Fortinet has issued a warning about a recently discovered critical vulnerability in its FortiOS SSL VPN system that could be actively exploited by attackers. The vulnerability in Fortinet network security solutions poses a significant threat to organizations. It allows unauthenticated attackers to gain remote code execution (RCE) capabilities through maliciously crafted requests.
Fortinet VPN RCE Vulnerability Uncovered
This flaw, identified as CVE-2024-21762 / FG-IR-24-015, poses a severe risk with a CVSS rating of 9.6 due to its potential exploitation in cyber-attacks. Also, the heart of this alert is an out-of-bounds write vulnerability within the FortiOS system. Such a flaw allows unauthenticated attackers to execute remote code through maliciously crafted requests.
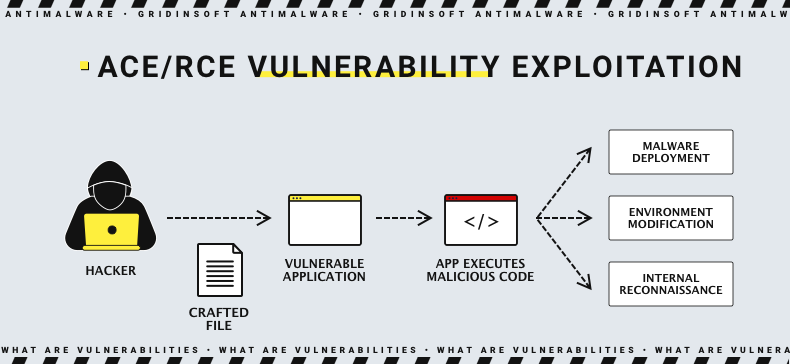
The amount of fuzz around this new vulnerability caused by the popularity of Fortinet networking solutions, along with the severity of the said vulnerability. Aside from the aspects mentioned above, RCE flaws can lead to system compromise and data theft. In some cases, they can also initiate ransomware or espionage attacks. In simple terms, it can simply be the reason for a company-wide cyberattack, with downtimes, leaked data and all the related “delights”.
This critical flaw was disclosed alongside other vulnerabilities, including CVE-2024-23113, which boasts an even higher severity rating of 9.8, and two medium-severity flaws, CVE-2023-44487 and CVE-2023-47537. However, these additional vulnerabilities are not currently marked as being actively exploited in the wild, unlike CVE-2024-21762.
Hackers Exploit Fortinet RCE Flaw
The disclosure of this vulnerability comes after it was revealed that Chinese state-sponsored threats known as Volt Typhoon have already exploited FortiOS vulnerabilities in the past. The deployment of custom malware such as Coathanger, a remote access trojan (RAT), suggests that adversaries are willing to do anything to exploit such vulnerabilities. This malware, in particular, has been used in attacks against the Dutch Ministry of Defense. This highlights the critical nature of the threats posed by such malware.
Still, as statistics show, the majority of exploitation cases happen after the vulnerability is publicly disclosed. Therehence, the best option will be to patch the flaw as soon as possible. Fortunately, the developer already offers the fixes for CVE-2024-21762.
Patch and Mitigation
The patch released by Fortinet brings affected FortiOS systems up-to-date, addressing the vulnerability and preventing potential exploitation by attackers. Fortinet recommends upgrading based on the following table:
| Version | Affected | Solution |
| FortiOS 7.6 | Not affected | Not Applicable |
| FortiOS 7.4 | 7.4.0 through 7.4.2 | Upgrade to 7.4.3 or above |
| FortiOS 7.2 | 7.2.0 through 7.2.6 | Upgrade to 7.2.7 or above |
| FortiOS 7.0 | 7.0.0 through 7.0.13 | Upgrade to 7.0.14 or above |
| FortiOS 6.4 | 6.4.0 through 6.4.14 | Upgrade to 6.4.15 or above |
| FortiOS 6.2 | 6.2.0 through 6.2.15 | Upgrade to 6.2.16 or above |
| FortiOS 6.0 | 6.0 all versions | Migrate to a fixed release |
The developer has provided guidance for those unable to immediately apply the necessary patches to mitigate this flaw. A possible mitigation strategy is to disable SSL VPN on affected FortiOS devices. While this step may impact remote access capabilities, it may be necessary to prevent exploitation. It’s crucial to note that merely disabling web mode is not considered a sufficient workaround for this vulnerability.





