Trojan:JS/FakeUpdate.HNAP!MTB is a detection of Microsoft Defender that flags a malicious program present in the system. It comes from the heuristic detection system, which scans for malware presence by the behavior; this allows for finding the most modern threats, yet can also lead to false positives.
The detection itself normally flags a JavaScript file that abuses a fake update technique. Users will only see a website that offers to start the update process, while all the malicious operations happen in the background. Such malware is typically used as a gateway for other viruses, i.e. it loads other malware and grants them highest privileges in the system.
Typically, such threats spread on shady websites that ask the visitor to download a file “to install a critical update”. Alternatively, FakeUpdate virus can hide in email spam messages and scripts from fake human verification sites.
Why Antivirus Shows Me the Trojan:JS/FakeUpdate.HNAP!MTB Detection?
Modern antivirus programs are designed to detect malware as soon as it appears in the system. Heuristic and AI detection systems in particular scan the running processes, seeking for any malicious patterns.

The appearance of Trojan:JS/FakeUpdate.HNAP!MTB detection means that the antivirus has found the file that matches the behaviour patterns it counts as malicious. It typically double-checks the detected item with a database of static signatures to verify that it is actually threatening or not.
However, when the database check fails for some reason, the false detection may appear. This is actually an often case with behavioral detection systems of Microsoft Defender.
Threat Behavior Summary
The real Trojan:JS/FakeUpdate.HNAP!MTB virus appears as a browser page that offers one to run an update. This is typically served under the sauce of an urgent security update, that all users should install immediately.

Under the guise of this update, the website downloads a malicious file, that the user is asked to launch. This file may contain pretty much any malware, but it is most common to see backdoors and spyware to use such propagation tactics.
Once launched, it will collect user information and passwords kept in the files of installed programs. Additionally, this virus can provide hackers with remote access to the system, meaning that they can connect to the infected computer at any time and perform any actions they want.
The symptoms that the user may observe are unremarkable. Malicious programs like Trojan:JS/FakeUpdate.HNAP!MTB tends to leave as little visual clues as possible. Yet in a few days or weeks one can see all the online accounts being hijacked, with their password changed. That is the result of hackers taking hold of data that the virus has leaked from the system.
Is Trojan:JS/FakeUpdate.HNAP!MTB a False Positive?
There are plenty of user reports online saying about Trojan:JS/FakeUpdate.HNAP!MTB detection flagging cache files of web browsers and other applications. The reason for this may be partly legit: it is possible that the user has visited a dodgy website with a fake Microsoft Edge/Chrome//Windows update banner, and it has left the program cache files.
There is also a possibility of totally legit pages using pieces of JavaScript code that fall under the definition of FakeUpdate. As JS is used massively in web development, it is quite obvious that some will get into web browser cache.
Nonetheless, such leftovers typically pose no threat to the system. If the detection happens again and again, you can simply clean the cache of the program so Microsoft Defender will have nothing to detect.
How to Remove Trojan:JS/FakeUpdate.HNAP!MTB?
Removing the threat is not an easy process, as modern malware aims at preventing any manual removal. For that reason, I recommend using GridinSoft Anti-Malware: it will quickly detect and delete any viruses present in the system.
Download and install Anti-Malware by clicking the button below. After the installation, run a Full scan: this will check all the volumes present in the system, including hidden folders and system files. Scanning will take around 15 minutes.
After the scan, you will see the list of detected malicious and unwanted elements. It is possible to adjust the actions that the antimalware program does to each element: click "Advanced mode" and see the options in the drop-down menus. You can also see extended information about each detection - malware type, effects and potential source of infection.
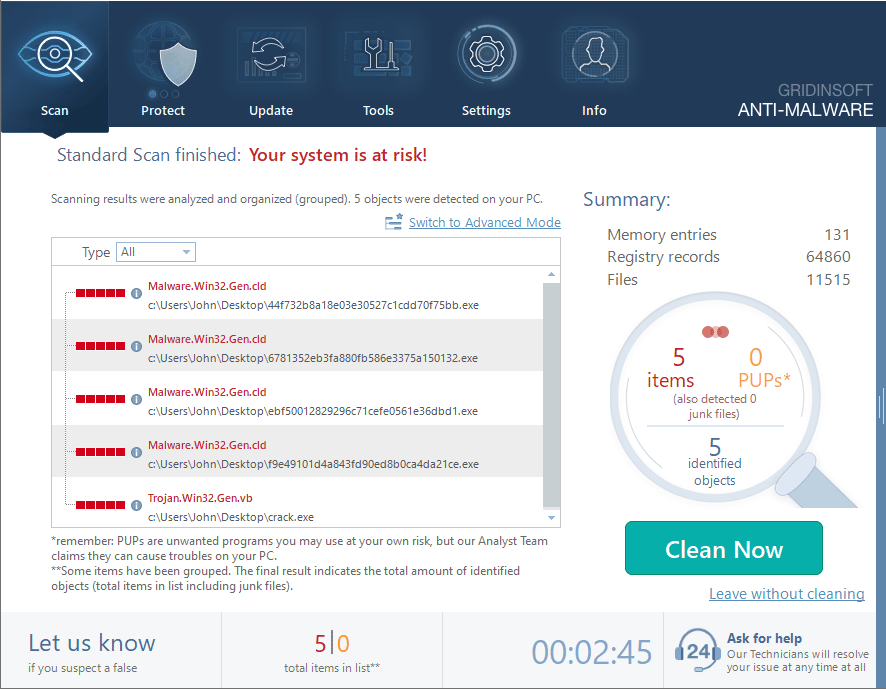
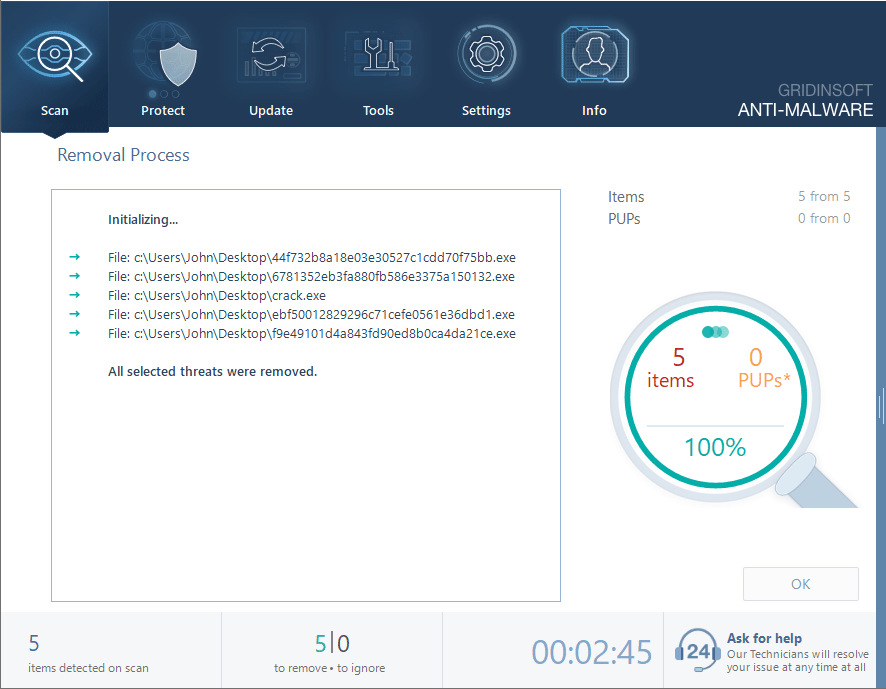
Click "Clean Now" to start the removal process. Important: removal process may take several minutes when there are a lot of detections. Do not interrupt this process, and you will get your system as clean as new.
Removing False Positive Detection
If you suspect that the detection is a false positive, you may try a few things to stop the detection from appearing. The first one is stopping the antivirus from flagging the file. For this, open Microsoft Defender and go to Virus and Threat Protection tab. Here, find the Protection History sub-menu.
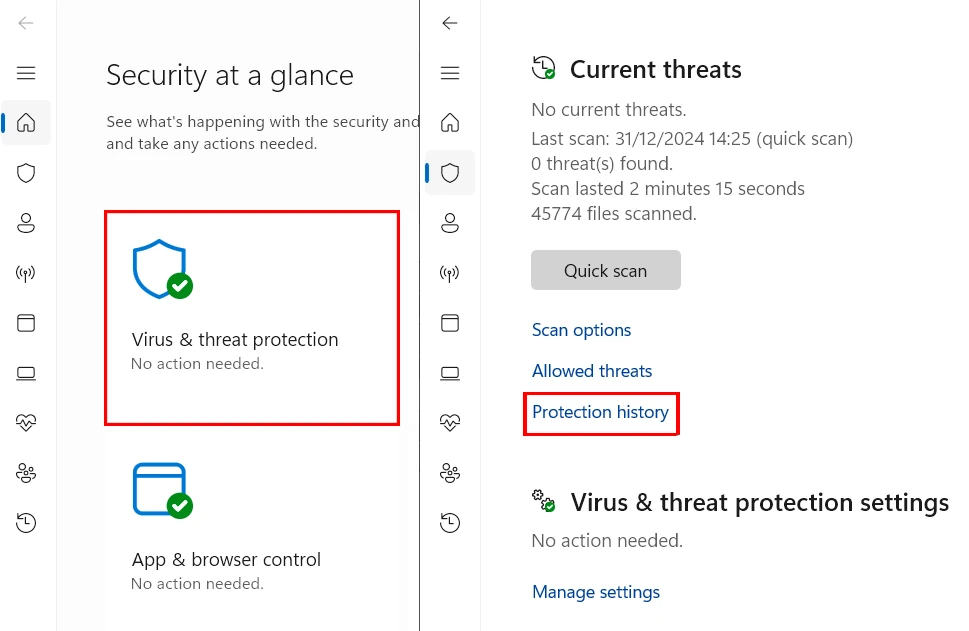
Here, you need to find the detection and click it. The Action menu will appear, where you need to pick the Ignore option. This commands Microsoft Defender to ignore the file in further scans.
Alternatively, you can remove the file that the antivirus falsely flags as dangerous. It is especially convenient when it appears in web browser cache files. Browsers typically have a section in settings where you can wipe the cache in one click.
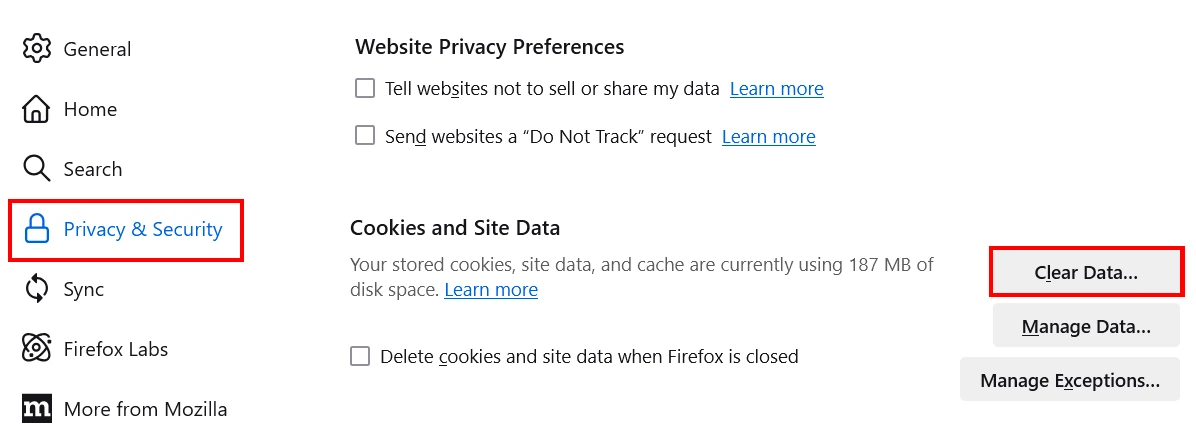
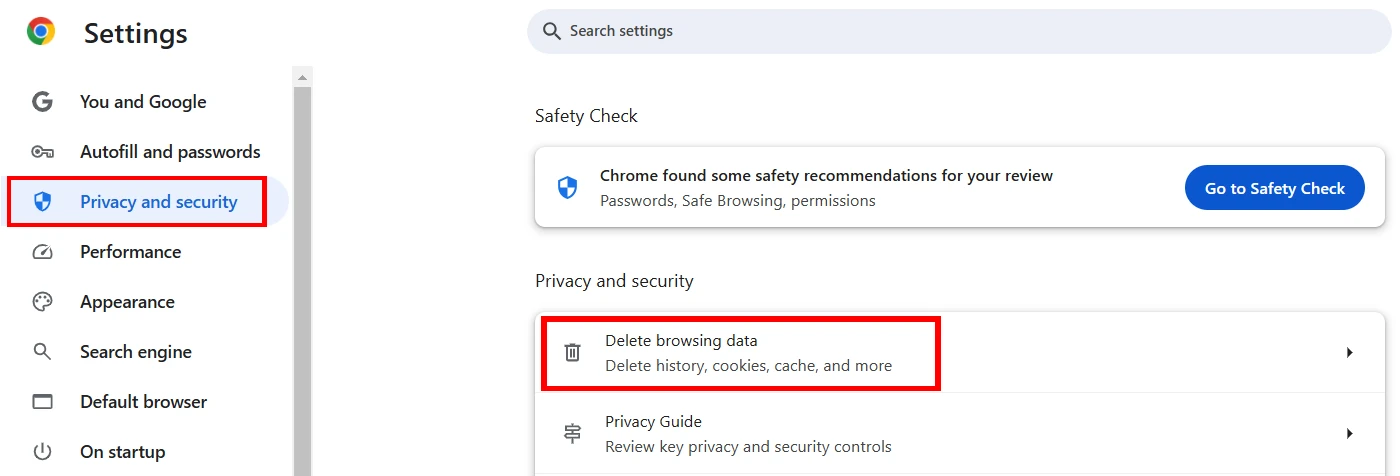
For Google Chrome and Edge, go to Settings → Privacy and Security, find and click the Delete browsing data button. This deletes not only cache, but also all the temporary files that the browser creates, so you may expect a small boost in browsing speed.
For Mozilla Firefox, open Settings → Privacy and Security, and find the Cookies and Site Data block. Here, click the Clear Data button and make sure the Temporary cached files and pages option is opted in. Press “Clear” to delete the cache.