If you’re seeing Trojan:Win32/Acll detected by your antivirus, your computer might be running slow. You might notice your CPU fan spinning constantly. Strange processes are eating up your system resources. Your personal information could be at risk.
This guide will help you remove this stealer malware completely. Follow these step-by-step instructions to eliminate the threat. We’ll start with manual methods you can try right now.
| Detection Name | Trojan:Win32/Acll |
| Alternative Names | Python/Acll, Stealer.Acll, Infostealer.Acll |
| Threat Type | Information Stealer / Spyware |
| Programming Language | Python (compiled to executable) |
| Primary Function | Steals passwords, cryptocurrency wallets, browser data, and personal information |
| Targeted Data | Browser credentials, crypto wallets, FTP/VPN settings, system information, keystrokes |
| Affected Systems | Windows 7, 8, 8.1, 10, 11 (32-bit and 64-bit) |
| Common Sources | Pirated software, malicious email attachments, fake system utilities |
| Distribution Methods | Software bundles, fake fan controllers, UEFI utilities, malicious downloads |
| Persistence Method | Registry startup entries, scheduled tasks, DLL sideloading |
| Data Exfiltration | Telegram API, cloud services (OneDrive, Azure), encrypted connections |
| Network Behavior | Connects to multiple IP addresses, uses HTTPS for data transmission |
| Risk Level | High – Can steal financial information and cryptocurrency wallets |
| Removal Difficulty | Medium – Requires registry cleanup and scheduled task removal |
| First Detected | 2024 (recent discovery, actively spreading) |
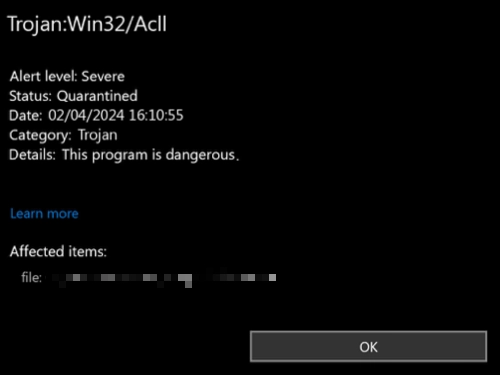
What is Trojan:Win32/Acll?
Trojan:Win32/Acll is a stealer malware coded in Python. It targets your sensitive information. The malware steals login credentials, personal details, and financial data. It can grab files from your computer. It does keylogging to capture what you type. It manipulates your clipboard and performs other spyware activities.
The malware spreads through malicious software downloads and malicious email attachments. Some samples mimic hardware management tools. They pretend to be fan controlling utilities and UEFI parameter modifiers. This trick helps them get highest system privileges.
Technical Analysis
Before starting its malicious activities, Acll performs environment checks. It looks for signs of virtualization to avoid analysis. The malware checks these registry locations:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\Hidden
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\SystemCertificates
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Lsa\FipsAlgorithmPolicy
These keys contain certificate stores and security settings. The malware uses code obfuscation to avoid detection, similar to techniques used by other heuristic threats.
System Persistence
After checking the environment, Acll creates mutexes to prevent multiple instances:
Local\SM0:3648:304:WilStaging_02
Local\SM0:5144:304:WilStaging_02
The malware adds itself to Windows Task Scheduler for regular startups. It also creates registry entries to run at system startup:
schtasks /create /f /RU "%USERNAME%" /tr "%ProgramData%\WinTrackerSP\WinTrackerSP.exe" /tn "WinTrackerSP HR" /sc HOURLY /rl HIGHEST
Registry entry:
HKEY_USERS\%SID%\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\ExtreamFanV5
The malware uses DLL sideloading through this command:
C:\Windows\System32\wuapihost.exe -Embedding
Data Collection Targets
Acll specifically targets cryptocurrency wallets and sensitive user data. It collects passwords as hashes or plaintext. The malware searches browser folders and shared password storage locations:
C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\
C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Edge\User Data\
C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\BraveSoftware\Brave-Browser\User Data
C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Vivaldi\User Data
C:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Opera Software\Opera GX Stable
C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Yandex\YandexBrowser\User Data
For cryptocurrency wallets, it targets these locations:
C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Coinomi\Coinomi\wallets
C:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Electrum\wallets
C:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Ethereum\keystore
C:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Exodus\exodus.wallet
C:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\atomic\Local Storage\leveldb
C:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\bytecoin
The malware also targets FTP and VPN credentials. It looks for FileZilla, OpenVPN, and NordVPN settings. If you had any passwords stored on the infected device, you should reset all passwords immediately.
Data Exfiltration Methods
Acll sends stolen data to command and control servers. Some samples use Telegram bot as an intermediate server:
https://api.telegram[.]org/bot7006468177:AAEjUyc53owWdXWMasYo_ZE1Y7t2sH1O718/sendMessage
https://api.telegram.org/bot7006468177:AAEjUyc53owWdXWMasYo_ZE1Y7t2sH1O718/sendDocument
The malware also uses cloud services including OneDrive, Microsoft Azure, and EdgeCast. It connects to these IP addresses:
TCP 204.79.197.203:443
TCP 34.117.186.192:443
TCP 149.154.167.220:443
TCP 20.99.186.246:443
Manual Removal Steps
You can remove Trojan:Win32/Acll manually by following these steps. This process requires careful attention to detail. Make sure to follow each step completely.
Step 1: Boot into Safe Mode
Safe Mode prevents the malware from starting automatically. This makes removal easier and safer.
- Press Windows key + R to open Run dialog
- Type “msconfig” and press Enter
- Go to Boot tab
- Check “Safe boot” and select “Minimal”
- Click OK and restart your computer
Step 2: Identify Malicious Processes
Open Task Manager to find suspicious processes. Acll often runs under different names to hide itself.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager
- Click on “More details” if needed
- Look for processes with these characteristics:
- High CPU usage for unknown processes
- Processes running from %ProgramData% or %AppData% folders
- Processes with names like “WinTrackerSP.exe” or “ExtreamFanV5”
- Right-click suspicious processes and select “End task”
Step 3: Delete Malicious Files
Navigate to common malware locations and delete suspicious files. Be careful not to delete legitimate system files.
- Open File Explorer
- Navigate to these folders:
- %ProgramData%\WinTrackerSP\
- %AppData%\Local\Temp\
- %AppData%\Roaming\
- Look for recently created folders with random names
- Delete any suspicious files and folders
- Empty the Recycle Bin
Step 4: Clean Startup Programs
Remove malware entries from startup programs to prevent automatic execution.
- Press Windows key + R
- Type “msconfig” and press Enter
- Go to Startup tab
- Look for suspicious entries, especially:
- Entries pointing to %ProgramData%\WinTrackerSP\
- Entries with names like “ExtreamFanV5”
- Uncheck suspicious entries
- Click OK
Step 5: Registry Cleanup
Clean malware entries from Windows Registry. This step requires caution as incorrect registry changes can damage Windows.
- Press Windows key + R
- Type “regedit” and press Enter
- Navigate to these registry keys:
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- Look for entries with suspicious names or paths
- Right-click suspicious entries and select “Delete”
- Close Registry Editor
Step 6: Check Scheduled Tasks
Remove malicious scheduled tasks that restart the malware.
- Press Windows key + R
- Type “taskschd.msc” and press Enter
- In Task Scheduler, expand “Task Scheduler Library”
- Look for tasks with suspicious names like “WinTrackerSP HR”
- Right-click suspicious tasks and select “Delete”
- Restart your computer in normal mode
Automatic Removal with GridinSoft Anti-Malware
Manual removal can be complex and time-consuming. For a faster, more reliable solution, GridinSoft Anti-Malware offers automatic detection and removal of stealer malware. Professional anti-malware software can find hidden components and registry changes that you might miss.
Download and install Anti-Malware by clicking the button below. After the installation, run a Full scan: this will check all the volumes present in the system, including hidden folders and system files. Scanning will take around 15 minutes.
After the scan, you will see the list of detected malicious and unwanted elements. It is possible to adjust the actions that the antimalware program does to each element: click "Advanced mode" and see the options in the drop-down menus. You can also see extended information about each detection - malware type, effects and potential source of infection.
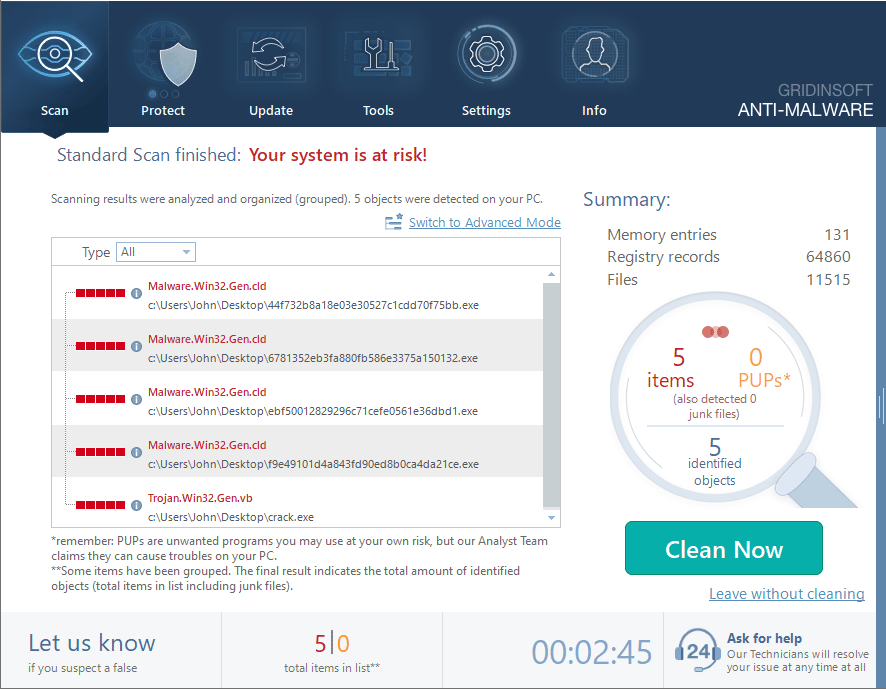
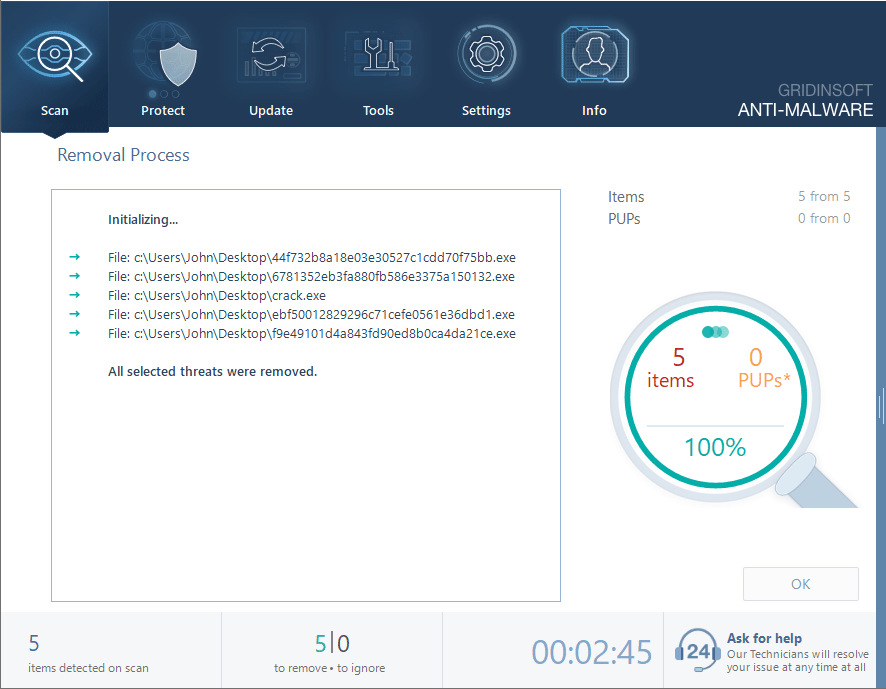
Click "Clean Now" to start the removal process. Important: removal process may take several minutes when there are a lot of detections. Do not interrupt this process, and you will get your system as clean as new.
Browser Cleanup
Remove Malicious Browser Extensions
Stealer malware like Acll often installs browser extensions to monitor your activity. Remove any suspicious extensions you don’t recognize.
Google Chrome
- Launch the Chrome browser.
- Click on the icon "Configure and Manage Google Chrome" ⇢ Additional Tools ⇢ Extensions.
- Click "Remove" next to the extension.
If you have an extension button on the browser toolbar, right-click it and select Remove from Chrome.
Mozilla Firefox
- Click the menu button, select Add-ons and Themes, and then click Extensions.
- Scroll through the extensions.
- Click on the … (three dots) icon for the extension you want to delete and select Delete.
Microsoft Edge
- Launch the Microsoft Edge browser.
- Click the three dots (…) menu in the top right corner.
- Select Extensions.
- Find the extension you want to remove and click Remove.
- Click Remove again to confirm.
Alternatively, you can type edge://extensions/ in the address bar to access the extensions page directly.
Opera
- Launch the Opera browser.
- Click the Opera menu button in the top left corner.
- Select Extensions ⇢ Manage extensions.
- Find the extension you want to remove and click the X button next to it.
- Click Remove to confirm.
Alternatively, you can type opera://extensions/ in the address bar to access the extensions page directly.
Reset Your Browser
If you suspect browser-based data theft, reset your browser completely. This removes any malicious modifications and restores default settings.
Google Chrome
- Tap on the three verticals … in the top right corner and Choose Settings.
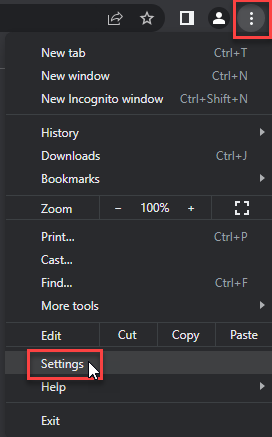
- Choose Reset and Clean up and Restore settings to their original defaults.
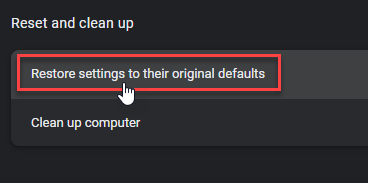
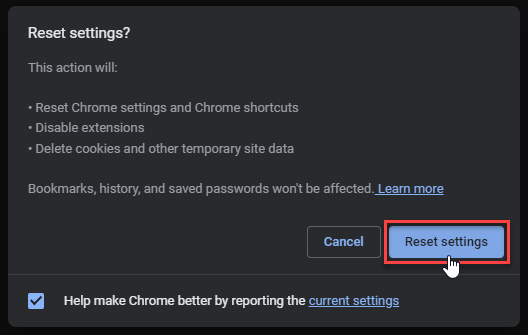
- Tap Reset settings.
Mozilla Firefox
- In the upper right corner tap the three-line icon and Choose Help.
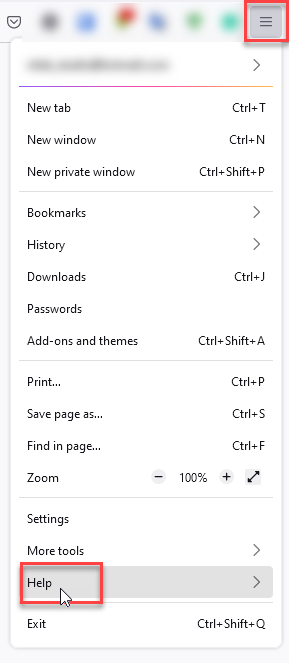
- Choose More Troubleshooting Information.
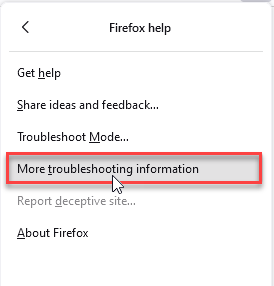
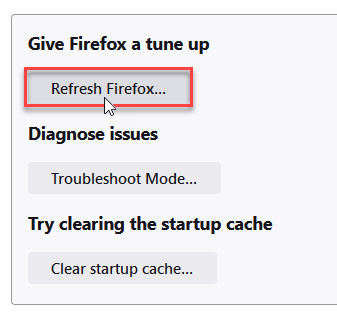
- Choose Refresh Firefox… then Refresh Firefox.
Microsoft Edge
- Tap the three verticals.
- Choose Settings.
- Tap Reset Settings, then Click Restore settings to their default values.
Opera
- Launch the Opera browser.
- Click the Opera menu button in the top left corner and select Settings.
- Scroll down to the Advanced section in the left sidebar and click Reset and clean up.
- Click Restore settings to their original defaults.
- Click Reset settings to confirm.
Alternatively, you can type opera://settings/reset in the address bar to access reset options directly.
How to Prevent Future Infections
Protecting yourself from trojan malware requires good security habits. Here’s how to stay safe:
Avoid Pirated Software
Cracked games and pirated software are common malware sources. Always download software from official websites. Pay for legitimate software when possible.
Be Careful with Email Attachments
Never open suspicious email attachments. Scam emails often contain malware. Verify sender identity before opening any attachments.
Keep Windows Updated
Install Windows security updates promptly. Updates fix vulnerabilities that malware exploits. Enable automatic updates for better protection.
Use Strong Passwords
Create unique passwords for different accounts. Consider using a password manager. Enable two-factor authentication where available.
Monitor System Performance
Watch for signs of infection like slow performance or high CPU usage. Suspicious processes might indicate malware presence.
Backup Important Data
Regular backups protect your data from theft and ransomware. Store backups offline or in secure cloud storage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Trojan:Win32/Acll and why is it dangerous?
Trojan:Win32/Acll is an information stealer that targets your personal data, passwords, and cryptocurrency wallets. It’s dangerous because it can steal financial information and sell it to cybercriminals. The malware runs quietly in the background while collecting your sensitive data.
How did Trojan:Win32/Acll get on my computer?
Most infections come from malicious game hacks or malicious email attachments. Some variants pretend to be system utilities like fan controllers. Always download software from official sources to avoid infection.
Can I remove Trojan:Win32/Acll manually?
Yes, you can remove it manually using the steps in this guide. However, manual removal requires technical knowledge and patience. Missing any components could leave your system vulnerable. Automatic removal tools are usually more reliable.
Is it safe to delete the processes and files mentioned?
The specific files and processes mentioned in this guide are associated with Acll malware. However, always verify file locations and names before deleting anything. When in doubt, use professional anti-malware software to avoid accidentally deleting system files.
How can I prevent Trojan:Win32/Acll in the future?
Avoid downloading cracked software and be cautious with email attachments. Keep Windows updated and use reputable antivirus software. Regular system scans can catch threats before they cause damage.
What if manual removal doesn’t work?
If manual removal fails, the malware might have deeper system integration. Use GridinSoft Anti-Malware for thorough automatic removal. Professional tools can detect hidden components and registry modifications that manual methods might miss.
Should I change all my passwords after infection?
Yes, change all passwords immediately after removing the malware. This includes online accounts, cryptocurrency wallets, and any stored passwords. Use strong, unique passwords for each account.
Can Trojan:Win32/Acll steal cryptocurrency?
Yes, this malware specifically targets cryptocurrency wallets including Electrum, Exodus, and Ethereum keystores. If you had crypto wallets on the infected computer, move your funds to new wallets immediately after cleaning the infection.





