Spear phishing is a type of phishing attack that targets specific individuals or organizations typically through malicious emails. For example, cybercriminals can pretend to be a trusted person or organization and thus try to make the victim enter confidential data, such as logins and passwords, or install malware. Such attacks are divided into the whaling and spear phishing subtypes.
The Difference Between Spear Phishing & Phishing
In general, these two attacks are somewhat similar. Both involve sending emails (or other messages) with the sender’s name spoofed. The difference is the number of emails sent; phishing emails are sent to thousands of random people in large volumes. In addition, these emails are usually not personalized. Instead, they contain a link to a malicious or phishing site.
A phishing email is an email that masquerades as an actual promotional email (notifications and stuff) or a human email but either asks you to follow links to phishing sites or asks you to run one of the attached files. The main problem with such emails is that they can be so well-designed that even an experienced user might think they are real.
Such emails might also contain an attachment with a virus already embedded in it, or this file might contain some text with a link to a phishing site. Since many email systems have started checking attachments for viruses, this type is much less common.
Spear phishing is a more advanced and targeted attack. It targets a particular person or group of people in which the scammers are interested. Such attacks are not as common as phishing because they require a lot more preparation and research into the victim and their behavior for the attack to look as natural as possible and not to raise suspicions.

To accomplish this, scammers may introduce themselves as colleagues or family members. The main goal of such actions is to gain the victim’s trust. Scammers carefully collect any information about the victim, for example, on their social media pages. Here are some of the spear-phishing attack methods scammers use:
- CEO Fraud: The attacker pretends to be a manager or other superior and manipulates the victim into performing unauthorized actions. These attacks are mainly aimed at junior employees.
- Whaling attacks: Such attacks are designed for managers and employees who have access to confidential information. This attack aims to make a mistake and unknowingly allow the person to leak information or make a large money transfer
- Business email compromise (BEC): In this case, a hacked or fake email address of the company is used, and this method is counted on the trust of employees.
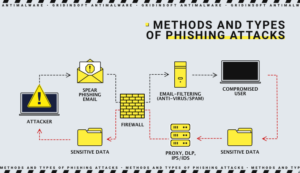
As practice – the pandemic has contributed to the development of spear phishing attacks because working remotely has allowed fraudsters to run rampant. The primary purpose of Spear Phishing is to steal confidential information. This can be:
- User credentials. Such information is valuable because the accounts can be used for even more sophisticated attacks. Or they can be sold on the darknet.
- Personal information. Full names, addresses, and phone numbers are useful, as the previous point, but can also be used for identity theft.
- Money. One of the pursuits of phishing is to trick the user into providing card details and transferring money to the scammer.
How to Defend from Attacks?
Since the main vulnerability is the human factor, it is first and foremost important to know what spear phishing emails look like and equally important to train employees to distinguish potentially dangerous emails and react to them correctly. A few rules can help you avoid substantial problems:
- Pay attention to the sender’s address and the contents of the email, mainly if it contains a link. On no account, you click on links. Also, don’t download or open attachments unless the email is from a trusted sender. Such attachments can easily infect your system, install adware, trojan, or keyloggers, and steal valuable information.
- Always keep your software up to date. Timely software updates help eliminate vulnerabilities that malware can exploit if downloaded.
- Encrypt important data. Even if your data is stolen, encryption will prevent an intruder from taking advantage of it.
- Use two-factor authentication. This is the most safe way to secure your online account. If an attacker finds out your login and password, two-factor authentication will prevent them from logging into your account.
- Do not use simple passwords. Although password picking is not as popular now as it used to be, its risks still exist. About 90% of all passwords can be cracked by hackers in less than 6 hours. So don’t use the same password at home and work. If it’s compromised, malefactors can cause immense damage to both you and your company.
- Use reliable antivirus software. Even if you accidentally open the attachment, the antivirus will not let it do its dirty work. There are special programs that block phishing sites. But first, study the reasons why an antivirus is important: the benefits of using it, the important points.
- Watch what you post on social media. Nothing provides as much useful information about us as our social media accounts. Unfortunately, thanks to the information in the questionnaire in the public domain, attackers can find every detail and build a phishing attack based on this information. To avoid this, specify your profile’s privacy settings, do not unnecessarily publish such data as phone number and place of work, and especially refrain from publications related to work.
Summarizing the above, we see that common sense is the most effective remedy against spear phishing attacks. It is not always possible to avoid attacks, but it is always possible to defend against them. The ultimate method of countering any form of computer phishing is with anti-malware software. We suggest you try GridinSoft Anti-Malware, which can handle these functions perfectly.