In March 2024, threat analysts detected a new ransomware group, called Red Ransomware. The group, which began its activities during the waning days of prominent groups such as Lockbit and ALPHV, has quickly established a presence in cyberspace.
Who is Red Ransomware?
Red Ransomware, also known as Red CryptoApp, first revealed itself on March 5, 2024, immediately drawing attention to their activities by publishing the data of 11 victims on a Darknet leak site they called “Wall of Shame”. The original research uncovers the use of classic extortion techniques, but with utilization of modern technological approaches, including AI for negotiation. The ransomware group shows a high degree of premeditation by publishing the data of all victims at the same time. This is believed to have been done shortly to increase psychological pressure on future targets.
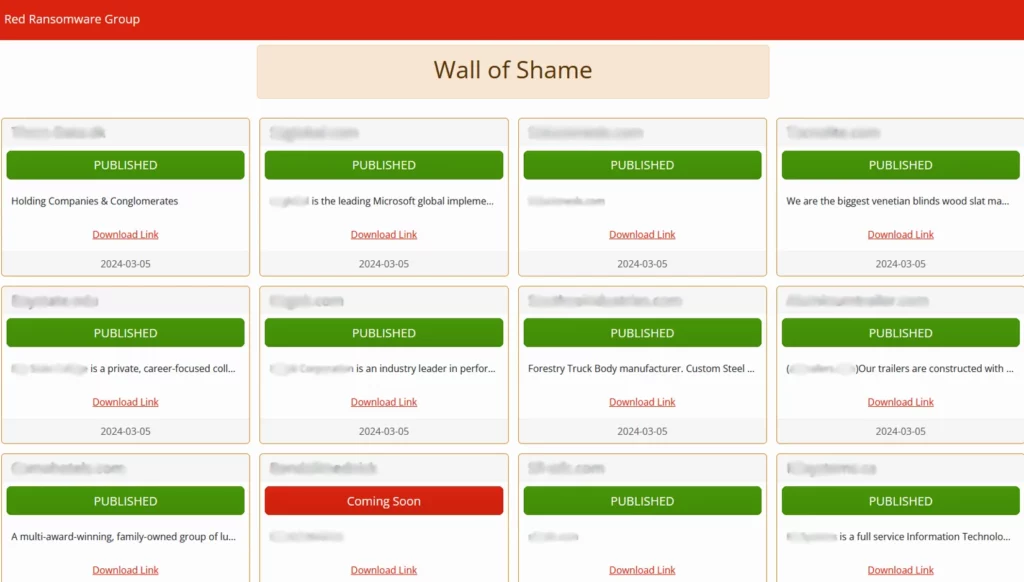
(All victim data is stored in a “Dataprojects” folder archived in ZIP format along with each victim’s name.)
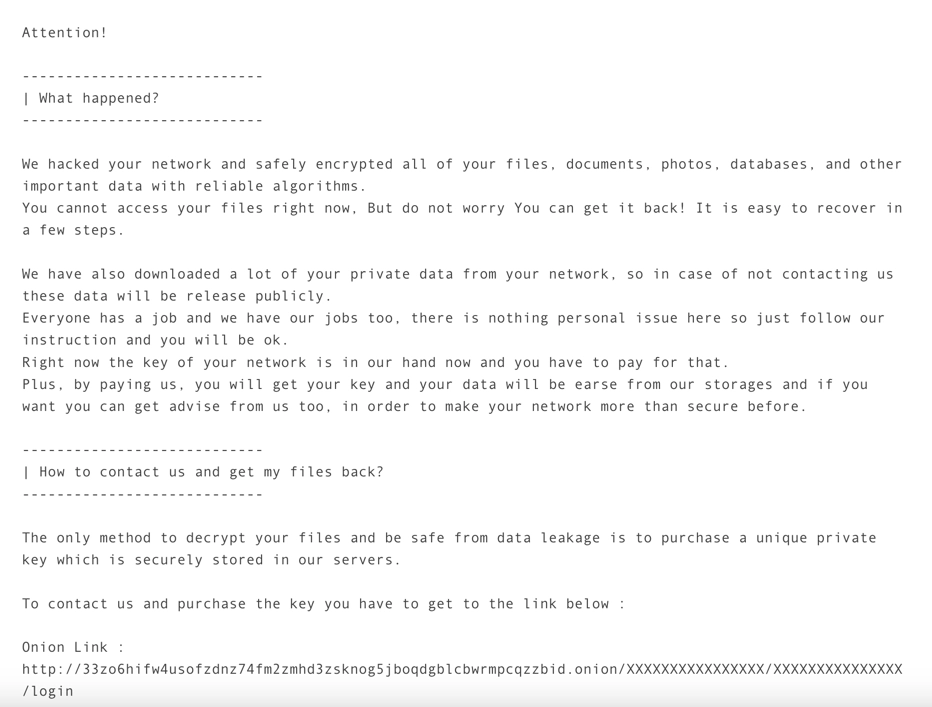
The ransom note used by the Red CryptoApp group:
Victims of Red Ransomware
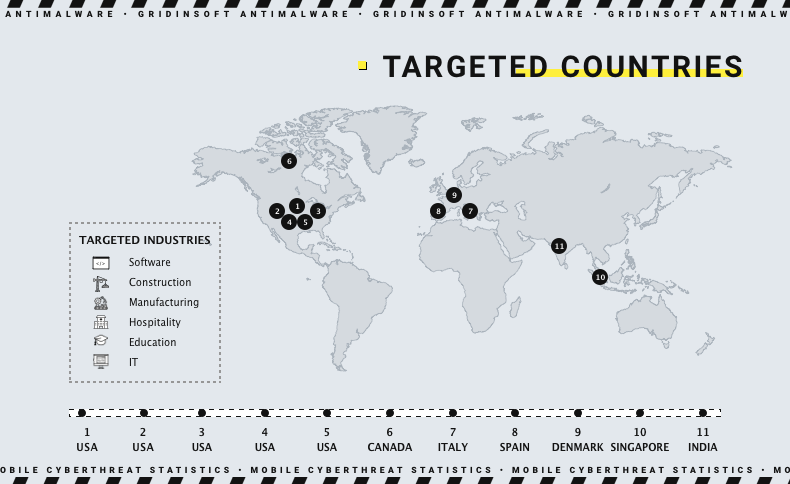
The profile of Red Ransomware victims shows that they select their targets from specific sectors and countries, suggesting a specific target selection strategy. The main victims are businesses from the United States, from a whole pack of different economic sectors, including educational and legal. Aside from the US companies, hackers also listed victims from Canada, Singapore, Mexico, Spain, Italy, India, and Denmark.
How does Red Ransomware work?
The Red Ransomware group uses a number of techniques to hack into and control targeted systems. Each attack is a serious threat to organizations in various industries.
Initial Access
Red Ransomware begins its attack by infecting systems using phishing emails or exploiting vulnerabilities in software. All user files get a new extension .REDCryptoApp and cannot be accessed without a special key. Imagine that in an instant all your data is encrypted and inaccessible.
Target audience
Red Ransomware covers a wide range of targets, including countries such as the United States, Canada, Singapore, Mexico, Spain, Italy, India and Denmark. So far information technology, legal services, hospitality, transportation, manufacturing, education, electronics, and retail are the main targets. However, this hints that the group selects victims where maximum financial gain can be achieved.
Victim negotiation
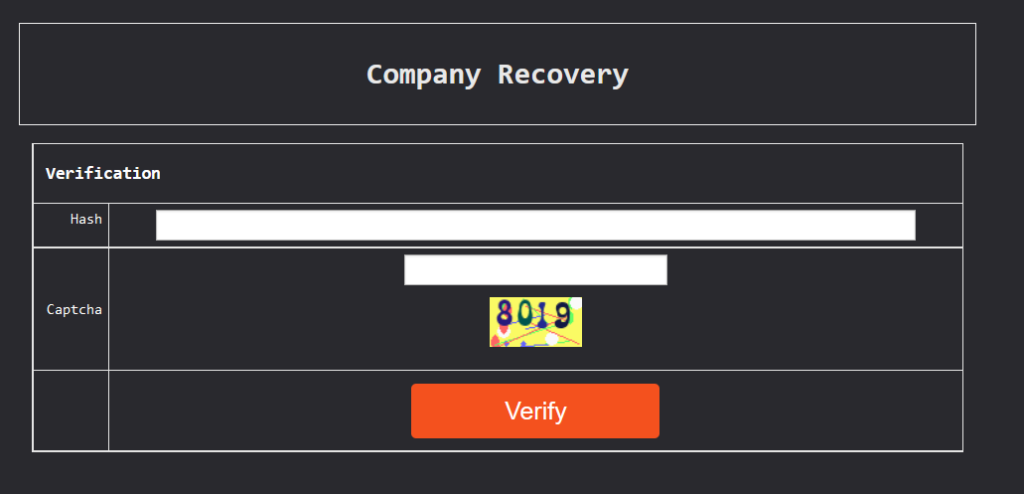
To contact victims, a unique URL is provided on the TOR network for ransom negotiations. The interface for communication is well designed. There is a login panel where victims enter a unique hash code to access a chat window for negotiation. And for confirmation, you have to solve a captcha to get through to the chat.
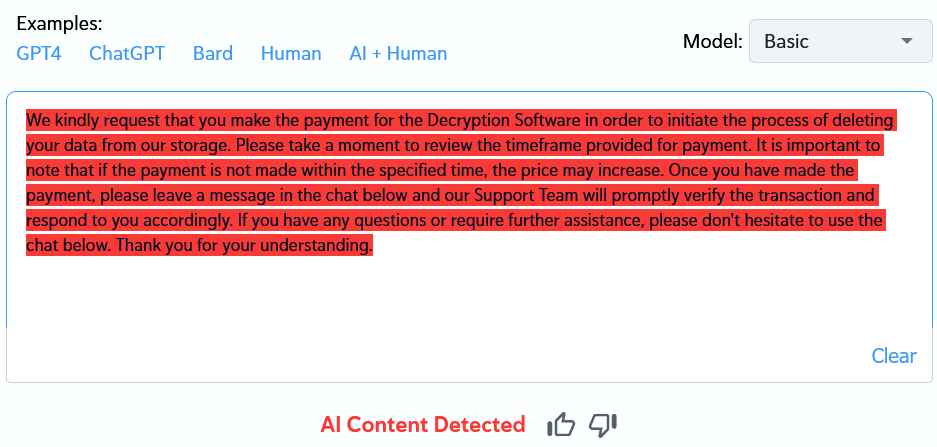
Use of AI
Also, communicating with victims is like talking to a well-tuned bot. Apparently, they’re using AI to automate communication. This allows them to dialog with multiple victims at the same time.