Cybersecurity experts have discovered a new variant of Chaes malware called “Chae$4”. This malware targets the banking and logistics industries and significant content management platforms.
New Chae$4 Malware Targets Banking and Logistic Industries.
According to a report, researchers have discovered an advanced variant of Chaes malware that predominantly targets e-commerce customers in Latin America. Chae$4 is an infostealer malware, discovered back in early 2023. Usually, it can be stealing bank data, intercepting bank payments, stealing personal data, and controlling infected computers. It is spread via phishing emails containing links or malicious code attachments. When the user opens the link or attachment, the malicious code is downloaded to the computer and installs Chae$4.
Once installed, Chae$4 monitors the user’s browser activity, including entering data into banking forms. The malware can also intercept bank payments and send them to attackers. Chae$4 can also be used to steal user’s personal information such as passwords, logins, and credit card numbers. It was named “Chae$4” because it was the fourth major malware version and had a debugging seal labeled Chaes in the main module. It threatens customers of well-known platforms and banks, including WhatsApp Web, MetaMask, Mercado Libre, Mercado Pago, Caixa Bank, and Itau Bank. Additionally, services such as WordPress, Magento, Drupal, and Joomla are affected.
What is Chaes Malware?
Chaes malware first appeared in mid-2020. It included using multiple programming languages and LOLbins and was adept at stealing sensitive financial data. In November of that year, experts published the first study of Chaes malware. The following research was published in January 2022 and indicated increased Chaes activity in the fourth quarter of 2021. In addition, the details of its behavior became known. Thus, the developers significantly improved the infection chain communication with C2 and added new integrations.
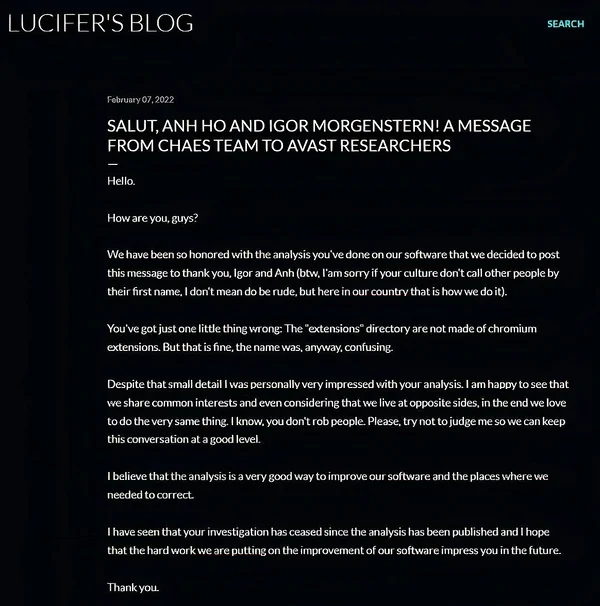
In February 2022, Chaes malware developers published a response to the research. The attacker was impressed with the analysis and thanked the experts for their work. In addition, he specified that thanks to the analysis, he could fix the flaws that had been discovered. However, it is unclear whether one person or a group is behind the development of Chaes, as the address was addressed both in the person of one person and in the plural. However, the experts labeled the attacker “Lucifer” since the blog name and identifier for contacting C2 was “lucifer6”.
Chae$4 Malware Update – What’s New?
Since version 4 has been significantly revised, all of the above applies to the first three versions for the most part. In terms of the latest version, improvements include an improved code architecture and modularity, as well as new levels of encryption and stealth capabilities. In addition, the move to Python has resulted in lower detection rates by traditional means.
Seven different modules were identified during the analysis. These modules can be updated independently without changing the core functionality. The malware has several modules, including one for identification and data gathering, an online module for monitoring active victims, a credential stealer and clipper module, and modules for stealing data from specific banks and browsers. It also has a module for uploading files to the C2 server. This version has re-implemented previous modules with improved functionalities and unique techniques.
How to protect yourself against Chae$ 4?
Since Chae$ 4 is a fileless malware, meaning it does not create any files on the victim’s computer, making it more difficult to detect and remove. However, here are some tips on how to protect yourself against Chae$4:
- Keep your software up to date. Software updates are an integral part of using any device. They include security patches that protect you from malware attacks.
- Use a firewall. It will help prevent cyberattacks from outside. In other words, a firewall can block unauthorized access to your computer.
- Back up your data regularly. This way, you can restore your data if infected with malware.
- Use protecting software. Anti-malware solution will be the last line of defense and protect your device if you are not vigilant. It will detect and remove malware if it has infiltrated the machine.





