New update of RustBucket Malware introduced several changes. Now the malware is more securely fixed in the systems of its victims and evades detection by security software. Though the most concerning feature there is its enhanced ability to attack macOS.
What is RustBucket malware?
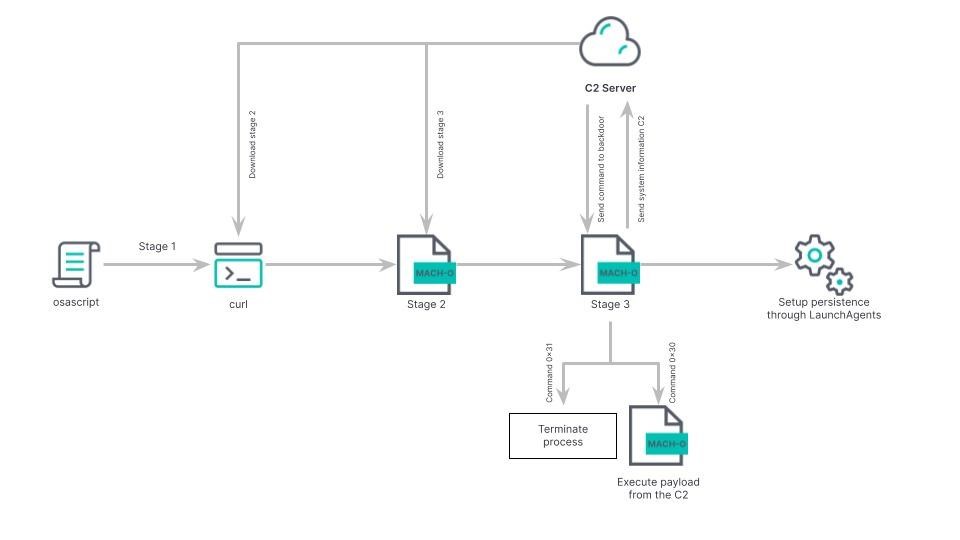
Researchers from Jamf Threat Lab discovered RustBucket in the spring of 2023. They described it as an AppleScript-based backdoor capable of extracting the second stage payload from a remote server. This malware is associated with North Korean hackers from the BlueNoroff group (REF9135 in the Elastic Security Labs classification). They are reportedly related to a larger threat cluster called Lazarus.
Malware of the second stage, compiled in Swift, arrives from the C2 server. Is is a binary file based on Rust and Objective-C. This malware has extensive data collection capabilities and is also capable of extracting and running additional Mach-O files or shell scripts on a compromised system. Interestingly, this was the first BlueNoroff malware specifically designed to attack macOS users, although a .NET version of RustBucket has since appeared with a similar feature set.
Typically, such attacks start with phishing emails, and hackers also use fictitious identities specially created for this purpose on social networks (for example, on LinkedIn). Their campaigns tend to target financial institutions in Asia, Europe and the United States, suggesting that the group’s activities are aimed at generating illegal income and evading sanctions. In general, the attacks are based on the macOS installation file, which installs a hidden but working PDF reader. An important aspect of these attacks is the fact that the malicious activity only starts after this PDF file startup in the malicious reader.
The version of RustBucket discovered by Elastic Security Labs is most notable for its unusual pinning mechanism, the use of dynamic DNS (docsend.linkpc[.]net), as well as a number of measures that are aimed at hiding the activity of hackers.
What then?
RustBucket malware appears to be just another malicious utility in hands of politically-motivated hackers. Lazarus as the most notorious North Korean hack group significantly expanded its activity in 2023, so it is not a hollow threat now. To be sure about your secureness against such dangers, I can advice you to follow these tips.
- Control all email messages you’re going to interact with. Email spam has become a prevalent malware spreading way back in the days. Specifically, Lazarus actors prefer it to other spreading ways. Strange topic, dubious attachments, unusual sender’s address – all such things should raise suspicion. By being vigilant, you can cut almost a half of possible malware injections.
- Use reliable anti-malware software. Well, vigilance is important, but you can never be sure you’re right. Hackers invent new methods of malware injection every day, and you can never predict them. For that reason, a proactive solution is simply essential. There are solutions for individuals, small companies and large organizations – so you will have wide range of possible options.





