PUA:Win32/GameHack is potentially unwanted software associated with tools used for hacking games or gaining unfair advantages over other players. This category typically includes cheats, trainers, and other software that injects itself into other processes.
PUA:Win32/GameHack Overview
PUA:Win32/GameHack is a generic Microsoft Defender detection for potentially unwanted programs (PUAs) associated with cheats or game hacking tools. While these programs are not always truly malicious, they can pose security risks or violate the terms of service of legitimate software. Also, the use of such software can lead to game or system instability, as not all of such programs are tested well enough. However, the main danger is that these programs can spread other malware or serve as a vector for its distribution.
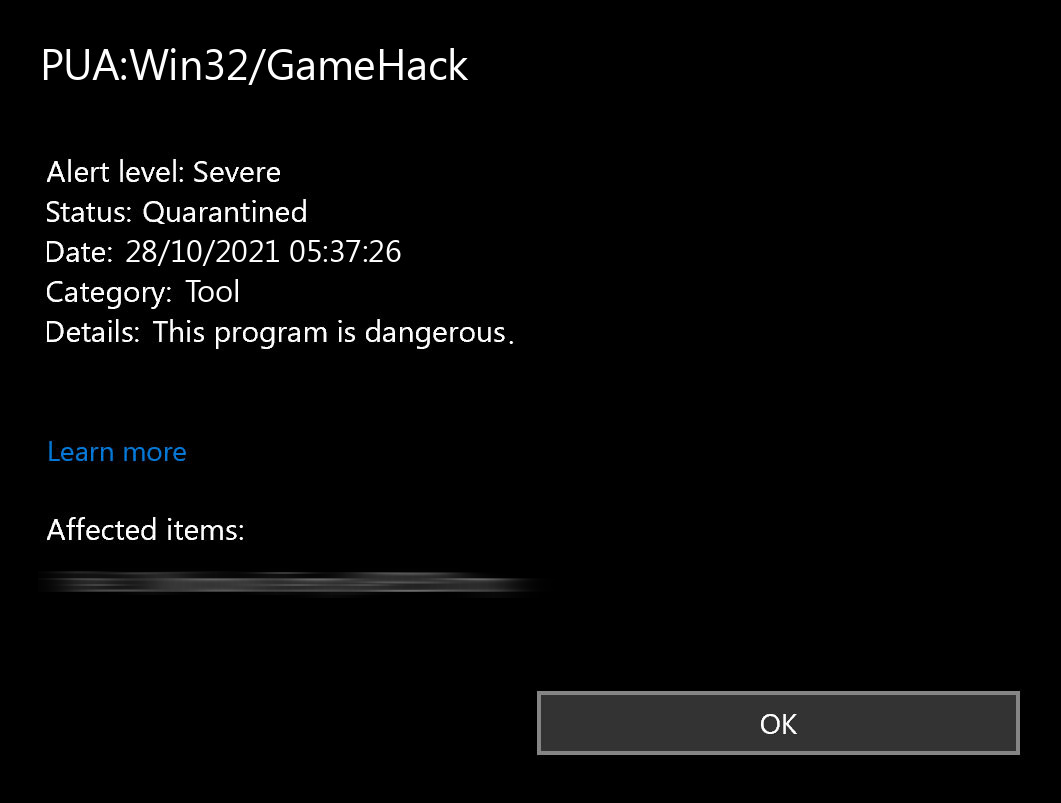
The main reason for this is that using these tools requires disabling the system’s security software. This gives the green light to any threats that are contained in the GameHack. The file may contain encrypted or compressed data, which allows you to evade detection or conceal its true functionality. Some versions modify or create registry keys, which may as well serve as a cover for malicious activities.
Technical Analysis
Let’s examine how PUA:Win32/GameHack behaves on the target system. For the test sample, I have chosen Solara.dir, a cheat for one popular cubic game. When the executable file is launched, the system process rundll32.exe is accessed by several instances of the cheat.
"C:\Windows\system32\rundll32.exe"
"C:\Windows\system32\rundll32.exe" "C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Temp\Solara/Microsoft.Web.WebView2.Core.dll",#1
"C:\Windows\system32\rundll32.exe" "C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Temp\Solara/Microsoft.Web.WebView2.WinForms.dll",#1
The first thing the app does is check the system for a virtual environment or sandbox. It checks some values in the system, including:
\REGISTRY\MACHINE\HARDWARE\ACPI\DSDT\VBOX__
\REGISTRY\MACHINE\HARDWARE\DESCRIPTION\System\SystemBiosVersion
\REGISTRY\MACHINE\HARDWARE\DESCRIPTION\System\VideoBiosVersion
Main Functionality
Next, the chosen cheat performs its primary function. It uses an archiver to unpack the files of a cheat:
"C:\Windows\SysWOW64\unarchiver.exe" "C:\Users\user\Desktop\Solara.Dir.zip"
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\7za.exe "C:\Windows\System32\7za.exe" x -pinfected -y -o"C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Temp\t1244hhg.u4j" "C:\Users\user\Desktop\Solara.Dir.zip"
Most files are unpacked into a temporary directory, into a randomly named folder. The latter is a rather concerning behavior: programs rarely use such strange names:
C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Temp\t1244hhg.u4j\Solara
C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Temp\t1244hhg.u4j\Solara\Microsoft.Web.WebView2.Core.dll
C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Temp\t1244hhg.u4j\Solara\Monaco\combined.html
C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Temp\t1244hhg.u4j\Solara\Monaco\fileaccess
Further, the GameHack program then executes scripts using the Command Prompt. It primarily targets the files that it has just dropped, but the functionality of such requests closely resembles what dropper malware can do.
"C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe" /c "cd ^"C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Temp^" && C:\Windows\system32\wscript.exe ^"C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Temp\Solara/Monaco/fileaccess/index.js^"
"C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe" /c "cd ^"C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Temp^" && C:\Windows\system32\wscript.exe ^"C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Temp\Solara/Monaco/fileaccess/node_modules/accepts/index.js^"
"C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe" /c "cd ^"C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Temp^" && C:\Windows\system32\wscript.exe ^"C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Temp\Solara/Monaco/fileaccess/node_modules/array-flatten/array-flatten.js^"
These manipulations with Command Prompt are accompanied by the calls to several other elements. Once again, I cannot see a sign of malicious activity in this case, but it is as edgy as it can get.
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe -k DcomLaunch -p
C:\Windows\System32\RuntimeBroker.exe -Embedding
C:\Windows\System32\conhost.exe C:\Windows\system32\conhost.exe 0xffffffff -ForceV1
After these commands, the cheat can inject its code into the game process, adding features that give the player an unfair advantage. These features might include the ability to fly, unlock all inventory, or other advantages that give the player an unfair edge over others. Once again, I’d emphasize that such actions go against the rules of the vast majority of games.
Is PUA:Win32/GameHack False Positive?
Sometimes GameHack can be a false positive detection. In most cases, this is because of how anti-cheat solutions operate. Anti-cheat systems often work at the low-level of the system, injecting their code into the game process, checking the integrity of files, and analyzing network traffic. In other words, anti-cheat systems can use similar methods as cheats, which can trigger anti-malware detections.
False positive detections typically disappear quickly, unlike real hacks, as the developers promptly contact anti-malware vendors to resolve these issues. In addition, they can inform users about it on official platforms and advise them to add the game folder to the exceptions, which can be a practical solution.
How To Remove PUA:Win32/GameHack?
If you encounter a GameHack detection and suspect it’s not a false positive, here’s what you can do. You can use GridinSoft Anti-Malware to help you get rid of this and other threats, just follow the instructions below:
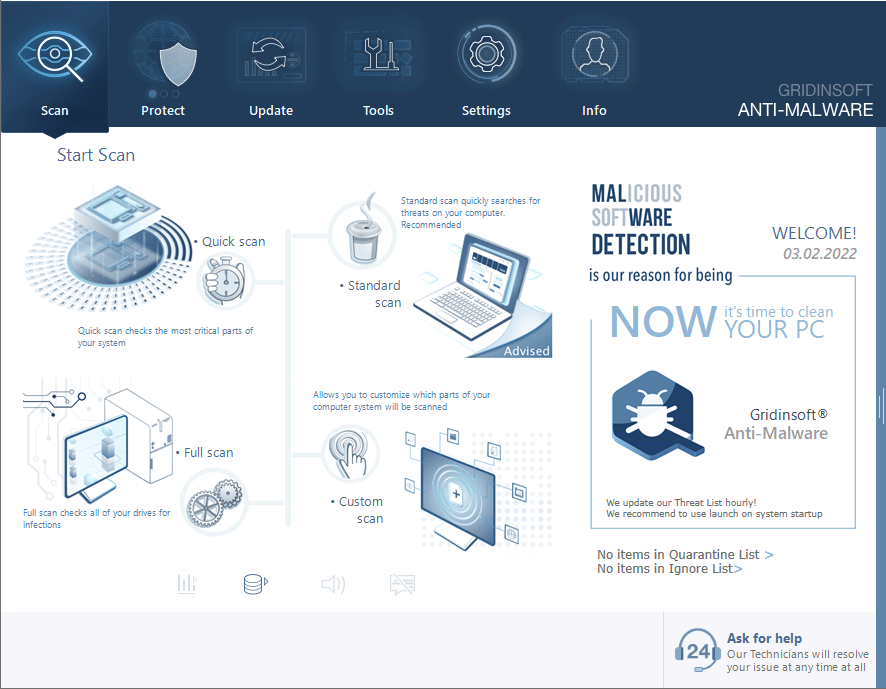
Download and install Anti-Malware by clicking the button below. After the installation, run a Full scan: this will check all the volumes present in the system, including hidden folders and system files. Scanning will take around 15 minutes.
After the scan, you will see the list of detected malicious and unwanted elements. It is possible to adjust the actions that the antimalware program does to each element: click "Advanced mode" and see the options in the drop-down menus. You can also see extended information about each detection - malware type, effects and potential source of infection.
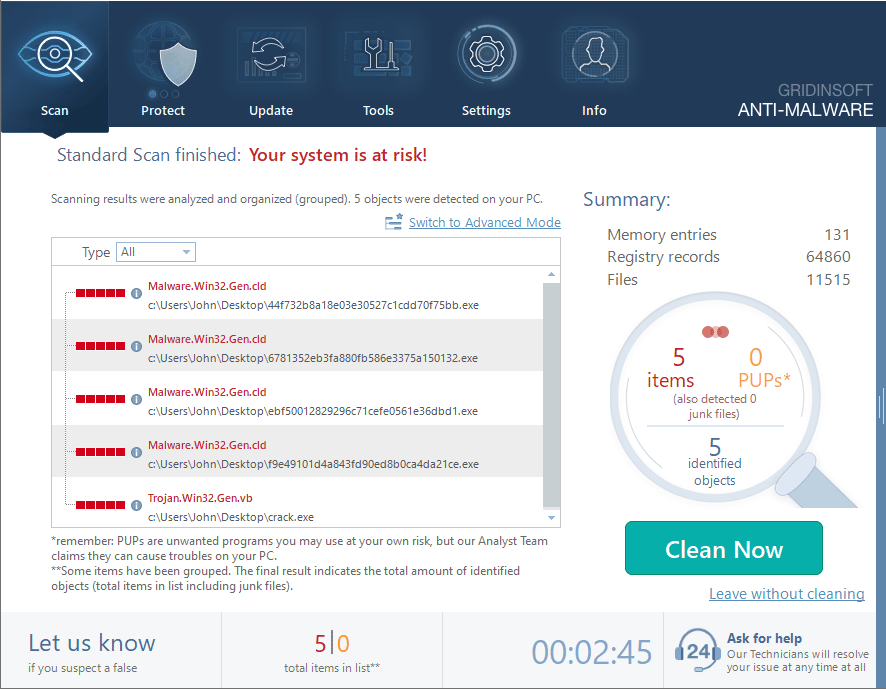
Click "Clean Now" to start the removal process. Important: removal process may take several minutes when there are a lot of detections. Do not interrupt this process, and you will get your system as clean as new.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is PUA:Win32/GameHack a virus?
PUA:Win32/GameHack is not strictly classified as a virus but rather as a Potentially Unwanted Application (PUA). It’s typically associated with game cheating tools or trainers that modify game processes to provide unfair advantages. While not inherently malicious like traditional viruses, these applications can compromise system security by requiring disabled antivirus protection and may serve as vectors for actual malware distribution.
Can PUA:Win32/GameHack damage my computer?
While PUA:Win32/GameHack itself may not directly damage your computer, it can lead to system instability, game crashes, and security vulnerabilities. The biggest risk comes from disabling security software to run these cheating tools, which leaves your system exposed to other threats. Additionally, many game hack tools are poorly coded and tested, potentially causing system conflicts or memory leaks that affect performance.
Will using PUA:Win32/GameHack get my gaming account banned?
Yes, using PUA:Win32/GameHack or similar game cheating tools carries a high risk of getting your gaming account permanently banned. Game developers employ sophisticated anti-cheat systems that can detect when game files or processes are being manipulated. Most popular online games have strict policies against cheating, and violations typically result in immediate account termination without possibility of appeal.
How can I tell if PUA:Win32/GameHack is a false positive?
To determine if a PUA:Win32/GameHack detection is a false positive, check if the flagged file belongs to a legitimate game or anti-cheat system. Research the specific file online to see if other users have reported similar detections. Check the game developer’s official forums or support channels, as they often address known false positive issues. If the detection occurred immediately after installing a legitimate game from an official source, it’s more likely to be a false positive than if it appeared after downloading unofficial game modifications.
Why does PUA:Win32/GameHack use randomly named folders?
PUA:Win32/GameHack and similar game hacking tools use randomly named folders and obfuscation techniques for several reasons: to evade detection by anti-malware programs that scan for known file paths, to bypass game anti-cheat systems that monitor for suspicious files, and to make manual removal more difficult. This behavior is a red flag that indicates the software is designed to hide its presence and activity, which is why security software flags it as potentially unwanted.
Protect Your Gaming Experience
Rather than risking your accounts and computer security with game hacks, consider these safer alternatives:
- Practice legitimate techniques to improve your gaming skills
- Join gaming communities to learn tips and strategies from experienced players
- Use officially supported mods that enhance gameplay without breaking rules
- Participate in custom servers where certain modifications may be allowed
Learn more about other potentially unwanted applications that might affect your system security.