. Do not interrupt this process, and you will get your system as clean as new.