It is hard to imagine something more harmful than ransomware. Besides the danger for your files and PC, it also deals a significant damage to quite a material thing – your wallet. $500, $1000, or even $5-7k4 ransom for separate corporations. In this article we will talk about the modern ransomware trends, facts about the spreading of ransomware, and statistics that make the hair move.
5 facts about ransomware spreading
IT security succeeded in counteraction to ransomware
A lot of companies who suffered from ransomware reported about increasing the security in all eight functional areas. But such improvements were also reported in the corporations that had no experience in ransomware attacks. Is it a reason to call ransomware the global stimulus for cyber security rise? Maybe, but the price of such a “lesson” can be very high.
The carelessness of people is the biggest problem
The biggest share of ransomware attacks are done with the “help” of the workers who know nothing about cybersecurity or even internet hygiene. They are clicking the dubious links in the email, opening the attachments without any doubt and sharing the confidential information, like corporate emails. Such people are able to multiply by zero any cybersecurity shield, because the main assumption is that there is no information leaks from the inner part of the corporation.
Ransomware developers are more active than they have ever been
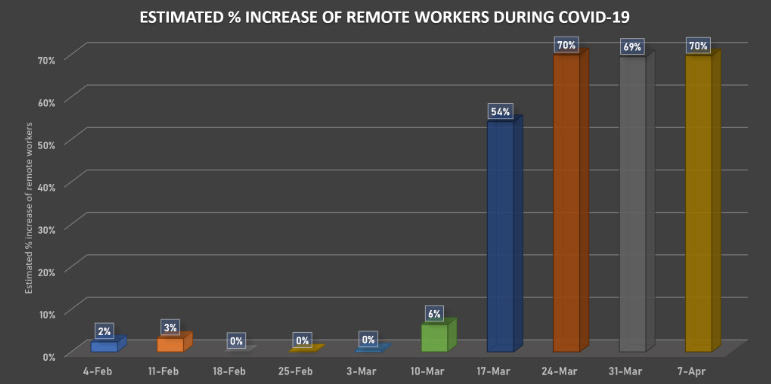
2020 is a year when 75% of the planet population started working online. And the more information is moving through the common network instead of corporate, the bigger the chances to steal something valuable and then ask for the ransom to keep this information away from the public. And besides the data leak risks, there is also a great opportunity for malware distributors to inject the ransom trojan. Last will inject the hacktool, which will crack the passwords of the whole network, and then launch the ransomware.
Artificial intelligence as a new cybersecurity trend
Through 2019, AI usage in cybersecurity at all and in breach analysis in particular rose 58%5, and kept going in 2020. Corporations show the enormous interest in the machine learning systems, that gives the ability to detect and protect the security breaches before it can be used by cyber burglars. And, as practice shows, security solutions based on the AI are able to detect the vulnerabilities much faster and more correct than the cybersecurity experts do.
Rise of cyber burglars appetites
As it was mentioned, cybercriminals became enormously active in 2020. But stats are so bad only for solitary users. Corporations were under attack since 2017, scoring about 50-55% of attacked companies among ones which took part in the poll. Nowadays, the share of corporations under attack rose to 68% (compared to 56% in 2019), together with the corresponding increase in the average ransom paid by the single company – up to $8.1k in 2020, compared to $5.9k in 2019 and $4.3k in 2018.
Saying about the statistics
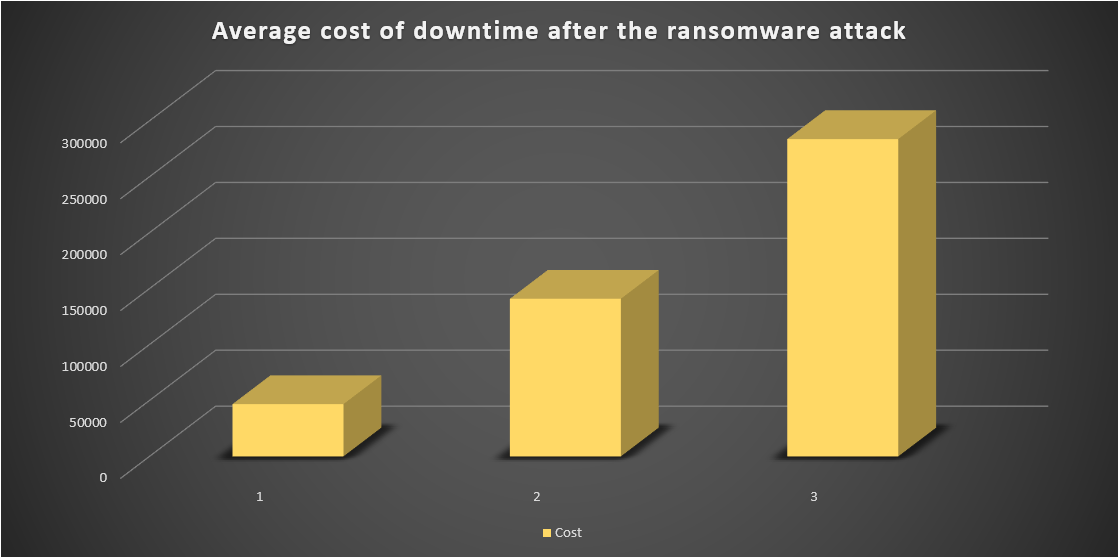
The main harm ransomware does is neither file encryption nor data leak. The biggest cost that appears because of ransomware attack is the cost for downtime. Workers are not able to do their job when the files they need are encrypted and readme.txt files are everywhere. Nonetheless, corporations are still obligated to pay the salary to their employees, and pay the penalty for the delays in goods or services delivery. Some little companies were literally buried by such consequences of ransomware activity. Here is the graphic which shows the average downtime costs:
It is also interesting that ransomware developers have their favourite targets. No, not corporations – the whole countries and sectors of economy. Such targeting is likely caused by the payability of the local business – the more money is rolling in the corporations of this sector – the bigger the chance that the ransom will be paid. Of course, low level of cybersecurity development is also a reason for such statistics, but this factor is likely complementary then initial.
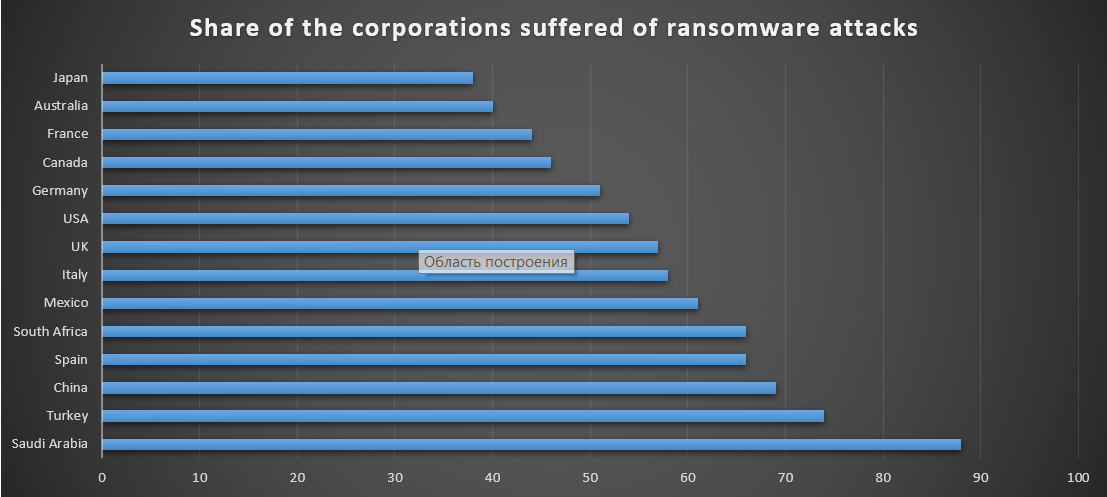
As you can see, the biggest share of companies under attack to total companies is in the Saudi Arabia. The second place is after Turkey, which has significantly less share of attacked companies; China is on the 3rd place. All other countries in the list has the shares which differ on 2-5%, so such a big gap for Saudi Arabia is likely caused by the complex activity of mentioned factors – low cybersecurity level, great interest of ransomware developers and large turnover.
Unfortunately, the detailed statistics about the sectors that are favourite among the ransomware developers is available only for the USA. Here it is:
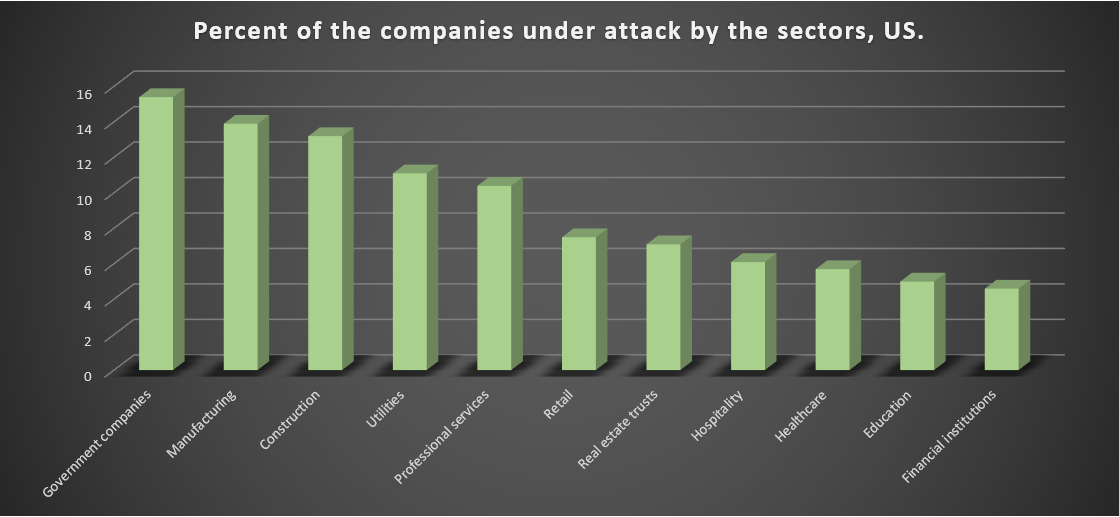
Government organizations and large part of the real sector of the economy is under attack. The last place with the share that is 3 times less than the governmental companies has is after financial services. It means that the cybersecurity level in last ones is much higher than in governmental structures: both financials and government have a lot of valuable information and money supply, so the chance of getting the ransom as well as blackmailing with the threats of selling the confidential information is equal.
Ransomware penetration statistics is also available only for Northern America. As it was mentioned at the beginning of the article, the reason for the majority of attacks is low level of cybersecurity knowledge among users. Using the PC without understanding of all hazards is like smoking near the opened gasoline barrel. But while gasoline barrel explosion can harm you and, maybe, someone who was unlucky to be close to you, cyber attack will harm the whole corporation in the described way.
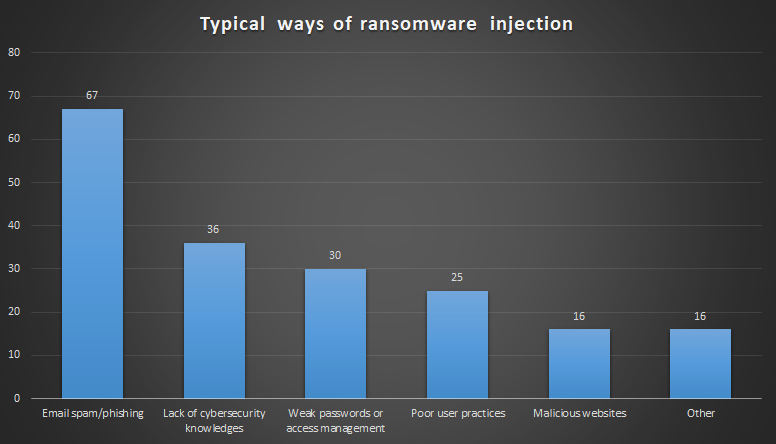
The way ransomware spreads through all computer networks is worth a separate article. Saying short, it acts together with other viruses and hack tools, cracking the passwords of the whole corporate network, and then injecting the ransomware with a backdoor in every PC it can reach. At the same time, ransomware developers steal confidential information (if such is present on the attacked computers) and sell it in the darknet.
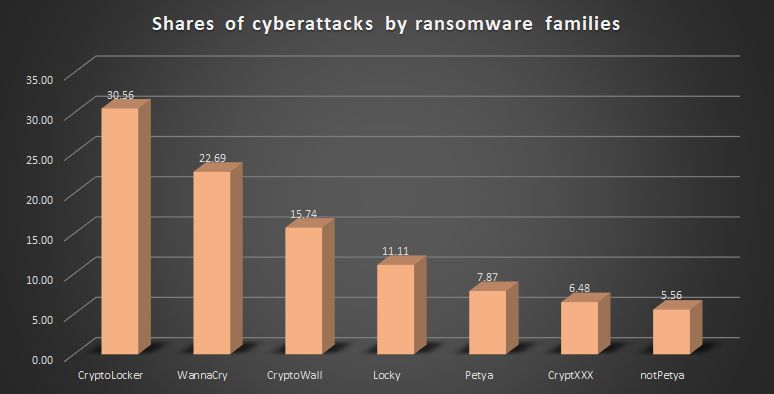
Popular types of ransomware
This characteristic is unusually stable in the constantly-changing computer environment. Old-but-gold WannaCry6 has been moved to the second place by the CryptoLocker family only this year; in 2019, first one was leading with a significant gap. Third and fourth places have quite small shares – the total share of CryptoWall and Locky together is less than CryptoLocker share. Petya, CryptXXX and notPetya have the shares that are close by size, but compared even to the Locky their activity is weak.
- About DOPPELPAYMER - ransomware with the increased requests
- Artifical Intilligence usage in cybersecurity
- The most famous WannaCry attack
- About DOPPELPAYMER – ransomware with the increased requests
- Artifical Intilligence usage in cybersecurity
- The most famous WannaCry attack




