Scammers are using a misleading GitHub page to distribute Legion Stealer to fans of rogue PUBG games. Under the guise of cheats, users download malware.
Legion Stealer Attacks PUBG Players
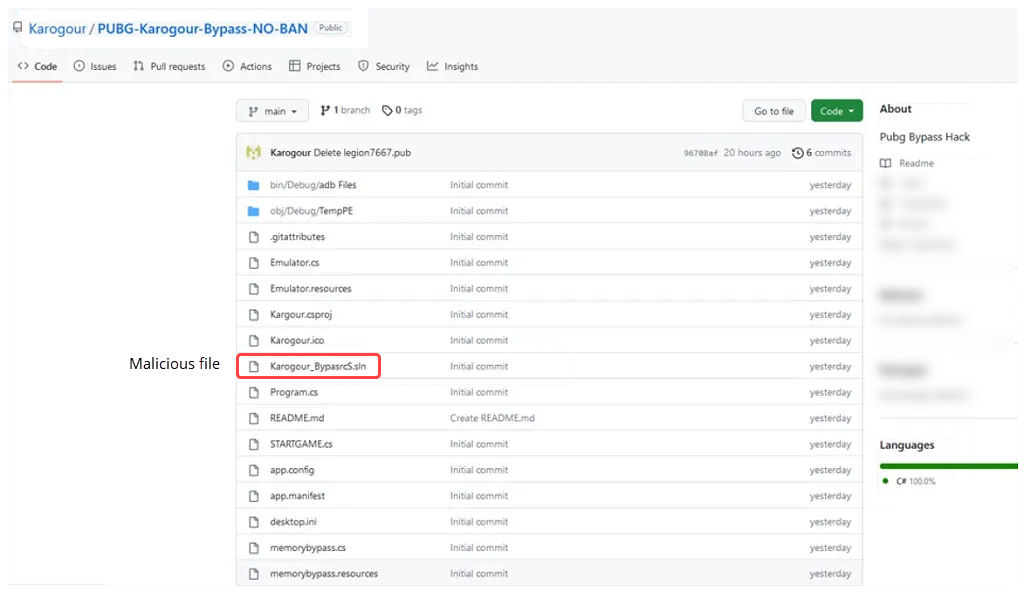
Cyble Research and Intelligence Labs (CRIL) recently uncovered a fraudulent GitHub page pretending to be a PUBG bypass hack project. However, instead of providing game hacks, it distributes a malicious file. Although GitHub is a legitimate code hosting platform, Threat Actors (TAs) also misuse it to distribute malware through repositories. They develop repositories that seem to contain authentic or appropriate code, but they have hidden malware. When users download the project and execute the solution (.sln) file, it unknowingly installs an information stealer named “Legion Stealer” on their systems as a payload.
Nobody likes a cheater
To understand the problem, you need to understand the cause. The problem is quite simple in this scenario – some players desire to gain an unfair advantage over their opponents. Specifically, a PUBG bypass hack is a form of exploit or cheat used by players to gain an unfair advantage. These hacks bypass the game’s anti-cheat systems, enabling players to use cheats such as aimbots, wallhacks, speed hacks, and other unfair gameplay advantages. Using these hacks allow a player to dominate over others, as it can foresee and outplay anyone. However, it is essential to note that using bypass hacks violates the game’s terms of service and can result in penalties, including temporary or permanent bans.
Btw, this tactic is something that has been introduced previously. In the early days of online games, when anti-cheat systems were beginning to appear, it was fashionable to punish cheaters by Winlocks. Thus, the cheater was sent the file, masked as another cheat or hack. But once such a file was launched, Winlock was blocking the computer. Though nowadays, tactics are different, and hackers prefer stealing personal information rather than asking for a single-time ransom.
Is It Safe Using Cheats After All?
As we said earlier, the user receives Legion Stealer malware instead of the game cheats. After being executed, Legion Stealer carries out several commands. These commands involve altering the settings of Windows Defender, collecting data from the registry, and obtaining details about the system. These actions aim to avoid detection, prevent unauthorized access, and take advantage of any weaknesses in the affected system. After performing the defense evasion techniques, the stealer gathers next system information:
- Computer name
- OS name
- RAM size
- UUID
- CPU/GPU details
- Product key
- Region
- Country
- Time zone
- Cellular data connectivity
- Proxy/VPN usage
- Reverse DNS
It then checks for web browsers:
- Brave
- Chrome
- Chromium
- Comodo Dragon
- Edge
- Epic Privacy
- Iridium
- Opera/Opera GX
- Slimjet
- UR Browser
- Vivaldi
- Yandex
Thus it accesses sensitive information such as passwords and cookies. Stealer is also interested in cryptocurrency wallets. It scans the system for:
- Armory
- AtomicWallet
- Bytecoin
- Coinomi
- Electrum
- Ethereum
- Exodus
- Guarda
- Jaxx
- Zcash
When it found them, it read files in their respective directories. Of course, such malware will not get past other games on the infected machine. It also focuses on Minecraft session files, extracting information from follow applications:
- Badlion
- CheatBreakers
- Impact
- Feather
- Lunar
- Meteor
- Microsoft Store
- Novoline
- Palladium
- PolyMC
- Rise
- TLauncher
In addition, the program also collects session files from messaging applications like Discord and Telegram, Roblox cookies, webcam images, and screenshots of the victim’s system.
Gamers often feel tempted to use cheats or hacks to gain an unfair game advantage. So, some malicious individuals exploit this desire by disguising their malware as game cheats or hacks. However, it takes one to know one.




