Facebook has been hit by a wave of fake ads that offer what looks like AI services. In fact, those are scam pages that trick people into installing malware.
AI Scam in Facebook Ads
The use of social media for cybercrime, in general, is nothing new. However, to maintain effectiveness, sometimes fraudsters have to adjust their tactics and adapt to current trends. Another “innovation” from cybercriminals was discovered by CheckPoint Research (CPR) experts. According to their report, fraudsters are using Facebook as a platform for their dirty deeds. Since the hottest topics are AI-related, scammers are using them as bait. Such pages often contain mentions of ChatGPT, Google Bard, or Midjourney. For the best effect, scammers heavily embellish their “services”. For example, some pages have names like Bard New, Bard Chat, and G-Bard AI, and some are not shy to name themselves GPT-5.
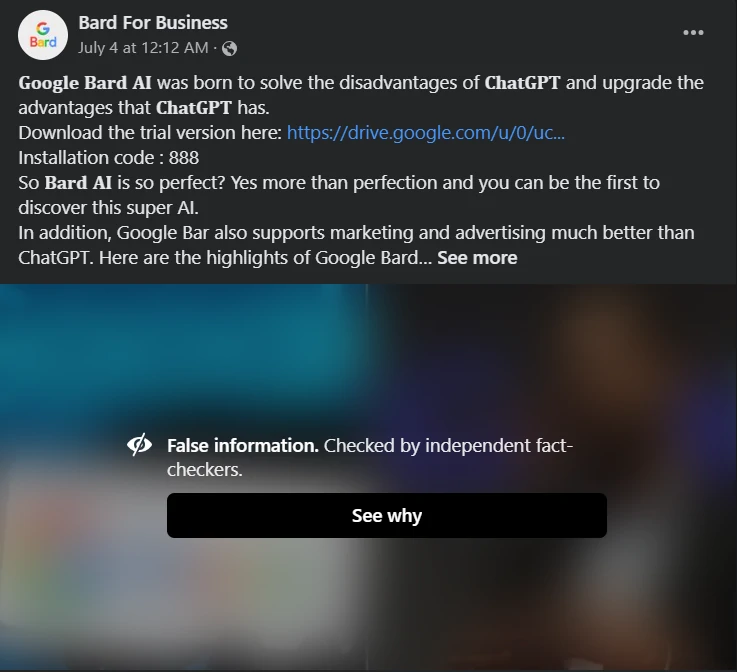
Obviously, many people fall for it. The main reason is that real services are unavailable in some countries, so many people can’t distinguish fakes from real ones. Moreover, the abundant number of discussions, comments, and likes make users believe in the genuinity of these posts. However, in the end, naive users are tricked into downloading and installing malware. In turn, this malware steals valuable information from the victim’s computer. This includes online passwords (banking, social networks, games, etc.), crypto wallets, and any information stored in the browser.
How does it happen?
I already mentioned that hackers create Facebook groups on AI-related topics. To look legitimate and attractive, they fill it with different content – mostly legit at this point. Next, users and algorithms come into play. As unsuspecting folks comment and like the content, Facebook promotes it into recommendations and user feeds. As a result of this manipulation, fraudulent pages can have more than two million followers, which is also compelling. Though all these pages have one thing in common – they all link to a site that offers “additional functionality”. Some links promote an application, some – a password-protected archive under the guise of necessary files for the engine, or have just one button, “Get started”. However, each option will bring malware to your PC instead of the promised one.
Fake AI Groups on Facebook Spread Infostealers
Info stealers are the primary infection that spreads through this scheme. These malicious programs aim to collect sensitive and personal data from infected devices. They scan the infected system for valuable information such as logins, passwords, bank card details, social accounts, and other sensitive information. Next, the info stealer starts secretly collecting data and transmits it to the attackers over the internet. Crooks use the data collected by info stealers for financial scams, identity theft, blackmail, or selling on the dark web.
Security Recommendations
Unfortunately, genuine artificial intelligence services cannot always influence fraudulent schemes. Therefore, it is essential that users educate themselves, recognize the risks, and remain vigilant against such schemes. Since phishing is the basis of such cyber attacks, the attackers’ main goal is to convince the victim that they are legitimate. Here are some of the ways to detect a phishing attack:
- Download software from trusted sources. Since Facebook groups are not trusted sources (even if they appear to be), we do not recommend downloading software for your computer from it. Instead, we recommend using the app or the company’s official website.
- Ignore Display Names. You should avoid falling victim to phishing scams and focus on verifying the sender’s email or web address. Phishing sites and emails can manipulate display names to appear legitimate, but checking the source is the best way to ensure authenticity and trustworthiness.
- Verify the Domain. It is common for crooks to utilize domains with slight misspellings or those that appear to be credible. It is essential to be cautious of these misspellings as they can be a sign of phishing attempts.
- Use reliable antimalware software. In addition to the above recommendations, having additional protection is a good idea. Even if you miss a link, an anti-malware solution will neutralize the threat before deployment.