$34.6 million in cryptocurrency could be at risk from StilachiRAT, a complex remote access trojan first detected by Microsoft Incident Response in November 2024. Unlike conventional ransomware that announces its presence, this digital threat operates silently in the background, monitoring user activities until it identifies the perfect moment to drain cryptocurrency wallets. According to Microsoft’s detailed analysis published in March 2025, once installed, it becomes nearly impossible to remove without specialized tools due to its advanced persistence mechanisms.
The name “Stilachi” comes from Italian for “spike,” combined with RAT (Remote Access Trojan) – reflecting its sharp, piercing ability to penetrate security defenses. As Bitdefender reported on March 18, 2025, what makes this threat particularly concerning is its “impressive arsenal of malicious capabilities” and its laser-focused targeting of cryptocurrency wallets.
How StilachiRAT Works: Technical Analysis
According to Microsoft’s Security Blog, StilachiRAT isn’t just another generic malware variant. It was built specifically to hunt down cryptocurrency wallets. Microsoft Security Intelligence’s investigation revealed a consistent pattern across infected systems – cryptoassets vanish without a trace, often before victims realize they’ve been compromised.
Source: Based on Microsoft Security Intelligence StilachiRAT capability analysis
Security researchers who investigated the malware described it as “the malware equivalent of trying to remove superglue with your bare hands,” highlighting both its effectiveness and the difficulty in eliminating it once it has infected a system.
Target List: Wallets in StilachiRAT’s Crosshairs
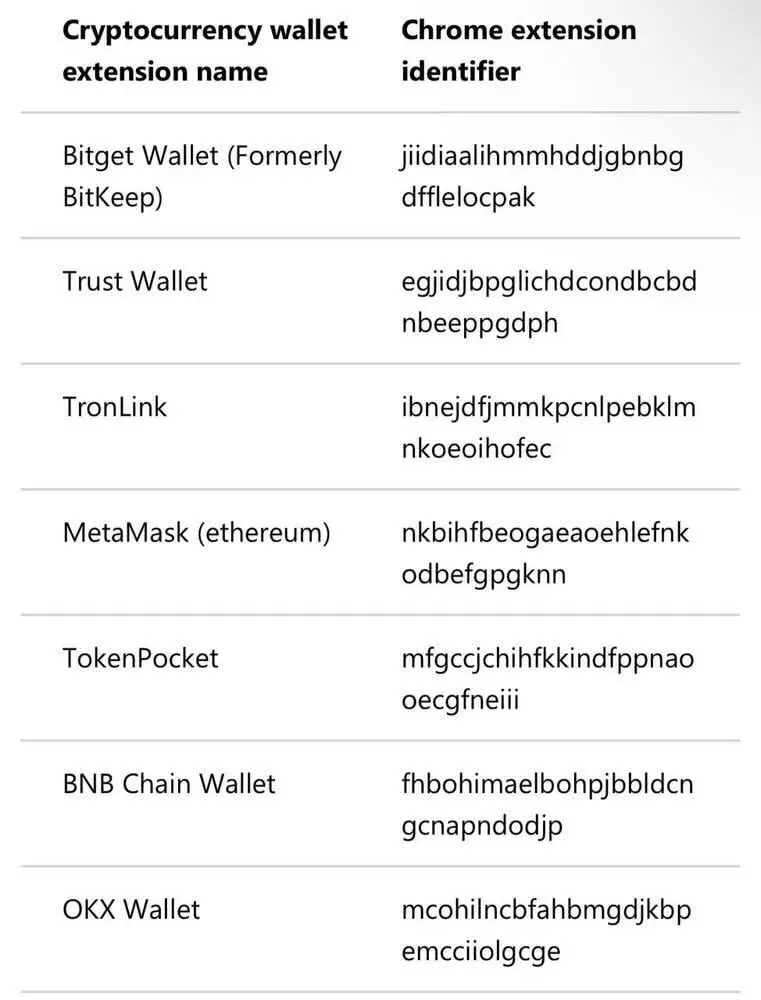
According to Quorum Cyber’s threat intelligence report, StilachiRAT doesn’t discriminate between blockchain ecosystems. It specifically targets 20 different cryptocurrency wallet extensions used in the Google Chrome browser, including:
- MetaMask
- Coinbase Wallet
- Trust Wallet
- BNB Chain Wallet
- Bitget Wallet
- Braavos – Starknet Wallet
- Compass Wallet for Sei
- ConfluxPortal
- Fractal Wallet
- Keplr
- Leap Cosmos Wallet
- Manta Wallet
- OKX Wallet
- Phantom
- Plug
- Sui Wallet
- Station Wallet
- TokenPocket
- TronLink
- Solflare
While documented cases of theft attributed specifically to StilachiRAT remain limited due to its recent emergence, the potential impact on cryptocurrency holders is significant. As Microsoft noted, the malware can capture wallet addresses, private keys, and other sensitive information that allows attackers to access and steal digital assets stored in these wallets.
Anatomy of the Threat: How StilachiRAT Operates
Initial Reconnaissance
When StilachiRAT first infiltrates a system, it immediately begins mapping the digital environment. According to Microsoft’s analysis, it performs comprehensive system reconnaissance that includes:
Inventorying all hardware IDs and BIOS serial numbers, checking for webcams and microphones (potentially for future spying), mapping installed applications with special focus on financial software, and creating a unique tracking ID to mark the system in attacker databases.
This intelligence-gathering creates a complete profile of the target system, helping attackers identify high-value targets worth focusing on. As Quorum Cyber notes, the malware appears to prioritize systems based on potential cryptocurrency value.

Credential Theft Mechanism
Microsoft’s security team discovered that StilachiRAT uses an ingenious technique to breach Google Chrome’s security:
The malware locates Chrome’s master “encryption_key” file in the user directory, decrypts this key using built-in Windows functions, uses the master key to unlock the saved passwords vault, and extracts every stored credential in seconds.
The speed and efficiency of this attack means that by the time users realize what’s happening, their cryptocurrency accounts may have already been compromised.
Cryptocurrency Extraction Engine
According to Bitdefender’s analysis, the core malicious functionality in StilachiRAT is contained in a component called WWStartupCtrl64.dll. This module is specifically engineered for cryptocurrency theft:
It systematically scans the registry for installed wallet extensions, extracts wallet configuration files containing encryption keys, searches for backup seed phrases stored in text files or screenshots, and transmits private keys to attackers in real-time.
Unlike basic malware that causes system slowdowns, StilachiRAT operates with remarkable stealth. Microsoft noted that victims often only discover the theft days later when checking their wallet balances.
Self-Healing Persistence Mechanism
What makes StilachiRAT particularly difficult to remove is its intricate self-healing capability. As detailed in Bitdefender’s report:
“The malware can be launched either as a standalone component or a Windows service. Regardless of its form, the malware uses a watchdog thread that regularly checks if the RAT’s executable or dynamic link library (DLL) files are present on the system. If the components are not found, the malware recreates them using an internal copy generated during the initialization phase.”
Microsoft security engineers noted that the malware can maintain backup copies in unexpected locations, reinstall itself within seconds of removal attempts, and create multiple registry startup entries as fallbacks.
Identity Impersonation
StilachiRAT goes beyond data theft by enabling attackers to impersonate legitimate users. According to Quorum Cyber’s analysis, the malware:
Identifies active Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) sessions, clones security tokens and privileges, launches applications using the compromised identity, and can move through corporate networks as an authorized user – bypassing standard security checks by using legitimate credentials.
This capability makes it particularly dangerous in enterprise environments where it can exploit trusted connections to access sensitive systems and cryptocurrency exchange accounts.
Clipboard Monitoring
Microsoft’s analysis confirmed that StilachiRAT constantly monitors clipboard contents for valuable data:
It captures clipboard contents at high frequency, uses pattern matching to identify wallet addresses, passwords and private keys, can trigger immediate theft operations when it detects valuable data, and operates with minimal performance impact to avoid detection.
This clipboard monitoring capability is particularly effective against cryptocurrency users who frequently copy and paste wallet addresses or seed phrases, unaware that the malware is intercepting this sensitive information.
Advanced Evasion Techniques
StilachiRAT employs various methods to avoid detection, as detailed by multiple security firms:
It regularly erases Windows Event Logs to cover its tracks (particularly logs with Event IDs 1102 and 104), detects virtual machines and sandbox environments used by security researchers, changes its code signature to evade antivirus detection, and uses encrypted communication that mimics normal HTTPS traffic.
Command and Control Infrastructure
According to Quorum Cyber, the malware maintains contact with its operators through a well-designed two-channel system:
“The malware communicates with a command-and-control (C2) server using domain names that are intentionally scrambled or disguised, and instead of using standard IP address formats, the malware encodes IP addresses in a binary format.”
It utilizes common ports (53, 443, 16000) to blend with normal traffic and accepts remote commands that can control virtually every aspect of the infected system. This connection allows attackers to manually take control when high-value targets are identified.
Distribution Methods
While Microsoft has not definitively determined how StilachiRAT is initially delivered, security researchers have identified several potential infection vectors:
Fake wallet extensions: Counterfeit versions of legitimate cryptocurrency wallet extensions that look identical to the real ones.
Phishing campaigns: Emails and messages claiming to be from cryptocurrency exchanges offering “security updates” or “verification requirements.”
Compromised downloads: Modified installers for legitimate software that secretly bundle the malware.
Cracked software: Pirated applications and activation tools containing trojan payloads.
According to Ken Colburn’s analysis in AZ Central, “It doesn’t matter what browser you’re using if you open the wrong file or click the wrong link” – highlighting that StilachiRAT’s delivery methods target user behavior rather than specific technical vulnerabilities.
Effective Protection Against StilachiRAT
Standard antivirus protection may not be sufficient against this evolving threat. Security experts recommend a multi-layered approach:
- Verify wallet extensions thoroughly: Only install from official web stores after carefully verifying the developer, review count, and installation numbers.
- Use hardware wallets: Keep significant cryptocurrency holdings in cold storage devices like Ledger or Trezor that never connect directly to the internet.
- Implement browser security features: As Ken Colburn notes in AZ Central, “Edge combined with Windows Defender SmartScreen can reduce your exposure to malicious websites and risky downloads,” though third-party security solutions offer more comprehensive protection regardless of browser choice.
- Enable application control: Use Windows features to restrict execution to known, trusted software.
- Monitor event logs: Be vigilant for cleared logs, especially Event IDs 1102 and 104, which may indicate anti-forensic activity.
- Deploy specialized security software: According to Bitdefender, “Dedicated software like Bitdefender Ultimate Security can keep your devices clean of RATs, viruses, worms, zero-day exploits, ransomware, spyware, rootkits and other digital threats.”
- Isolate cryptocurrency activities: Consider using a dedicated device exclusively for cryptocurrency transactions, separated from everyday browsing.
- Perform regular security audits: Scheduled checks for unusual services and registry entries can help detect compromise early.
StilachiRAT Removal Procedure
If you suspect infection, immediate action is critical:
Advanced User Removal Process
Be aware that StilachiRAT actively resists removal attempts. According to Microsoft’s analysis, the malware’s self-healing capabilities make manual removal exceptionally challenging. If you have the technical expertise:
- Disconnect from the internet immediately
- Boot into Safe Mode with Networking (press F8 during startup)
- Open Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) and terminate suspicious processes
- Check Services console for unfamiliar services, especially those with randomized names
- Remove suspicious browser extensions from Chrome
- Use Registry Editor to search for and remove startup entries
- Run multiple security tools to verify complete removal
Important warning: StilachiRAT’s self-repair mechanisms make manual removal extremely difficult. Missing even a single component can result in complete reinfection within minutes.
Recommended Solution: Specialized Removal
For most users, dedicated anti-malware software is the most effective option. GridinSoft Anti-Malware provides a specific removal protocol for StilachiRAT that targets all components simultaneously. This approach:
- Neutralizes the malware’s self-repair mechanism before beginning removal
- Identifies and eliminates all components in a coordinated operation
- Thoroughly cleans infected browser profiles and extensions
- Restores security settings modified by the malware
Click the banner below to download GridinSoft Anti-Malware and follow the installation prompts to clean your system from StilachiRAT.
Recovery Prospects After Cryptocurrency Theft
The reality of cryptocurrency theft presents significant challenges for recovery:
Unlike traditional financial fraud where banks can reverse transactions, blockchain transactions are fundamentally irreversible by design. When private keys are compromised, attackers can authorize transfers that cannot be undone by any central authority.
However, there are limited scenarios where recovery might be possible:
- Exchange intervention: If stolen funds were transferred to a regulated cryptocurrency exchange, immediate reporting with transaction IDs and wallet addresses may allow the exchange’s security team to freeze assets.
- Law enforcement: The FBI’s Cyber Division and similar agencies have developed capabilities for tracking cryptocurrency crime, with several successful recovery cases documented.
- Blockchain analytics: Companies specializing in cryptocurrency tracing may help identify exchange deposit points where funds could potentially be recovered.
For any chance of recovery, document these details immediately:
- The exact time theft was discovered
- Transaction IDs of unauthorized transfers
- Destination wallet addresses
- Any evidence regarding how the system was compromised
Timing is critical – successful recovery cases typically involve reporting within hours of the theft, before funds can be laundered through multiple wallets.
The Emerging Threat Landscape
StilachiRAT represents an evolution in cryptocurrency-targeting malware. As noted by Bitdefender, while it has only been “spotted in the wild a few times” as of March 2025, its advanced capabilities make it a significant concern for cryptocurrency holders.
According to Microsoft’s security team, “What makes this threat different is its focus. It’s not trying to infect millions of computers—it’s hunting specifically for crypto holders and executing perfect heists. One successful infection can yield more profit than thousands of traditional ransomware victims.”
For cryptocurrency users, the implications are clear: securing digital assets requires specialized security measures beyond standard practices. As Ken Colburn noted in AZ Central, “This malware warning is a serious reminder of the threats we all face, but it’s not a browser-specific flaw — it’s a wake-up call for users who aren’t taking security seriously.”
Protection begins with awareness and requires ongoing vigilance. The most effective defense combines secure hardware wallets, isolated computing environments, and specialized security tools designed to counter the specific techniques used by cryptocurrency-targeting malware like StilachiRAT.
Stay informed and protected – the security of your cryptocurrency depends on it.
References
- Microsoft Incident Response. (2025, March 17). StilachiRAT analysis: From system reconnaissance to cryptocurrency theft. Microsoft Security Blog.
- SC World. (2025, March 18). Novel sophisticated StilachiRAT malware emerges. SC World.
- Colburn, K. (2025, March 23). Does switching from Google Chrome to Edge defend against the StilachiRAT malware? AZ Central.
- Quorum Cyber. (2025, March 20). StilachiRAT: A New Remote Access Trojan Posing a Significant Threat. Quorum Cyber Threat Intelligence.
- Constantinescu, V. (2025, March 18). Researchers Discover New ‘StilachiRat’ Malware. Bitdefender Hot for Security Blog.





