The South African hack group Automated Libra is looking for new approaches to use the resources of cloud platforms for cryptocurrency mining: hackers bypass CAPTCHA on GitHub.
Let me remind you that we also wrote that Hackers force users to solve CAPTCHA, and also that New hCaptcha bypass method may not affect Cloudflare’s security.
According to Palo Alto Networks, in recent times, attackers are using a new system to solve CAPTCHAs, abusing CPU resources more aggressively for mining, and also mixing freejacking with Play and Run techniques.
For the first time, Automated Libra operations were discovered by Sysdig analysts last fall. Then the researchers gave a name to the found malware cluster PurpleUrchin and suggested that this group specializes in freejacking, that is, they abuse free or time-limited access to various services (GitHub, Heroku and Buddy) to mine cryptocurrency at their expense.
Now Palo Alto Networks experts have studied the activity of this group in more detail, analyzing more than 250 GB of collected data and collecting more information about the infrastructure and methods of attackers.
According to experts, the automated campaigns of these attackers are abusing CI/CD services, including GitHub, Heroku, Buddy, and Togglebox, to create new accounts and run cryptocurrency miners in containers. But if Sysdig analysts only identified 3,200 malicious accounts belonging to PurpleUrchin, then Palo Alto Networks reports that since August 2019, hackers have created and used more than 130,000 accounts on the mentioned platforms.
In addition, it turned out that the attackers used containers not only for mining itself, but also for trading the mined cryptocurrency on various platforms, including ExchangeMarket, crex24, Luno and CRATEX.
At the same time, the researchers confirm that freejacking is an important aspect of Automated Libra operations, but write that Play and Run tactics are also of great importance. This term usually refers to attackers who use paid resources to make a profit (in this case, using cryptocurrency mining), but refuse to pay bills until their accounts are frozen. Once locked out, they drop the accounts and create new ones.
As a rule, Automated Libra uses stolen personal data and bank card information to create premium accounts on VPS and CSP platforms, leaving a trail of unpaid debts.
In such cases, attackers use as many server resources as possible before losing access. This is in stark contrast to the freejacking tactic, where the miner tries to remain invisible and uses only a tiny fraction of the server’s capacity.
In addition, according to experts, an interesting feature of the Automated Libra attacks is the CAPTCHA solution system, which helps hackers create many accounts on GitHub automatically. To do this, the attackers use ImageMagic and convert the CAPTCHA images to their RGB equivalents and then use “identify” to determine the asymmetry of the red channel.
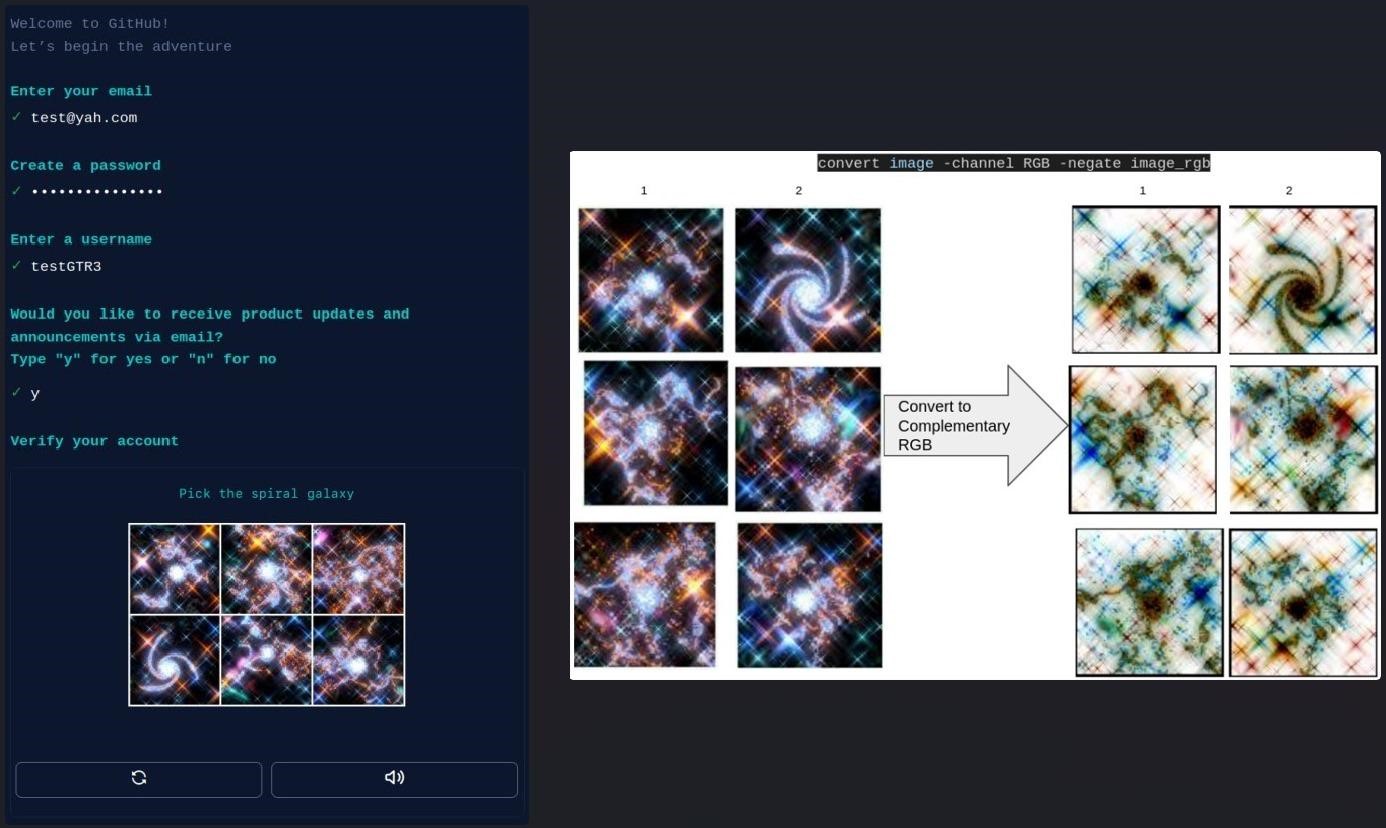
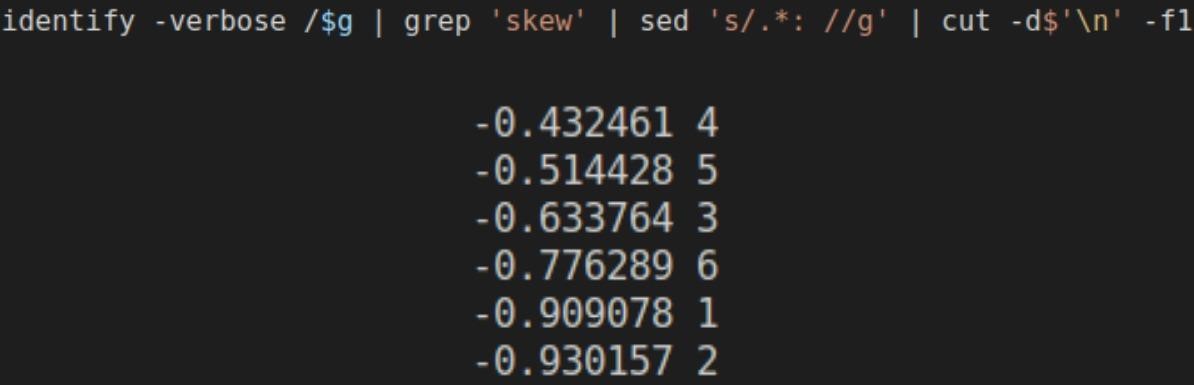
The values obtained in this way are used to rank the images in ascending order, and the automated tool selects the image that leads the resulting list. Usually, that is exactly what is correct.




