Ivanti has alerted its customers to a critical authentication bypass vulnerability in its Cloud Services Appliance (CSA) solution. This security flaw allows remote attackers to gain administrative privileges without needing to authenticate or interact with a user, as they can bypass authentication through an alternate path or channel.
Critical Ivanti CSA Authentication Bypass Patched
Ivanti has released critical updates to address major security flaws across several products, including the Cloud Services Appliance, Connect Secure, and Policy Secure. These vulnerabilities, if left unpatched, expose organizations to significant risks such as Remote Code Execution (RCE) and administrative takeover of systems.
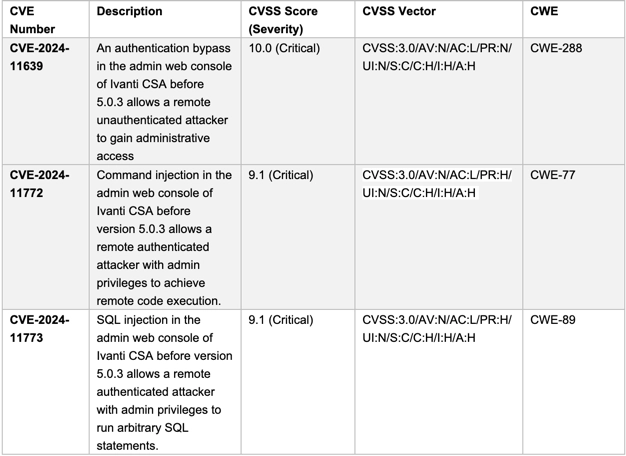
The most critical flaw patched is CVE-2024-11639, a maximum-severity authentication bypass vulnerability with a CVSS score of 10.0, the highest possible severity. This flaw affects CSA versions 5.0.2 and earlier and allows attackers to exploit an alternate authentication pathway, effectively bypassing all security measures without requiring credentials or user interaction. Once exploited, an attacker gains full administrative control over the CSA system, putting sensitive enterprise environments at substantial risk.
Ivanti’s December security updates also addressed several high-severity vulnerabilities across various products. These flaws included issues like arbitrary file deletion and insecure permission settings, which could allow attackers to modify critical components.
The affected products include Ivanti Desktop and Server Management, Endpoint Manager, Security Controls, Configuration Manager, Neurons for Patch Management and Neurons Agent Platform, and Ivanti Sentry. Company provides an extensive datasheet regarding the fixed flaws, and recommends installing the updates as soon as possible.
Ivanti as a Target for Advanced Threats
Ivanti products have gained massive popularity amongst threat actors in terms of exploiting them for initial access and lateral movement. For example, in October 2024, attackers exploited CVE-2024-8190 along with two other undisclosed vulnerabilities that we covered in a separate article. Similarly, in September 2024, another critical flaw, CVE-2024-8963, in the Cloud Services Appliance (CSA) was exploited in real-world attacks.
In the latest updates, the company also addressed two additional critical vulnerabilities in CSA. The first, CVE-2024-11772 (CVSS 9.1), is a command injection flaw in the CSA admin web console. This vulnerability allows authenticated administrators to execute arbitrary commands remotely, potentially leading to a full system compromise. The second, CVE-2024-11773 (CVSS 9.1), is an SQL injection flaw that lets authenticated users run arbitrary SQL queries, exposing sensitive data or enabling further attacks.
What to Do?
Ivanti recommends upgrading to CSA version 5.0.3 as soon as possible to address these critical vulnerabilities. Although no active exploitation of these issues has been reported, that’s no reason to put off upgrading until later.
Additionally, Ivanti has released patches for two critical vulnerabilities in Connect Secure and Policy Secure products. The first, CVE-2024-11633 (CVSS 9.1), is an argument injection flaw that allows authenticated administrators to execute arbitrary code remotely. The second, CVE-2024-11634 (CVSS 9.1), is a command injection vulnerability affecting both products, which can also result in unauthorized code execution. To protect against these vulnerabilities, the
company recommends upgrading to Connect Secure 22.7R2.4 and Policy Secure 22.7R1.2.