The release of DeepSeek AI chatbot gave a push for an enormous number of DeepSeek scams that trick users in a variety of shady activities. Some of them just aim at charging money for services that are free by design, others try collecting users’ personal information or even infect them with malware. In this article, I show my in-depth analysis of these sites, explain the risks one faces when using them, and show how to recognize them early on.
What are DeepSeek Scams?
It is hard to comprehend the sensation that was the DeepSeek R1 model on release. It has become a #1 newsletter headline for almost a week, though sometimes for its security issues and database leaks. But just a few days following the public release of the model, fraudulent actors began their attempts to earn their dirty coin on this news.
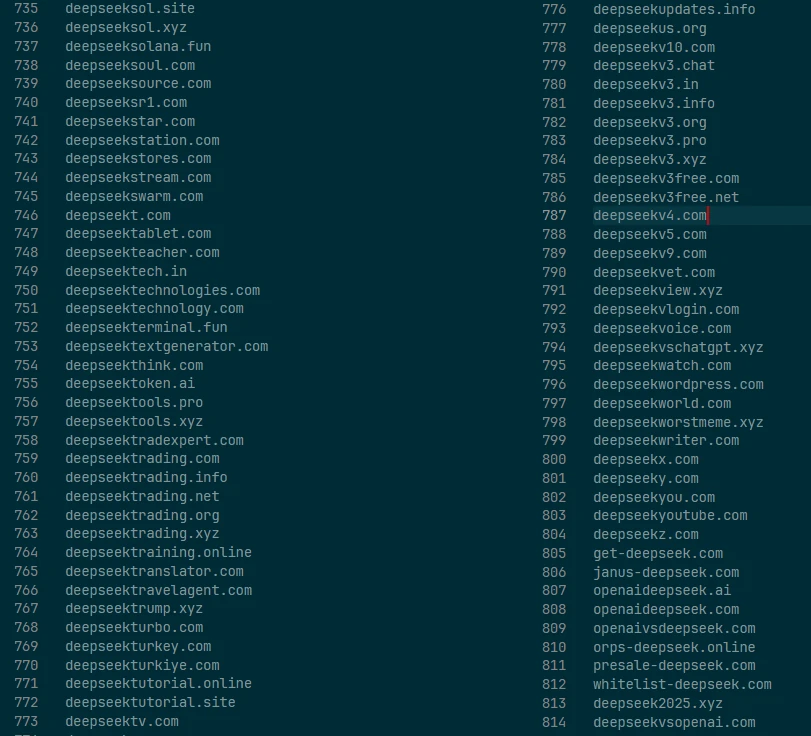
In a snap of a finger, hundreds of websites were registered, offering pretty much the same appearance and contents. “Access world’s most innovative AI model for a small fee” – that is the motto that unites them all. The sole fact of some guys charging money for a thing that is available for free already makes it dubious.
You can feel deja vu at this point, as the same exact thing happened upon the public release of ChatGPT 3, the “first” AI chatbot of them all. Similarly to modern days with DeepSeek scams, con actors were taking a free model, and offering it as a “paid” GPT-4 at a corresponding price. But this time, the scope is much more extensive.
But what GridinSoft network security analysis team observed to the moment is over 800 domains registered less than a week ago, all dedicated to DeepSeek and related topics. Some offer access to the model, despite it being free, some use all the fuss to promote scam crypto tokens, and others spread outright malware. Quite a lot of them are taken down after less than a few days after being brought up online. Let’s have a closer look at what they are and how they work.
How do DeepSeek Scams Work?
Two key things DeepSeek scams rely upon are users’ lack of awareness about potential threats, combined with the rush to get the new technology. This is what allows even the most ridiculous tricks to work correctly. In that state, folks don’t question even outright dodgy and strange things, leave alone well-designed scams.
Scam campaigns typically start with a promotion campaign happening in social media. Fraudsters can buy ads in the media, or use spoofed accounts/bots to post hundreds of posts, targeting as wide of an audience as possible.
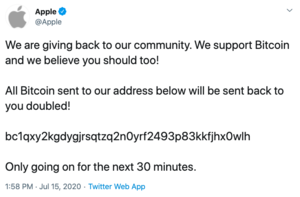
Upon opening any of these shady websites, users face an offer to log in and introduce a payment to start using the service. If it is a crypto scam page we are talking about, it would most likely ask for a payment for a non-existent DeepSeek crypto token. In either case, money and personal information is the main focus.

With the “DeepSeek R1 access” websites, the scam is not outright obvious. It may really provide access to the model, but why would one pay for a free model? Even if someone runs their local model to avoid staggeringly bad downtime of the official site, the capacity of their solution will be even lower. Setting up your own local version may just be a much more cost-efficient solution.
For crypto scams that offer early staking in “DeepSeek meme coin”, things are much more straightforward. Users pay the money, hoping to get into the hype train early (probably motivated by TrumpCoin and MelaniaCoin examples), and get nothing in return. Websites simply shut down after a few days, with money and alleged tokens gone.
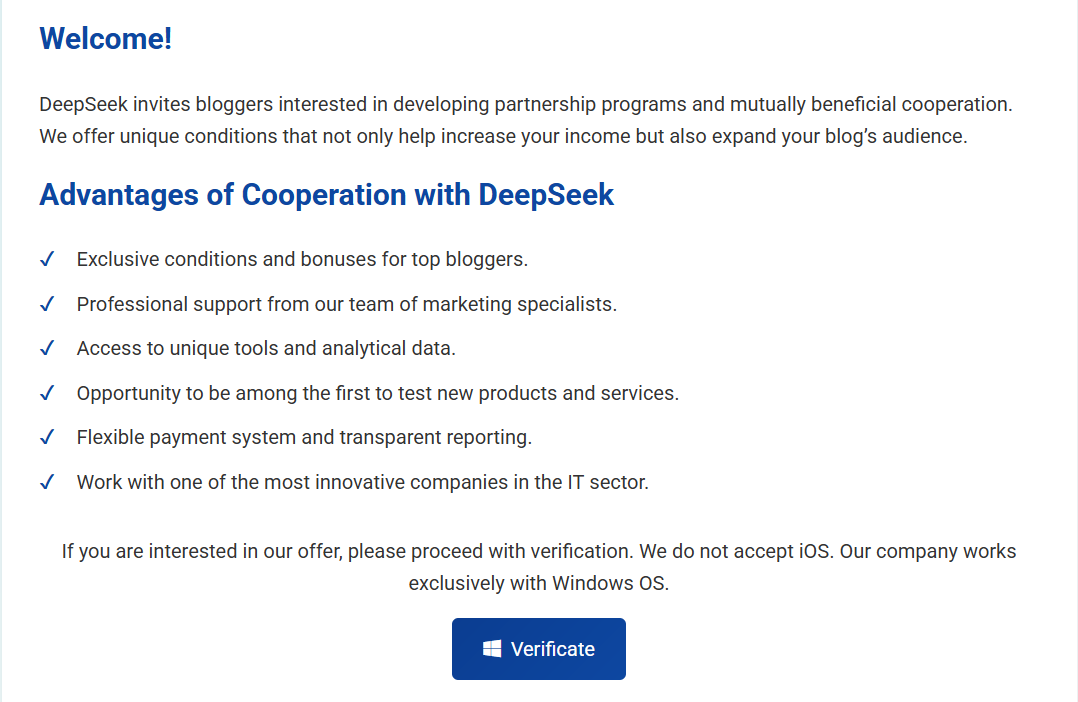
There is also a small amount of pages that spread quite literal malware, using the trick with verification. Under different guises – from “show that you’re using a correct OS” to “verify you are human”. Upon clicking the button, a more classic fake captcha page appears. The latter asks the user to open PowerShell and execute the malicious script that was copied to the clipboard as soon as they’ve opened the website.
Some of the websites also offer APK files to install on your Android smartphone. The very idea of running an questionable installer already has a bad smell to it. Absence of any legitimate explanation for the file adds even more suspicion, though for users eager to get their hands on the new technology, these red flags are non-existent.
How to recognize scam DeepSeek websites?
For now, at the beginning of February 2025, there are no other official pages of DeepSeek other than deepseek.com. There are also no mobile applications for any platform, though I am sure they will appear in future akin to how OpenAI made their app for ChatGPT. Same is true for crypto tokens: DeepSeek as a company never announced the release of any cryptocurrency projects.
With all that being said, one can make a simple conclusion: any pages other than the said official site that offer any services are fraudulent to a certain extent. To verify whether the app or a service is real, visit their website and check the blog: there will be information about a service shall it be real and legit.
Though, it may sometimes be problematic to find this news, especially when a website posts lots of new content. To simplify the searching, consider using GridinSoft Website Reputation Checker: this free tool will return you a verdict about the website’s legitimacy in less than 30 seconds.






Very informative post. I had been looking for something like this for days. Yours was the most helpful by far. I appreciate the effort you put into making this easy to follow. Well done!